...
Contributors
kalyana@huawei.com
Name | Organization | Email | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aihua Guo (point of Contact) | Huawei Technologies | aihuaguo@huawei.com | ||
| Satish K | HuaweiTechonologiesHuawei Technologies | satishk@huawei.com | ||
| Dhruv Dhody | Huawei | TechonologiesTechnologies | dhruv.dhody@huawei.com | |
| Young Lee | Huawei | TechonologiesTechnologies | leeyoung@huawei.com | |
| Haomian Zheng | Huawei | TechonologiesTechnologies | zhenghaomian@huawei.com | |
| Kalyana | Huawei Techonologies | Huawei Technologies | kalyana@huawei.com | |
| Tao Liu | Huawei Technologies | liutao61@huawei.com | ||
| Fan Cheng | Huawei Technologies | chengfan2@huawei.com | ||
| Yixiao Chen | Huawei Technologies | yixiao.chen@huawei.com | ||
| Patrick Liu | Huawei Technologies | Patrick.Liu@huawei.com | ||
| Jongyoon Shin | SK Telecom | jongyoon.shin@sk.com | ||
| Junhee Lee | SK Telecom | ok0315@sk.com | ||
| Bin Yeong Yoon | ETRI | byyun@etri.re.kr | ||
| ChunglaeCho | ETRI | clcho@etri.re.kr | ||
| TaeyoungKim | S & T Soft | kty@sntsoft.co.kr | ||
| Peter Park | KT | peter.park@kt.com | ||
| TaehyunKwon | ETRI | thkwon@etri.re.kr | ||
| ChansungPark | ETRI | chansung18@etri.re.kr |
Overview
ACTN refers to the set of virtual network operations needed to
orchestrate, control and manage large-scale multi-domain TE networks
so as to facilitate network programmability, automation, efficient
resource sharing, and end-to-end virtual service aware connectivity
and network function virtualization services.
...
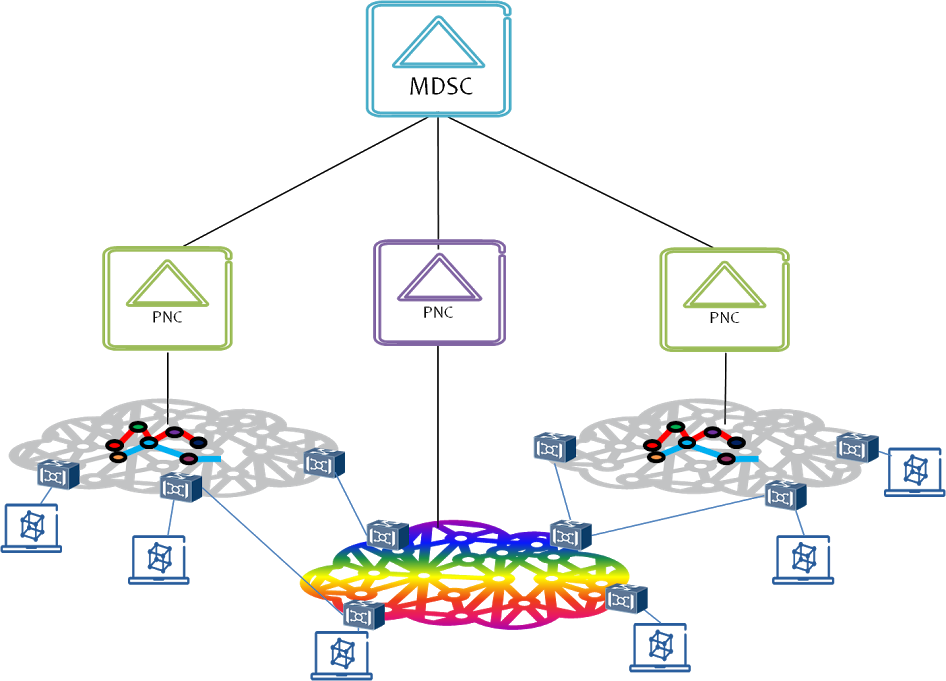
. CNC - Customer Network Controller - . MDSC - Multi Domain Service Coordinator - . PNC - Physical Network Controller -
Customer Network Controller
A Virtual Network Service is instantiated by the Customer Network
Controller via the CMI (CNC-MDSC Interface). As the Customer Network
Controller directly interfaces the application stratum, it
understands multiple application requirements and their service
needs. It is assumed that the Customer Network Controller and the
MDSC have a common knowledge on the end-point interfaces based on
their business negotiation prior to service instantiation. End-point
interfaces refer to customer-network physical interfaces that
connect customer premise equipment to network provider equipment.
In addition to abstract networks, ACTN allows to provide the CNC
with services. Example of services include connectivity between one
of the customer's end points with a given set of resources in a data
center from the service provider.
...
The MDSC (Multi Domain Service Coordinator) sits between the CNC
(the one issuing connectivity requests) and the PNCs (Physical
Network Controllersr - the ones managing the physical network
resources). The MDSC can be collocated with the PNC, especially in
those cases where the service provider and the network provi
der are the same entityarethesameentity.
The MDSC istheonly building block of thearchitecture that is aistheonlybuildingblock of thearchitecturethatisa
ble to implement all the four ACTN main functionalities, i.e. multi
domain coordination function, virtualization/abstraction function,
customer mapping function and virtual service coordination. The key
point of the MDSC and the whole ACTN framework is detaching the
network and service control from underlying technology and help
customer express the network as desired by business needs. The MDSC
envelopes the instantiation of right technology and network control
to meet business criteria. In essence it controls and manages the
primitives to achieve functionalities as desired by CNC
A hierarchy of MDSCs can be foreseen for scalability and
administrative choices. In order to allow for a hierarchy of MDSC,
the interface between the parent MDSC and a child MDSC must be th
e same as the interface between the MDSC and the PNC. This does not
introduce any complexity as it is transparent from the perspectiveperspec
tive of the CNCs and the PNCs and it makes use of the same interfaceinterfac
e model and its primitives as the CMI and MPI.
A key requirement for allowing recursion of MDSCs is that a single
interface needs to be defined both for the north and the south
bounds. In order to allow for multi-domain coordination a
1:N relationship must be allowed between MDSCs and between MDSCs and PNCs
(i.e. 1 parent MDSC and N child MDSC or 1 MDSC and
N PNCs)
. In addition to that it could be possible to have also a M:1 relationship
between MDSC and PNC to allow for network resource partitioning/
sharing among different customers not necessarily connected to the
same MDSC (e.g. different serviceprovidersdifferentserviceproviders).
Physical Network Controller
The Physical Network Controller is PhysicalNetworkControlleris the one in charge of configuring
the network elements, monitoring the physical topology of the
network and passing networkandpassing it, either raw orabstractedraworabstracted, to the MDSC.
The PNC, in addition to being in charge of controlling the physicalthephysical
network, is able to implement two of the four ACTN main
functionalities: multi domain coordination function and
virtualization/abstraction function
A hierarchy of PNCs can be foreseen for scalability and
administrative choicesadministrativechoices.
Implementing ACTN in ONOS
via PCEP
Supporting VN operations in PCEP for ACTN
via Yang (RestConf / gRPC etc)
IETF ACTN architecture, YANG models and PCE-P protocols for NBI
- ACTN Requirements https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-ietf-teas-actn-requirements/
- ACTN Framework Generic Info Modelfor ACTN - https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-leebelottiietf-teas-actn-infoframework/
- TE Topologybased on Topology YANG model https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-ietf-teas-yang-te-topo/
- TE Tunnel based on YANG model https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-ietf-teas-yang-te/ACTN extention are needed toextend/augemntthe above models/
- Service YANG model https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-zhang-teas-transport-service-model/
- OTN Service YANG model https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-sharma-ccamp-otn-service-model/
- WSON YANG model https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-ietf-ccamp-wson-yang/
- Stateful PCE https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-ietf-pce-stateful-pce/
- LSP State Synchronization for Stateful PCE https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-ietf-pce-stateful-sync-optimizations/
- Hierarchical PCE https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-ietf-pce-hierarchy-extensions/
- PCEP-LS extensions https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-dhodylee-pce-pcep-ls/
- PCEP-VN extensions https://datatracker.ietf.org/doc/draft-leedhody-pce-vn-association/
ACTN Project Development Overview
Hierarchical Topology Abstractions via Standard NBIs
VN (Virtual Network) Creation via PCEP
Supporting VN operations in PCEP
JIRA Tickets
IETF YANG NBI/SBI Jira server ONOS serverId 5d1f0fc4-df4d-33d0-b9b3-55f48bcc614d key ONOS-4840
ACTN MDSC Controller Jira server ONOS serverId 5d1f0fc4-df4d-33d0-b9b3-55f48bcc614d key ONOS-4874