...
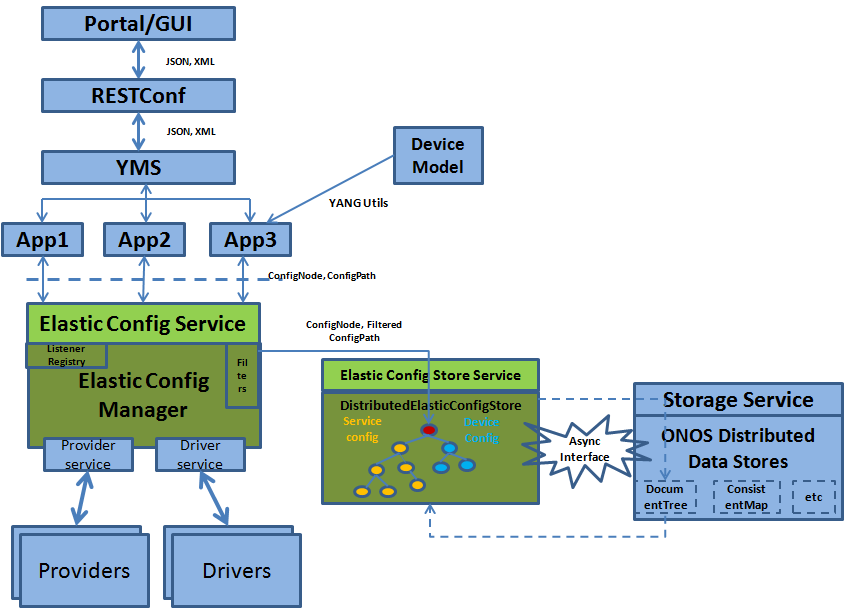
In ONOS, various abstractions collect configuration information pertaining to the network and network elements and store them in the implementation defined system wide models. But often in the brown fields, applications create or collect similar configuration information and work with their own individual information models (let us call this the "elastic configs"). Often these models are heterogeneous and most of them do not directly confirm to the models/abstraction within ONOS. The purpose of the elastic config subsystem is to provide suitable abstractions that would enable ONOS to consume/produce the "elastic configs" in a structured and extensible manner. Parking such "elastic configs" within ONOS would also allow opportunities for other abstractions (like drivers, providers etc.) to consume or apply them.
Components
The main components of this subsystem include the elastic config service, elastic config manger, elastic config store interface and the distributed elastic config store. Elastic config service is the gateway for applications to inject elastic configs to ONOS. Elastic config manger implements this service and is responsible for managing the distributed elastic config store; apart from managing the store, the manger can also do additional south facing processing. Elastic config store provides the APIs and the Distributed elastic config store provides the implementation of the store. the store implementation is wrapping the Document Tree primitive and is built on top of the ONOS Distributed storage implementation.
Two other important abstractions are the ConfigNode and ConfigNodePath.
APIs
Use Case
Next Steps