...
While legacy technologies require the manual configuration of multiple devices in the network, VPLS tries to make the process easier for network operators.
The current model expects that hosts to be connected together (any L3 device), sends into the network tagged packets (VLAN Ids)Hosts that get connected together can send in either untagged or VLAN tagged traffic, using either the same or different VLAN ids.
The User Guide assumes:
You already have knowledge on how ONOS generally works;
ONOS has been already installed OR or there’s a management machine ready to push bits to some target machines;
Different hosts have been directly attached to the OpenFlow data plane and they send out tagged packets using none or some (same or different) VLAN Ids.
Starting VPLS
VPLS can set to be installed and configured:
...
Manually, through the ONOS Command Line (CLI), typing "app activate org.onosproject.vpls";
Automatically at ONOS start up, adding the application name "vpls" to the list of apps to be started automatically, in the cell file. Specific startup details can be defined in its own the cell file , on the management machine, before pushing the ONOS bits. See example below:Below, an example is reported.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
# Basic VPLS topology export ONOS_NIC=192.168.56.* export OCI="192.168.56.101" export OC1="192.168.56.101" export OC2="192.168.56.102" export OCNOC3="192.168.56.103" export ONOS_APPS=drivers,openflow,vpls export ONOS_GROUP=sdn export ONOS_SCENARIOS=$ONOS/tools/test/scenarios export ONOS_TOPO=vpls export ONOS_USER=sdn export ONOS_USE_SSH=true export ONOS_WEB_PASS=rocks export ONOS_WEB_USER=onos topo vpls alias vpls-reset='stc net-teardown; stc teardown; topo geant; stc setup && stc net-setup' |
Configuring Configuring VPLS
VPLS relies on the ONOS network configuration subsystem, which is by default distributed on all ONOS nodes and shared by all ONOS applications.
In order to configure have a VPLS working, two things need to be donehappen:
Configure two Two or more interfaces need to be configured
At least one Configure one or more VPLS that associate the above interfaces configured together needs to be configured
The goal of the configuration process is to define what attachment points the hosts are connected to (so which DPID , twhich and which ports), and to associate them under the same overlay network, a VPLS. This will essentially determine what hosts should talk one each other (communicate together, and which don’t).
Both the interfaces the interface and the VPLS configuration itself configurations can be applied either:
Creating Defining a special network-cfg.json configuration file on the management machine, in $ONOS/tools/package/config, before pushing the ONOS bits to the target machines. In this case -while deploying- the network-cfg.json file will be copied over the target machines and parsed; this way is very convenient while developing, but it's not suggested for production deployments
Pushing the same network-cfg.json Pushing a JSON file at run-time, after ONOS has started, using the specific REST API;APIs. This can be done from the management machine, using the tool onos-netcfg (i.e. onos-netcfg {$IP} {NET_CFG_FILE})
From the ONOS CLI, using the interface and VPLS commands.
Configuration file format and syntax
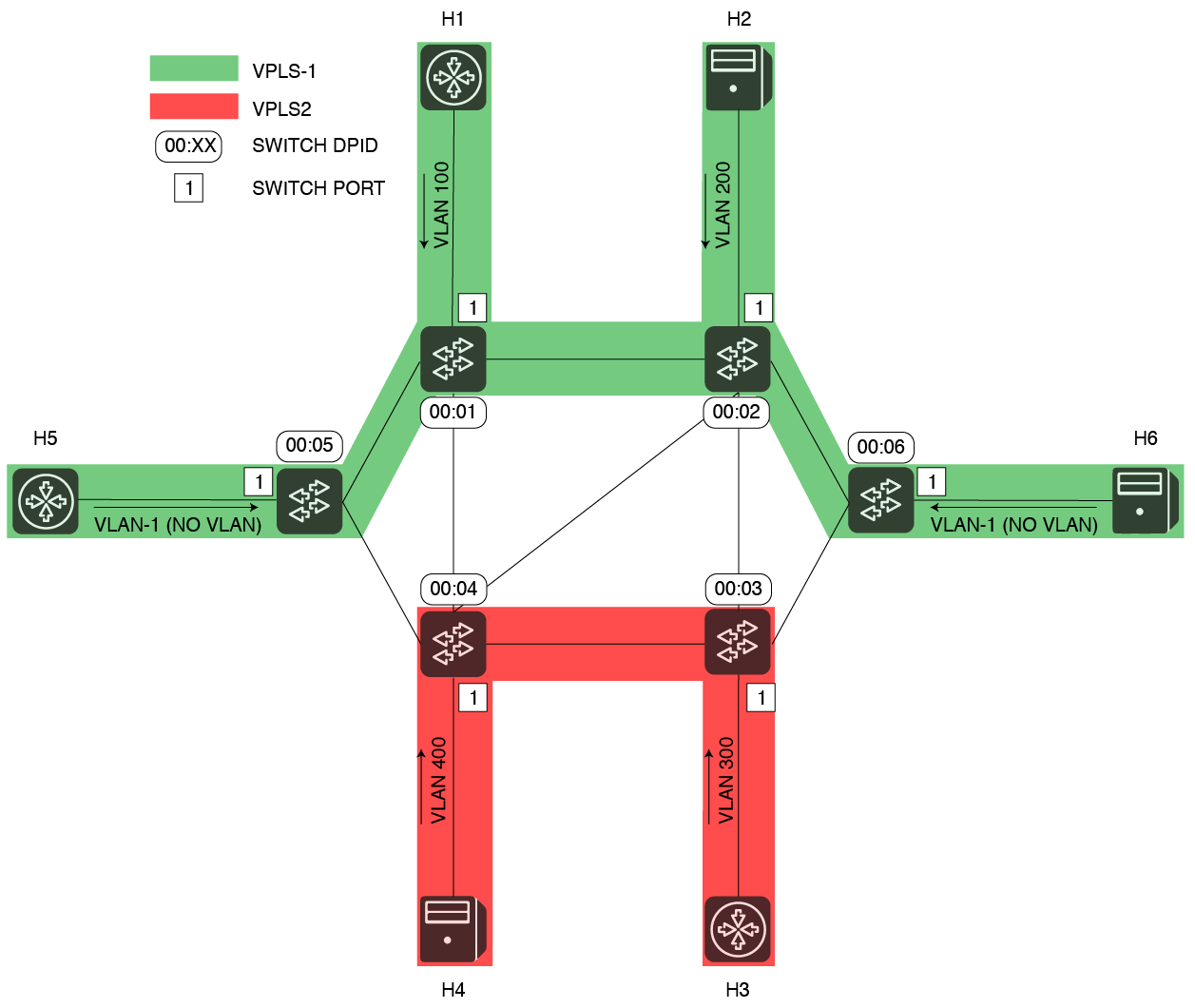
Let’s assume the following scenario:
In this example, five hosts are sending in tagged packets with different VLAN Ids. Two networks VPLSs will be created, one called VPLS-EXAMPLE-1 ( VPLS1 ) -in green, the second -; one called VPLS-EXAMPLE-2 ( VPLS2 ) -in red-. Three Four hosts will be grouped and connected in part of VPLS1, while other two will be associated to VPLS2.
...
VPLS name | VLAN Id | Interface Name | OF Switch DPID | OF Port Number | ||
VPLS1 | 10100 | vpls1h1h1 | 0000000000000001 | 1 | ||
VPLS1 | 200 | h2 | 0000000000000002 | 1 | ||
VPLS1 | 10 | vpls1h2 | -1 (no VLAN) | h5 | 00000000000000050000000000000004 | 1 |
| VPLS1 | 20 | vpls1h3 | 0000000000000003-1 (no VLAN) | h6 | 0000000000000006 | 1 |
VPLS2 | 30300 | vpls2h1h3 | 00000000000000040000000000000003 | 21 | ||
VPLS2 | 40400 | vpls2h2h4 | 00000000000000020000000000000004 | 1 |
In order to configure what has been described above, the following configuration should be pushed to ONOS (either before or after VPLS has been started).
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
{
"ports": {
"of:0000000000000001/1": {
"interfaces": [
{
"name": "vpls1h1h1",
"vlan": "10100"
}
]
},
"of:00000000000000040000000000000002/1": {
"interfaces": [
{
"name": "vpls1h2h2",
"vlan": "10200"
}
]
},
"of:00000000000000040000000000000003/21": {
"interfaces": [
{
"name": "vpls2h1h3",
"vlan": "30300"
}
]
},
"of:00000000000000030000000000000004/1": {
"interfaces": [
{
"name": "vpls1h3h4",
"vlan": "20400"
}
]
},
"of:00000000000000020000000000000005/1": {
"interfaces": [
{
"name": "vpls2h2h5",
"vlan": "40"
}
]
},
},
"appsof:0000000000000006/1" : {
"org.onosproject.vplsinterfaces" : {[
"vpls" : {
"vplsNetworksname" : ["h6"
}
{
]
}
},
"nameapps" : "VPLS1",{
"org.onosproject.vpls" : {
"interfacesvpls" : ["vpls1h1", "vpls1h2", "vpls1h3"]{
"vplsList" : },[
{
"name" : "VPLS2VPLS1",
"interfaces" : ["vpls2h1h1", "vpls2h2h2"]
, "h5", "h6"]
},
]{
}
}
}
} |
The same result can be achieved at run-time, using the interface configuration and VPLS CLI commands as follows (see section "CLI syntax" for more details):
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
onos> interface-add -v 10 of:0000000000000001/1 vpls1h1
onos> interface-add -v 10 of:0000000000000004/1 vpls1h2
onos> interface-add -v 20 of:0000000000000003/1 vpls1h3
onos> interface-add -v 30 of:0000000000000004/2 vpls2h1
onos> interface-add -v 40 of:0000000000000002/1 vpls2h2
onos> vpls-add VPLS1
onos> vpls-add-iface VPLS1 vpls1h1
onos> vpls-add-iface VPLS1 vpls1h2
onos> vpls-add-iface VPLS1 vpls1h3
onos> vpls-add VPLS2
onos> vpls-add-iface VPLS2 vpls2h1
onos> vpls-add-iface VPLS2 vpls2h2 |
As soon as two or more interfaces are added to the same VPLS network, intents to manage broadcast will be installed.
As soon as two or more hosts connected to the same VPLS get discovered by ONOS (and VPLS), intents to manage unicast traffic will be installed.
For more details on the VPLS architecture, internal workflow and intents used, please visit the VPLS Architecture Guide.
Mininet network file (topo-vpls.py)
Would you like to give VPLS a try, but it's too hard and long bringing up an entire network with hosts sending in packets on different VLANs? The mininet (python) file attached gives you an example of how to simulate a similar network. Just modify the file, creating the topology you like and letting Mininet point to your controller IP address.
CLI syntax
VPLS allows to define networks and attach or detach interfaces to them, also by command-line. There is also the option of cleaning all the state of the application for a clean start. Details on the CLI operations are detailed below:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
# Adds a new network
onos> vpls-add $VPLS_NETWORK
# Removes an existing network
onos> vpls-del $VPLS_NETWORK
# Shows the list of networks
onos> vpls-list
VPLS2
VPLS1
# Shows the list of attached interfaces (for a given network) or all the list of networks and interfaces in each of them (if no network is provided)
onos> vpls-show [$VPLS_NETWORK]
VPLS2: interface=[vpls2h1, vpls2h2]
VPLS1: interface=[vpls1h1, vpls1h2, vpls1h3] |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
# Adds an existing interface (in netcfg) to an existing network
onos> vpls-add-iface $VPLS_NETWORK $INTERFACE_NAME
# Removes an existing interface from an existing network
onos> vpls-del-iface $VPLS_NETWORK $INTERFACE_NAME |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
# Cleans the status of the VPLS application (i.e., removes networks, detaches interfaces and withdraws intents)
onos> vpls-clean |
Issues and Troubleshooting
Things not working as expected? Time to troubleshoot!
Hosts are not communicating? Do you have at least two interfaces configured and two hosts attached - using the same VLAN Id?
Is your configuration correct? Has it been correctly parsed? The first step is to checked if the configuration has been parsed and correct running at the ONOS CLI the command "interfaces". This should give you a list of interfaces configured in the system
Any exception? Type log:exception-display in the ONOS CLI to discover it.
Are hosts connected to your OpenFlow data plane? I a host start to send out packets into the OpenFlow network you should be able to see it, even if VPLS is not installed yet or no configuration is provided. Go in the ONOS CLI and type "hosts". As result, you should see something similar to this (100, 2000, 300 in this case are the VLAN Ids used):
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
onos> hosts
id=00:00:00:00:00:01/10, mac=00:00:00:00:00:01, location=of:0000000000000001/1, vlan=10, ip(s)=[10.0.0.1], configured=false
id=00:00:00:00:00:02/10, mac=00:00:00:00:00:02, location=of:0000000000000004/1, vlan=10, ip(s)=[10.0.0.2], configured=false
id=00:00:00:00:00:03/20, mac=00:00:00:00:00:03, location=of:0000000000000003/1, vlan=20, ip(s)=[10.0.0.3], configured=false
id=00:00:00:00:00:04/30, mac=00:00:00:00:00:04, location=of:0000000000000004/2, vlan=30, ip(s)=[10.0.0.4], configured=false
id=00:00:00:00:00:05/40, mac=00:00:00:00:00:05, location=of:0000000000000002/1, vlan=40, ip(s)=[10.0.0.5], configured=false |
Please, note that you should see results only for hosts that already sent traffic into the Network. This doesn’t happen for example with Mininet, where hosts are only processes without any application running by default.
Also, as in any related Intent based ONOS applications, there are certain best-practices to follow, to see what’s going in the Intent / Flow subsystems. Type "intents" to see the detailed list of intents, or "intent -s" for the intents summary.
Below is an approximation of what you should see for the network "VPLS2", after pinging between interfaces "vpls2h1" and "vpls2h2". Notice that two broadcast intents are installed at the beginning, and two unicast intents once the interfaces start pinging each other.
"name" : "VPLS2",
"interfaces" : ["h3", "h4"],
"encapsulation" : "vlan"
}
]
}
}
}
} |
The same result can be achieved at run-time, using the interface and VPLS CLI commands as follows (see section "CLI syntax" for more details):
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
onos> interface-add -v 100 of:0000000000000001/1 h1
onos> interface-add -v 200 of:0000000000000002/1 h2
onos> interface-add -v 300 of:0000000000000004/1 h3
onos> interface-add -v 400 of:0000000000000002/1 h4
onos> interface-add of:0000000000000005/1 h5
onos> interface-add of:0000000000000006/1 h6
onos> vpls create VPLS1
onos> vpls add-if VPLS1 h1
onos> vpls add-if VPLS1 h2
onos> vpls add-if VPLS1 h5
onos> vpls add-if VPLS1 h6
onos> vpls set-encap VLPS1 VLAN
onos> vpls create VPLS2
onos> vpls add-if VPLS2 h3
onos> vpls add-if VPLS2 h4 |
As soon as two or more interfaces are added to the same VPLS, intents to manage broadcast will be installed.
As soon as two or more hosts connected to the same VPLS will get discovered by ONOS (and VPLS), intents to manage unicast traffic will be installed.
For more details on the VPLS architecture, internal workflow and intents used, please visit the VPLS Architecture Guide.
Demo topology
Would you like to give VPLS a try, but it's too hard and long bringing up an entire network with hosts sending in packets on different VLANs? We made available a default topology file in ONOS for you!
The topology file is under $ONOS_ROOT/tools/test/topos. It consists of three files:
- The Mininet topology file
- The network-cfg.json ONOS configuration file
- The receipe file, to check that when the topology is instantiated the number of devices, hosts and links matches the expectations
You can just take these files as examples for your topologies / configurations, or you can use them automatically along with the tool stc net-setup, which makes very convenient to deploy ONOS and Mininet together in a couple of commands.
Using the topology file along with stc net-setup is very simple. Just few steps:
- Create one mininet machine and one or more ONOS target machines (ready to receive the ONOS bits). The mininet machine should have the same username and password of the ONOS machine(s) and you should be able to run on it as well as sudoer without password
- Define your cell file. Add to it the following variable: OCN=XXX.YYY.WWW.ZZZ, where XXX.YYY.WWW.ZZZ is the IP of your Mininet machine
- After you have loaded your cell file, run the command topo vpls. This will tell stc what topology to use.
- Now run stc setup && stc net-setup. This will first deploy ONOS on the remote nodes (stc setup). It will then deploy the Mininet topology and apply the related ONOS configuration.
- You will be able to access your mininet machine directly from the management machine,
CLI syntax
The applications allows to define and configured VPLSs also from a CLI. The paragraph below reports details about the CLI command syntax.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
# Creates a new VPLS
onos> vpls create {$VPLS_NAME}
# Deletes an existing VPLS
onos> vpls delete {$VPLS_NAME}
# Lists the configured VPLSs
onos> vpls list
Configured VPLSs
----------------
VPLS1
VPLS2
# Shows the list configured VPLSs, including their interfaces and the encapsulation type in use. If a VPLS name is specified, only the details for that VPLS are returned.
onos> vpls show [$VPLS_NAME]
Configured VPLSs
----------------
VPLS name: VPLS1
Associated interfaces: [h1, h2, h5, h6]
Encapsulation: NONE
----------------
VPLS name: VPLS2
Associated interfaces: [h3, h4]
Encapsulation: VLAN
----------------
# Sets the encapsulation type for a VPLS
onos> vpls set-encap {$VPLS_NAME} {VLAN|MPLS|NONE} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
# Adds an existing interface (in netcfg) to an existing VPLS
onos> vpls add-if {$VPLS_NAME} {$INTERFACE_NAME}
# Removes an existing interface from an existing VPLS
onos> vpls rem-if {$VPLS_NAME} {$INTERFACE_NAME} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
# Cleans the status of the VPLS application (i.e., deletes VPLSs, removes interfaces from existing VPLSs and withdraws intents)
onos> vpls clean |
Issues and Troubleshooting
Things not working as expected? Time to troubleshoot!
- Is VPLS running? Check with apps -a -s. Is VPLS there?
- Hosts are not communicating? Do you have at least two interfaces configured and two hosts attached? Are the VLANs correct ?
Is your configuration correct? Has it been correctly parsed? The first step is to check if the configuration has been loaded. Helpful commands are netcfg, interfaces, and the VPLS CLI commands (!!!! the VPLS configuration is not visible if the application is not started).
Any exception? Type log:exception-display in the ONOS CLI to discover it.
Are the hosts connected to your OpenFlow data plane? Have the hosts been discovered correctly by ONOS? If a host sends out packets into the OpenFlow network, you should be able to see it, even if VPLS is not installed yet or no configuration is provided. Go in the ONOS CLI and type "hosts". As result, you should see something similar to this:
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
onos> hosts
id=00:00:00:00:00:01/100, mac=00:00:00:00:00:01, locations=[of:0000000000000001/1], vlan=100, ip(s)=[10.0.0.1], name=h1, latitude=40.888148, longitude=-103.459878, configured=false
id=00:00:00:00:00:02/200, mac=00:00:00:00:00:02, locations=[of:0000000000000002/1], vlan=200, ip(s)=[10.0.0.2], name=h2, latitude=42.756945, longitude=-79.831317, configured=false
id=00:00:00:00:00:03/300, mac=00:00:00:00:00:03, locations=[of:0000000000000003/1], vlan=300, ip(s)=[10.0.0.3], name=h3, latitude=35.427493, longitude=-83.885831, configured=false
id=00:00:00:00:00:04/400, mac=00:00:00:00:00:04, locations=[of:0000000000000004/1], vlan=400, ip(s)=[10.0.0.4], name=h4, latitude=34.66229, longitude=-110.946662, configured=false
id=00:00:00:00:00:05/None, mac=00:00:00:00:00:05, locations=[of:0000000000000005/1], vlan=None, ip(s)=[10.0.0.5], name=h5, latitude=33.224634, longitude=-121.532943, configured=false
id=00:00:00:00:00:06/None, mac=00:00:00:00:00:06, locations=[of:0000000000000006/1], vlan=None, ip(s)=[10.0.0.6], name=h6, latitude=42.395459, longitude=-75.293563, configured=false |
Please, note that you should see results only for hosts that already sent traffic into the data plane. This sometimes doesn’t happen for example with Mininet, where hosts are only processes without any application running by default.
Also, as in any related intent-based ONOS applications, there are certain best-practices to follow, to see what’s going on with intents and flows. Type "intents" to see the detailed list of intents, or "intent -s" for the intents summary.
Below is an approximation of what you should see for the topology used in the example, assuming all hosts have already all been discovered and communicate together. Note that in this case, six intents for broadcast, and six intents for unicast are installed.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
onos> intents
id=0xa6, state=INSTALLED, key=VPLS1-uni-of:0000000000000006-1-00:00:00:00:00:06, type=MultiPointToSinglePointIntent, appId=org.onosproject.vpls
selector=[ETH_DST:00:00:00:00:00:06]
treatment=[NOACTION]
ingress=[of:0000000000000005/1, of:0000000000000001/1, of:0000000000000002/1], egress=of:0000000000000006/1
id=0x1a, state=INSTALLED, key=VPLS2-uni-of:0000000000000003-1-00:00:00:00:00:03, type=MultiPointToSinglePointIntent, appId=org.onosproject.vpls
selector=[ETH_DST:00:00:00:00:00:03]
treatment=[NOACTION]
constraints=[EncapsulationConstraint{encapType=VLAN}]
ingress=[of:0000000000000004/1], egress=of:0000000000000003/1
id=0xa7, state=INSTALLED, key=VPLS1-uni-of:0000000000000002-1-00:00:00:00:00:02, type=MultiPointToSinglePointIntent, appId=org.onosproject.vpls
selector=[ETH_DST:00:00:00:00:00:02]
treatment=[NOACTION]
ingress=[of:0000000000000005/1, of:0000000000000006/1, of:0000000000000001/1], egress=of:0000000000000002/1
id=0xa1, state=INSTALLED, key=VPLS1-brc-of:0000000000000005-1-FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF, type=SinglePointToMultiPointIntent, appId=org.onosproject.vpls
selector=[ETH_DST:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF]
treatment=[NOACTION]
ingress=of:0000000000000005/1, egress=[of:0000000000000006/1, of:0000000000000001/1, of:0000000000000002/1]
id=0xa5, state=INSTALLED, key=VPLS1-uni-of:0000000000000001-1-00:00:00:00:00:01, type=MultiPointToSinglePointIntent, appId=org.onosproject.vpls
selector=[ETH_DST:00:00:00:00:00:01]
treatment=[NOACTION]
ingress=[of:0000000000000005/1, of:0000000000000006/1, of:0000000000000002/1], egress=of:0000000000000001/1
id=0x1b, state=INSTALLED, key=VPLS2-uni-of:0000000000000004-1-00:00:00:00:00:04, type=MultiPointToSinglePointIntent, appId=org.onosproject.vpls
selector=[ETH_DST:00:00:00:00:00:04]
treatment=[NOACTION]
constraints=[EncapsulationConstraint{encapType=VLAN}]
ingress=[of:0000000000000003/1], egress=of:0000000000000004/1
id=0xa3, state=INSTALLED, key=VPLS1-brc-of:0000000000000006-1-FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF, type=SinglePointToMultiPointIntent, appId=org.onosproject.vpls
selector=[ETH_DST:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF]
treatment=[NOACTION]
ingress=of:0000000000000006/1, egress=[of:0000000000000005/1, of:0000000000000001/1, of:0000000000000002/1]
id=0x0, state=INSTALLED, key=VPLS2-brc-of:0000000000000003-1-FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF, type=SinglePointToMultiPointIntent, appId=org.onosproject.vpls
selector=[ETH_DST:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF]
treatment=[NOACTION]
constraints=[EncapsulationConstraint{encapType=VLAN}]
ingress=of:0000000000000003/1, egress=[of:0000000000000004/1]
id=0x1 | ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
onos> intents id=0x0, state=INSTALLED, key=VPLS2-brc-of:00000000000000020000000000000004-1-FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF, type=SinglePointToMultiPointIntent, appId=org.onosproject.vpls selector=[ETH_DST:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF] treatment=[NOACTION] constraints=[EncapsulationConstraint{encapType=VLAN}] ingress=of:00000000000000020000000000000004/1, egress=[of:00000000000000040000000000000003/21] id=0x10xa0, state=INSTALLED, key=VPLS2VPLS1-brc-of:00000000000000040000000000000001-21-FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF, type=SinglePointToMultiPointIntent, appId=org.onosproject.vpls selector=[ETH_DST:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF] treatment=[NOACTION] ingress=of:0000000000000004/2, egress=[0000000000000001/1, egress=[of:0000000000000005/1, of:0000000000000006/1, of:0000000000000002/1] id=0x100xa2, state=INSTALLED, key=VPLS2VPLS1-unibrc-of:0000000000000002-1-00FF:00FF:00FF:00FF:00FF:05FF, type=MultiPointToSinglePointIntentSinglePointToMultiPointIntent, appId=org.onosproject.vpls selector=[ETH_DST:00FF:00FF:00FF:00FF:00FF:05FF] treatment=[NOACTION] ingress=[of:0000000000000004/2], egress=of:0000000000000002/1 id=0x11 ingress=of:0000000000000002/1, egress=[of:0000000000000005/1, of:0000000000000006/1, of:0000000000000001/1] id=0xa4, state=INSTALLED, key=VPLS2VPLS1-uni-of:00000000000000040000000000000005-21-00:00:00:00:00:0405, type=MultiPointToSinglePointIntent, appId=org.onosproject.vpls selector=[ETH_DST:00:00:00:00:00:0405] treatment=[NOACTION] ingress=[of:0000000000000006/1, of:0000000000000001/1, of:0000000000000002/1], egress=of:00000000000000040000000000000005/21 |
Are intents installed?
Yes! (we’re happy!).
No! Ops….let’s check flows, since 1 intent is composed by one or more flows!
Type "flows pending-add" to see if there’s any flow for which ONOS still not received an installation confirmation
Type "flows" to see the detailed list of flows - installed or not by the system
...
, flows -s for a summary
Still having issues? Write to us. We can help! Mailing Lists