Table of Contents maxLevel 4
Team
| maxLevel | 4 |
|---|
| Name | Organization | |
|---|---|---|
| Adarsh M | Huawei Technologies | adarsh.m@huawei.com |
| Bharat Saraswal | Huawei Technologies | bharat.saraswal@huawei.com |
| Gaurav Agrawal | Huawei Technologies | gaurav.agrawal@huawei.com |
| Janani B | Huawei Technologies | janani.b@huawei.com |
| Sathish Kumar M | Huawei Technologies | sathishkumar.m@huawei.com |
| Suchitra H N | Huawei Technologies | suchitra.hn@huawei.com |
| Vidyashree Rama | Huawei Technologies | vidyashree.rama@huawei.com |
| Vinod Kumar S | Huawei Technologies | vinods.kumar@huawei.com |
| Shankara | Huawei Technologies |
Requirements for Hummingbird Release
| Requested By | Requirements | Suggested Priority (high - Middle -Low) | Current Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thomas Vachuska | Thanks for the demo of the YANG utilities at today’s TST meeting. While a lot of good work was done in the last release, I was a little bit surprised that the codec functionality was pushed off to the next release - and that NB-related concerns superseded SB-related ones. In my view, this is the basic value of using the YANG models - as it provides the ability to consume/produce XML payloads that are complaint with the model in a structured manner via Java API. We have a set of use-cases for this to control/configure devices via NETCONF. Presently we have to accomplish this using hand-crafted XML and we were hoping to use the YANG tools-generated codecs for this. Consequently the SB use of YANG is of much more importance to us than the NB use of YANG - at least for the near-term. In the Hummingbird release we need to be able to use the YANG tools generated artifacts together with our existing NETCONF sub-controller to produce driver implementations for several packet and optical devices. For this reason, I would like to request that this work be prioritized over anything else with respect to other YANG-related work. In order for that to happen, I think a number of other important questions will have to be answered and accounted for in the overall design of the YANG utilities:
| High | reviewing |
| Ali Al-Shabibi | JSON or JSON-Schema Intermediary Representation. It would be nice if we could go from YANG to JSON or JSON-Schema because from this IR format we can easily go to XML or JSON or some other format that another protocol may want to use. As you probably know, Netconf is only one of the southbound to deliver payloads other ones such as gRPC or REST can be used. | medium | |
| Marc De Leenheer | Support for OpenROADM YANG models. The specification contains two parts, a service-level model (NB) and a device-level model (SB). The first phase has already started, we want to integrate the device model into ONOS by early Q3 2016. In Q4 we will do the service level models. This is high priority work in collaboration with AT&T. | high | |
| Aihua Guo | In order to support the use of standard IETF YANG models as an NBI for hierarchical SDN control, it is expected that the following YANG data constructs be supported in the H releases: augment (partially supported in G release), identity, feature/if-feature, when, must, leafref, path, require-instance. These data constructs are defined by YANG 1.1, and most of the IETF YANG models contain those constructs written in YANG 1.1. | high |
Overview
YANG is a data modeling language used to model configuration & state data. Modeling languages such as SMI (SNMP), UML, XML Schema, and others already existed. However, none of these languages were specifically targeted to the needs of configuration management. They lacked critical capabilities like being easily read and understood by human implementers, and fell short in providing mechanisms to validate models of configuration data for semantics and syntax.
YANG Utils are the basic building block to achieve the final goal of abstracting the language based Syntax/Semantics processing by APPs.
The YANG modeled interfaces need to be implemented by corresponding application component. There are 2 parts in implementing the interface:
- syntax/semantics processing of the request/response being exchanged.
- business logic to compute the request.
We intend to abstract the applications from syntactic processing of information encoding with external world.We intend to provide a framework in which the applications only need to implement the business logic and seamlessly support any interface language like REST, NETCONF etc.
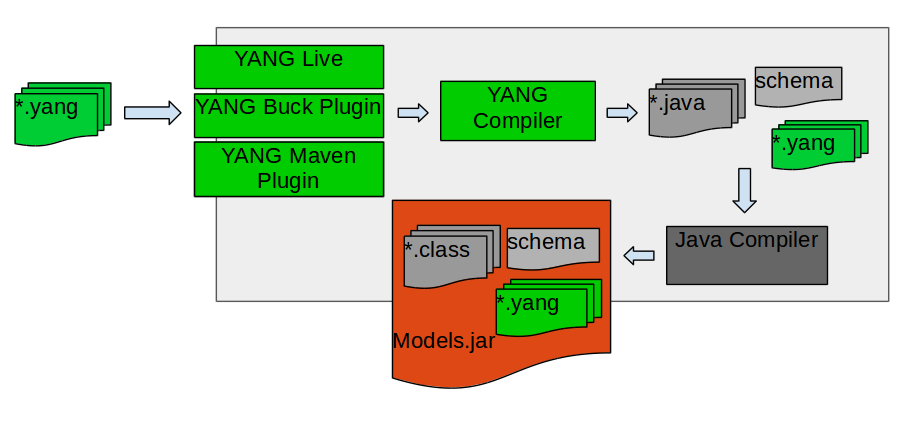
Steps to use YANG utils
Step1 : Create a test app and add YANG utils maven plugin to pom file’s build section
| Mahesh Poojary S | Huawei Technologies | |
| Rama Subba Reddy S | Huawei Technologies | |
| Sonu Gupta | Huawei Technologies | sonu.gupta@huawei.com |
| A U surya | Huawei Technologies |
Overview
YANG is a data modeling language used to model configuration & state data. Modeling languages such as SMI (SNMP), UML, XML Schema, and others already existed. However, none of these languages were specifically targeted to the needs of configuration management. They lacked critical capabilities like being easily read and understood by human implementers, and fell short in providing mechanisms to validate models of configuration data for semantics and syntax.
YANG tools are the basic building block to achieve the final goal of abstracting the language based Syntax/Semantics processing by APPs.
The YANG modeled interfaces need to be implemented by corresponding application component. There are 2 parts in implementing the interface:
- Syntax/semantics processing of the request/response being exchanged.
- Business logic to compute the request.
We intend to abstract the applications from syntactic processing of information encoding with external world.We intend to provide a framework in which the applications only need to implement the business logic and seamlessly support any interface language like REST, NETCONF etc.
Steps to use YANG tools
Yang Buck Plugin :
Step 1 : Create a test app and add yang dependency as shown below.
| Code Block |
|---|
COMPILE_DEPS = [
'//lib:CORE_DEPS',
'//lib:onos-yang-model',
]
yang_osgi_jar(
deps = COMPILE_DEPS,
name = 'onos-apps-l3vpn-yangmodel',
srcs = glob(['src/main/**/*.yang']),
visibility = [
'PUBLIC'
],
) |
Step 2: Create a folder structure as “src/main/yang” in the test app folder and place your YANG files in it.
Step 3 : Build using buck build onos command. Generated java code will be placed in default directory or in desired destination folder configured by user.
Yang Maven Plugin :
Step1 : Create a test app and add YANG tools maven plugin to pom file’s build section
| Code Block |
|---|
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.onosproject</groupId>
<artifactId>onos-yang-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.9</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<configuration>
<classFileDir>src/main/java</classFileDir>
|
| Code Block |
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.onosproject</groupId>
<artifactId>yangutils-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<configuration>
</configuration>
<goals>
<goal>yang2java</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build> |
Step 2 : Add dependency to pom file’s dependency section
| Code Block |
|---|
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.onosproject</groupId>
<artifactId>yangutils-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.onosproject</groupId>
<artifactId>onos-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.felix</groupId>
<artifactId>org.apache.felix.scr.annotations</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies> |
Step 3 : Plugin configuration supported in YANG utils
only if your yang file contains notification in it. You need to add dependencies for "onos-api".
Step 3 : Plugin configuration supported in YANG tools
Create a folder structure as “src/main/yang” in
Create a folder structure as “src/main/yang” in the test app folder and place your YANG files in it. In case user want to give desired path for source YANG files and generated java files, the following configuration can be appended to the above pom.xml file.
Code Block <configuration> <yangFilesDir>DesiredYangFilesPath</yangFilesDir><genFilesDir>DesiredGeneratedJavaFilesPath<<classFileDir>DesiredGeneratedJavaFilesPath</
genFilesDir>classFileDir> </configuration>
Step 4 : Execution Execution of application
Build using mvn clean install/ mvn install. Generated java code will be placed in default directory or in desired destination folder configured by user.
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
YANG utils constructs support/plan
Note:
|
YANG tools constructs support/plan
| YANG Construct | Supported |
|---|
| /Planned version | |
|---|---|
| anyxml | Not planned |
| argument |
| Hummingbird(partial support) | |
| augment | Goldeneye |
| uses-augment | Loon |
| base | Hummingbird |
| belongs-to | Goldeneye |
| bit |
| Hummingbird | |
| case | Goldeneye |
| choice | Goldeneye |
| config | Falcon |
| contact | Goldeneye Enhancement in Hummingbird |
| container | Falcon |
| default | Goldeneye Enhancement in Humminbird |
| description | Goldeneye Enhancement in Hummingbird |
| deviate | Not planned |
| deviation | Not planned |
| enum | Goldeneye |
| error-app-tag |
| Hummingbird |
| error-message |
| Hummingbird |
| extension |
| Hummingbird(partial support) | |
| feature | Hummingbird |
| fraction-digits |
| Hummingbird | |
| grouping | Goldeneye |
| identity | Hummingbird |
| if-feature | Hummingbird |
| import | Goldeneye Enhancement in Hummingbird |
| include | Goldeneye Enhancement in Hummingbird |
| input | Goldeneye |
| key | Goldeneye |
| leaf | Falcon |
| leaf-list | Falcon |
| length | Goldeneye |
| list | Falcon |
| mandatory | Falcon |
| max-elements | Goldeneye |
| min-elements | Goldeneye |
| module | Falcon |
| must | Hummingbird |
| namespace | Goldeneye |
| notification | Goldeneye |
| ordered-by | Not planned |
| organization | Goldeneye Enhancement in Hummingbird |
| output | Goldeneye |
| path | Hummingbird |
| pattern | Goldeneye |
| position | Goldeneye |
| prefix | Goldeneye |
| presence | Goldeneye |
| range | Goldeneye |
| reference | Goldeneye Enhancement in Hummingbird |
| refine | Not planned |
| require-instance |
| Hummingbird | |
| revision | Goldeneye Enhancement in Hummingbird |
| revision-date | Goldeneye |
| rpc | Goldeneye |
| status | Goldeneye Enhancement in Hummingbird |
| submodule | Goldeneye |
| type | Goldeneye |
| typedef | Goldeneye |
| unique |
| Kingfisher | |
| unknown | Kingfisher |
| units | Goldeneye |
| uses | Goldeneye Enhancement in Hummingbird |
| value | Goldeneye |
| when | Hummingbird |
| yang-version | Goldeneye |
| yin-element | Not Planned |
Built-in YANG data types support/plan
| Binary | Goldeneye Enhancement in Hummingbird |
| Bits | Goldeneye Enhancement in Hummingbird |
| boolean | Goldeneye |
| decimal64 | Goldeneye Enhancement in Hummingbird |
| empty | Goldeneye |
| enumeration | Goldeneye |
| identityref | Hummingbird |
| instance-identifier | Hummingbird |
| int8 | Goldeneye |
| int16 | Goldeneye |
| int32 | Goldeneye |
| int64 | Goldeneye |
| leafref | Hummingbird |
| string | Falcon |
| uint8 | Goldeneye |
| uint16 | Goldeneye |
| uint32 | Goldeneye |
| uint64 | Goldeneye |
| union | Goldeneye |
Generated JAVA Details
Common behavior
Identifier
The identifier name of YANG constructs are taken, and are used in java by converting it to lower camel case. Identifier names are allowed to have three special characters such as “-”, ”_”, “.”. Whereas, in java, we cannot use these special characters. These characters will be removed during conversion. Conversion takes place by following the below rules of lower camel case.
The first letter of the identifier will be a small letter. If the three special characters occur alone or in group, they will be removed and the consecutive letter will be capitalized.
name-conversion will be mapped as nameConversion
yang-._constuct-generation will be mapped as yangConstuctGeneration
When identifier name has a special character followed by a number, the following letter from the digits will be capitalized.
yang_123construct will be mapped to yang123Construct
In java file, class name or attribute name cannot have java keyword or start with digits. During the conversion into java, we add prefix to the identifier “yangAutoPrefix”, by default.
_123date will be mapped to yangAutoPrefix123Date
const will be mapped to yangAutoPrefixConst
As per camelcase conversion rules, no two consecutive letters will have capitalization and the last letter will also not be capitalized.
- ca-l.e_nder will be mapped to caLeNder
- tric-._k will be mapped to trick
If users input has capital case, the following will be the conversion methods.
TESTNAME will be mapped to testname
TEST-NAME will be mapped to testName
TestName will be mapped to testName
TEST3NAME will be mapped to test3Name
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
If an identifier for a construct contains java keywords, then it name will be prefixed with "yangAutoPrefix" in generated code. |
Namespace
The namespace is a mandatory statement in the module. We define namespace for URL/URI and for folder structure of generated java code. Here in ONOS YANG plugin, namespace forms a folder structure which in turn will be the package name in java.
The package will have “org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.” by default in it. The namespace will be added to the above and the folder structure will also be formed respectively. This becomes the parent package. The conversion from YANG namespace to the java package will take place as below.
The complete namespace will be changed to lowercase letters. When special characters or a group of special characters are found, it replaces those characters by dot.
"http://acme.example.com/system" will be mapped
as as org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20160427
In java the package cannot have folder name which begins with digits or java keyword. Incase if found in YANG file these will be converted by adding prefix “yangautoprefix”.
http://acme.123example.com/try" will be mapped
as as org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.yangautoprefix123example.com.yangautoprefixtry.rev20160427
- At the end of the package the revision in module will be added by the string rev<yyyymmdd>.If the revision does not exist in the YANG file current date will be appended to the package.
When a node appears, with child node in it, a new package will be generated under the parent package, for that node. The new package is, parent package appended with the node name. The class for that node will be placed under this newly created package.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : acme-system.yang
module acme-system {
namespace "http://acme.example.com/system";
prefix "acme";
organization "ACME Inc.";
contact "joe@acme.example.com";
description
"The module for entities implementing the ACME system.";
revision 2007-06-09 {
description "Initial revision.";
}
container system {
container login {
leaf message {
type string;
description
"Message given at start of login session";
}
}
}
.
.
.
} |
...
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : System.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem; . . . public interface System extends AugmentationHolder { . . . } File : Login.java package import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem.system.Login; /** * Abstraction . of an entity which represents the functionality of system. */ public interface System { /** * Returns the attribute login. public interface Login extends AugmentationHolder { * * @return login value of login */ Login login(); /** * Sets the attribute login. * . . * @param login value of login */ void login(Login login); } |
Javadocs
Currently Java doc will be generated as per ONOS javadoc guidelines.
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
YANG statements
Module
Overview
The primary unit of YANG is module. The module statement groups all the statements that belong to module together. The module statement argument is name of the module followed by sub-statements.
JAVA mapping
Module statement is mapped to
Service
interfaceinterface
Manager class
It includes:
a) java methods corresponding to the YANG RPC (Refer RPC section for more details)
b) If module contains notification, generated service interface will extend listener service (refer notification for more details)
It includes:
a ) Activate/Deactivate methods
b) If module contains child data nodes, getters and setters for those nodes will be generated for app developers to implement.
c)If module contains notification, generated manager class will extend ListenerRegistry(refer notification for more details) .
The manager class implements the service interface. The name of service interface and manager class is <module_name>Service.java and <module_name>Manager.java..The name of service interface is <module_name>Service.java .
c) If module contains augment the get and setter for augmented module will be generated.Info Service file will be generated only if RPC/Notification is present.
- Interface and implementation class (Note: for module implementation class will have name xxxxOpParam.java)
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : network.yang
module network {
yang-version 1;
namespace "urn:TBD:params:xml:ns:yang:nodes";
prefix nd;
organization "TBD";
contact
"WILL-BE-DEFINED-LATER";
description
"This module defines a common base model for a collection
of nodes in a network. Node definitions s are further used
in network topologies and inventories.";
revision 2014-03-09 {
description
"Initial revision.";
reference "draft-clemm-i2rs-yang-network-topo-04";
}
list networklist {
key "network-id";
leaf network-id {
type string;
}
leaf server-provided {
type boolean;
config false;
}
}
….
}rpc rpc-test {
input {
container cont {
leaf lf {
type string;
}
}
}
}
} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : NetworkService.java
| ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
File : NetworkService.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.tbd.params.xml.ns.yang.nodes.rev20140309; import java.util.List; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.tbd.params.xml.ns.yang.nodes.rev20140309.network.Networklist; public interface NetworkService { List<Networklist> getNetworklist(); void setNetworklist(List<Networklist> networklist); } File : NetworkManager.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.tbd.params.xml.ns.yang.nodes.rev20140309; import java.util.List; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Activate; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Component; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Deactivate; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Service; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.tbd.params.xml.ns.yang.nodes.rev20140309.network.rpctest.NetworklistRpcTestInput; import org.slf4j.Logger; import static org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.getLogger; @Component (immediate = true) @Service public class NetworkManager implements NetworkService { private final Logger log = getLogger(getClass()); @Activate public void activate() { /** * Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of network. */ public interface NetworkService { //TODO: YANG utils generated code/** * Service interface of log.info("Started");rpcTest. } * @Deactivate public void* deactivate() { //TODO: YANG utils generated code@param inputVar input of service interface rpcTest */ void log.info("Stopped"rpcTest(RpcTestInput inputVar); } File : Network.java package @Override public List<Networklist> getNetworklist() { //TODO: YANG utils generated code return null; } @Override public void setNetworklist(List<Networklist> networklist) { //TODO: YANG utils generated code } } |
Sub Module
Overview
The “submodule” groups all the statements that belongs to the submodule together. The "submodule" statement's argument is the name of the submodule, followed by a block of sub statements.
JAVA mapping
Submodule mapping to java is same as module and files with be generated in module’s namespace.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : acme-system.yang
module acme-system {
namespace "http://yang-central.org/ns/example/acme";
prefix acme;
include "acme-types";
leaf id {
type string;
}
}
File : acme-types.yang
submodule acme-types {
yang-version 1;
belongs-to "acme-system" {
prefix "acme";
}
leaf access-timeout {
type uint32;
}
leaf retries {
type uint8;
}
} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : AcmeSystemManager.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.yang.central.org.ns.example.acme.rev20160526; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Activate; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Component; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Deactivate; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Service; import org.slf4j.Logger; import static org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.getLogger; @Component (immediate = true) @Service public class AcmeSystemManager implements AcmeSystemService { private final Logger log = getLogger(getClass()); @Activateorg.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.tbd.params.xml.ns.yang.nodes.rev20140309; import java.util.List; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.tbd.params.xml.ns.yang.nodes.rev20140309.network.Networklist; /** * Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of network. */ public interface Network { /** * Returns the attribute networklist. * * @return networklist list of networklist */ List<Networklist> networklist(); /** * Sets the attribute networklist. * * @param networklist list of networklist */ void networklist(List<Networklist> networklist); /** * Adds to the list of networklist. * * @param addTo value of networklist */ void addToNetworklist(Networklist addTo); } File: NetworkOpParam.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.tbd.params.xml.ns.yang.nodes.rev20140309; import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Objects; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.tbd.params.xml.ns.yang.nodes.rev20140309.network.Networklist; import org.onosproject.yang.model.InnerModelObject; /** * Represents the implementation of network. * * <p> * valueLeafFlags identify the leafs whose value are explicitly set * Applicable in protocol edit and query operation. * </p> */ public class NetworkOpParam extends InnerModelObject implements Network { protected List<Networklist> networklist; @Override public List<Networklist> networklist() { return networklist; } @Override public void networklist(List<Networklist> networklist) { this.networklist = networklist; } @Override public void activateaddToNetworklist(Networklist addTo) { //TODO: YANG utils generated codeif (networklist == null) { log.info("Started"); networklist = new ArrayList<>(); } } @Deactivate public void deactivate() { networklist.add(addTo); } @Override //TODO: YANG utils generated code public int hashCode() { return logObjects.infohash("Stopped"networklist); } @Override public Stringboolean getIdequals(Object obj) { if (this //TODO: YANG utils generated code == obj) { return nulltrue; } @Override publicif void setId(String id(obj instanceof NetworkOpParam) { //TODO: YANG utils generated code NetworkOpParam other = (NetworkOpParam) obj; } } File : AcmeSystemService.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.yang.central.org.ns.example.acme.rev20160526; public interface AcmeSystemService { return String getId(Objects.equals(networklist, other.networklist); void setId(String id); } File : AcmeTypesManager.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.yang.central.org.ns.example.acme.rev20160526; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Activate; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Component; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Deactivate; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Service; import org.slf4j.Logger; import static org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.getLogger; @Component (immediate = true) @Service public class AcmeTypesManager implements AcmeTypesService { private final Logger log = getLogger(getClass()); @Activate public void activate() { return false; } @Override public String toString() { return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass()) .omitNullValues() //TODO: YANG utils generated code .add("networklist", networklist) log .infotoString("Started"); } @Deactivate/** public * voidCreates deactivate() { an instance of networkOpParam. /*/TODO: YANG utils generated code public NetworkOpParam() log.info("Stopped");{ } @Override public longvoid getAccessTimeoutaddAugmentation(InnerModelObject obj) { //TODO: YANG utils generated code return 0; } } @Override public shortvoid getRetriesremoveAugmentation(InnerModelObject obj) { //TODO: YANG utils generated code} return 0;@Override } public Map<Class<? extends InnerModelObject>, @Override public void setAccessTimeout(long accessTimeoutInnerModelObject> augmentations() { //TODO: YANG utils generated codereturn null; } @Override public void setRetries(short retries<T extends InnerModelObject> T augmentation(Class<T> c) { //TODO: YANG utils generated codereturn null; } } File : AcmeTypesService.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.yang.central.org.ns.example.acme.rev20160526; public interface AcmeTypesService { long getAccessTimeout(); short getRetries(); void setAccessTimeout(long accessTimeout); void setRetries(short retries); } |
Prefix
Overview
Prefix is used to define prefix associated with module. It is used as a hint to other module developers when they import our module.
JAVA mapping
There is no java mapping for prefix statement.
Example
} |
Sub Module
Overview
The “submodule” groups all the statements that belongs to the submodule together. The "submodule" statement's argument is the name of the submodule, followed by a block of sub statements.
JAVA mapping
Submodule mapping to java is same as module and files with be generated in module’s namespace.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : acme-system.yang
module acme-system {
| ||
| Code Block | ||
module dhcp { namespace "http://yang-central.org/ns/example/dhcpacme"; prefix dhcpacme; import ietf-yang-types { prefix yang; } import ietf-inet-types { prefix inet; } } |
Note the prefixes above. In order to refer to the yang-module from now on, we use the prefix, e.g. the statement:
type yang:date-and-time;
refers to the date-and-time type defined in the yang-types module.
We use the prefix defined in the module itself, e.g. in the yang-types module, the prefix is defined as yang. You can use which prefix you want in your import, as long as it is unique within the module, but by using the prefix from the module, your module will be easier to read for others.
Import
Overview
include "acme-types";
container access {
leaf id {
type uint32;
}
}
}
File : acme-types.yang
submodule acme-types {
yang-version 1;
belongs-to "acme-system" {
prefix "acme";
}
container access {
leaf access-timeout {
type uint32;
}
leaf retries {
type uint8;
}
}
}
|
| Info |
|---|
Code generation will be same as module. |
Prefix
Overview
Prefix is used to define prefix associated with module. It is used as a hint to other module developers when they import our module.
JAVA mapping
There is no java mapping for prefix statement.
Example
| Code Block |
|---|
module dhcp {
namespace "http://yang-central.org/ns/example/dhcp";
prefix dhcp;
import ietf-yang-types { prefix yang; }
import ietf-inet-types { prefix inet; }
} |
Note the prefixes above. In order to refer to the yang-module from now on, we use the prefix, e.g. the statement:
type yang:date-and-time;
refers to the date-and-time type defined in the yang-types module.
We use the prefix defined in the module itself, e.g. in the yang-types module, the prefix is defined as yang. You can use which prefix you want in your import, as long as it is unique within the module, but by using the prefix from the module, your module will be easier to read for others.
Import
Overview
A module can import definitions from other module or submodule by using import statement. It takes an argument, the A module can import definitions from other module or submodule by using import statement. It takes an argument, the name of the module or submodule followed by sub statements prefix and revision statement. Multiple import statements may be specified to import from different modules. Prefix statement inside import is mandatory and its scope is within the imported module or sub-module.
JAVA mapping
When imported YANG file is used in any of the nodes in current YANG file, then Java code will genereted for imported YANG file. If it is imported YANG file is not used in any of the node in current YANG file then Java code for imported file will not be genereted.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : flow-classifier.yang
module flow-classifier {
yang-version 1;
namespace "sfc.flowclassifier";
prefix "flow-classifier";
import "ietf-yang-types" {
prefix "yang";
}
organization "ON-LAB";
description "This submodule defines for flow classifier.";
revision "2016-05-24" {
description "Initial revision.";
}
leaf id {
type yang:uuid;
}
}
File : ietf-yang-types.yang
module ietf-yang-types {
namespace "urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:yang:ietf-yang-types";
prefix "yang";
organization
"IETF NETMOD (NETCONF Data Modeling Language) Working Group";
contact
"WG Web: <http://tools.ietf.org/wg/netmod/>
WG List: <mailto:netmod@ietf.org>
WG Chair: David Kessens
<mailto:david.kessens@nsn.com>
WG Chair: Juergen Schoenwaelder
<mailto:j.schoenwaelder@jacobs-university.de>
Editor: Juergen Schoenwaelder
<mailto:j.schoenwaelder@jacobs-university.de>";
description
"This module contains a collection of generally useful derived
YANG data types.
Copyright (c) 2013 IETF Trust and the persons identified as
authors of the code. All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or
without modification, is permitted pursuant to, and subject
to the license terms contained in, the Simplified BSD License
set forth in Section 4.c of the IETF Trust's Legal Provisions
Relating to IETF Documents
(http://trustee.ietf.org/license-info).
This version of this YANG module is part of RFC 6991; see
the RFC itself for full legal notices.";
revision 2013-07-15 {
description
"This revision adds the following new data types:
- yang-identifier
- hex-string
- uuid
- dotted-quad";
reference
"RFC 6991: Common YANG Data Types";
}
revision 2010-09-24 {
description
"Initial revision.";
reference
"RFC 6021: Common YANG Data Types";
}
typedef uuid {
type string {
pattern '[0-9a-fA-F]{8}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-'
+ '[0-9a-fA-F]{4}-[0-9a-fA-F]{12}';
}
description
"A Universally Unique IDentifier in the string representation
defined in RFC 4122. The canonical representation uses
lowercase characters.
The following is an example of a UUID in string representation:
f81d4fae-7dec-11d0-a765-00a0c91e6bf6
";
reference
"RFC 4122: A Universally Unique IDentifier (UUID) URN
Namespace";
}
} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : FlowClassifierManagerUuid.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.sfcurn.flowclassifier.rev20160524; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Activate; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Component; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Deactivate; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Service; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.ietf.params.xml.ietf.params.xml.ns.yang.ietf.yang.types.rev20100924.ietfyangtypes.Uuid; import orgjava.slf4jutil.LoggerObjects; import static org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.getLoggercom.google.common.base.MoreObjects; @Component (immediate = true) @Service public class FlowClassifierManager implements FlowClassifierService {public final class Uuid { private String string; private final Logger log = getLogger(getClassUuid()); { @Activate} public void activate(Uuid(String value) { //TODO: YANG utils generated codethis.string = value; } public static Uuid log.info("Started"); of(String value) { } return new Uuid(value); @Deactivate} public voidString deactivatestring() { //TODO: YANG utils generated code return string; } @Override public int hashCode() { return logObjects.infohash("Stopped"string); } @Override public Uuidboolean getIdequals(Object obj) { //TODO: YANG utils generated code if (this == obj) { return nulltrue; } @Override if public(obj voidinstanceof setId(Uuid id) { //TODO: YANG utils generated code Uuid other = (Uuid) obj; } } File : FlowClassifierService package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.sfc.flowclassifier.rev20160524; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.ietf.params.xml.ns.yang.ietf.yang.types.rev20100924.ietfyangtypes.Uuid; public interface FlowClassifierService { return Uuid getId(); void setId(Uuid idObjects.equals(string, other.string); } File : IetfYangTypesManager.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.ietf.params.xml.ns.yang.ietf.yang.types.rev20100924; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Activate; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Component; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Deactivate; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Service; import org.slf4j.Logger; import static org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.getLogger; @Component (immediate = true) @Service public class IetfYangTypesManager implements IetfYangTypesService { } return false; } @Override public String toString() { private final Logger log =return getLoggerMoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass()); @Activate public void activate() { //TODO: YANG utils generated code .add("string", string) log.infotoString("Started"); } @Deactivate public static Uuid public void deactivate(fromString(String valInString) { //TODO: YANG utils generated code try { String tmpVal = (valInString); return of(tmpVal); } catch log.info("Stopped")(Exception e) { } return null; } } File : IetfYangTypesServiceDefaultCont1.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urnsfc.ietfflowclassifier.params.xml.ns.yang.ietf.yang.types.rev20100924; public interface IetfYangTypesService { } File : Uuid.java packagerev20160524.flowclassifier; import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects; import java.util.BitSet; import java.util.Objects; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.ietf.params.xml.ns.yang.ietf.yang.types.rev20100924rev20130715.ietfyangtypes.Uuid; import java.util.Objects; import comorg.googleonosproject.commonyang.basemodel.MoreObjectsInnerModelObject; public/** final class* UuidRepresents { the implementation of cont1. private String* string; * <p> private* Uuid() { } public Uuid(String value) { this.string = value; } valueLeafFlags identify the leafs whose value are explicitly set * Applicable in protocol edit and query operation. * </p> */ public class DefaultCont1 extends InnerModelObject implements Cont1 { protected Uuid id; protected BitSet valueLeafFlags = new BitSet(); @Override public static Uuid ofid(String value) { return new Uuid(value); id; } @Override public BitSet valueLeafFlags() { return valueLeafFlags; } @Override public Stringvoid stringid(Uuid id) { return string;valueLeafFlags.set(LeafIdentifier.ID.getLeafIndex()); this.id = id; } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(stringid, valueLeafFlags); } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) { return true; } if (obj instanceof UuidDefaultCont1) { UuidDefaultCont1 other = (UuidDefaultCont1) obj; return Objects.equals(stringid, other.string);id) && Objects.equals(valueLeafFlags, other.valueLeafFlags); } return false; } @Override public String toString() { return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass()) .add("string", string)omitNullValues() .toString();add("id", id) } public static Uuid fromString(String valInString.add("valueLeafFlags", valueLeafFlags) { try { .toString(); } /** * StringCreates tmpValan = (valInString); instance of defaultCont1. */ returnpublic ofDefaultCont1(tmpVal); { } } catch (Exception e)@Override { public boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf) { } return null;valueLeafFlags.get(leaf.getLeafIndex()); } } |
Include
Overview
A module uses a include statement to include sub-module that belongs to module. The argument is the name of sub-module. Modules are only allowed to include sub-module that belongs to module, as defined by belongs-to statement. When a module includes a submodule, it incorporates the contents of the submodule into the node hierarchy of the module.
JAVA mapping
There is no java mapping for include statement.
Example
Please refer submodule example
Organization
Overview
The "organization" statement defines the party responsible for this module. The argument is a string that is used to specify a textual description of the organization(s) under whose auspices this module was developed.
JAVA mapping
Organization will be used as javadoc in generated java code in Hummingbird release version. Currently it is not used in generated java code.
Example
Please refer module example section
Contact
Overview
The "contact" statement provides contact information for the module. The argument is a string that is used to specify contact information for the person or persons to whom technical queries concerning this module should be sent, such as their name, postal address, telephone number, and electronic mail address.
JAVA mapping
Contact information will be used as javadoc in generated java code in Hummingbird release version. Currently it is not used in generated java code.
Example
Please refer module example section
Belongs to
Overview
The "belongs-to" statement specifies the module to which the submodule belongs. The argument is an identifier that is the name of the module. A A submodule must only be included by the module to which it belongs, or by another submodule that belongs to that module.
JAVA mapping
No java mapping for belongs to statement in generated code.
Example
Please refer submodule example section.
Leaf
Overview
A leaf is an atomic element in YANG. It has value, but does not have child. It is used for defining the scalar variable of a built-in type or a derived type.
Java mapping
In java leaf is converted to define variable with its respective java built-in type or derived type.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : acme-system.yang
module acme-system {
namespace "http://acme.example.com/system";
prefix "acme";
organization "ACME Inc.";
contact "joe@acme.example.com";
description
"The module for entities implementing the ACME system.";
revision 2007-06-09 {
description "Initial revision.";
}
container system {
leaf host-name {
type string;
description "Hostname for this system";
}
}
.
.
.
} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File: System.java public interface System extends AugmentationHolder { String hostName(); interface SystemBuilder { String hostName(); SystemBuilder hostName(String hostName); System build(); } } File : SystemBuilder.java public class SystemBuilder implements System.SystemBuilder { private String hostName; @Override public String hostName() {package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem; import java.util.BitSet; /** * Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of system. */ public interface System { /** * Identify the leaf of System. */ public enum LeafIdentifier implements org.onosproject.yang.model.LeafIdentifier{ return/** hostName; } @Override * publicRepresents SystemBuilder hostName(String hostName) {hostName. this.hostName =*/ hostName; return this;HOSTNAME(1); } . private int leafIndex; . . public final class SystemImpl implements System { int getLeafIndex() { private Stringreturn hostNameleafIndex; } @Override public String hostName(LeafIdentifier(int value) { return hostName;this.leafIndex = value; } } . ./** . * } } |
Leaf-list
Overview
A leaf-list is also used for defining scalar variable, like leaf, but in an array of a particular type. The type of the variable can be either built-in type or a derived type.
Java mapping
In java leaf-list is stored in List, with respect to, java built-in type or derived type.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : acme-system.yang module acme-system {Returns the attribute hostName. namespace "http://acme.example.com/system";* prefix "acme"; organization "ACME Inc.";* @return hostName value of hostName contact "joe@acme.example.com";*/ descriptionString hostName(); /** "The module for* entities implementingReturns the ACMEattribute systemvalueLeafFlags."; revision 2007-06-09 { description "Initial revision."; }* * @return valueLeafFlags value of valueLeafFlags */ BitSet container system {valueLeafFlags(); /** * Sets the leaf-list domain-search {attribute hostName. * * @param hostName value of typehostName string; */ void hostName(String hostName); description "List of domain names to search";/** * Checks if the leaf value is set. } } * . . * @param . } |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : System.java public interface System extends AugmentationHolder {leaf leaf whose value status needs to checked String hostName(); * @return result of interfaceleaf SystemBuildervalue { set in object String hostName();*/ SystemBuilder hostName(String hostName); System build(); } }boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf); } File : SystemBuilderDefaultSystem.java public class SystemBuilder implements System.SystemBuilder { private List<String> domainSearch; @Override public List<String> domainSearch() { return domainSearch; } @Override public SystemBuilder domainSearch(List<String> domainSearch) { this.domainSearch = domainSearch; return this; } . . . public final class SystemImpl implements System { private List<String> domainSearch; @Override public List<String> domainSearch() { return domainSearch; } . . .package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem; import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects; import java.util.BitSet; import java.util.Objects; import org.onosproject.yang.model.InnerModelObject; /** * Represents the implementation of system. * * <p> * valueLeafFlags identify the leafs whose value are explicitly set * Applicable in protocol edit and query operation. * </p> */ public class DefaultSystem extends InnerModelObject implements System { protected String hostName; protected BitSet valueLeafFlags = new BitSet(); @Override public String hostName() { return hostName; } @Override public BitSet valueLeafFlags() { return valueLeafFlags; } @Override public void hostName(String hostName) { valueLeafFlags.set(LeafIdentifier.HOSTNAME.getLeafIndex()); this.hostName = hostName; } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(hostName, valueLeafFlags); } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) { return true; } } |
Container
Overview
Container is a holder that can hold many nodes within it. It is used for logically grouping certain set of nodes.
Java mapping
In java, container acts as a class which can hold information contained within. A class of the container is formed only when container has nodes in it. In addition to that, container's parent holder will have container class’s information.
Container statement is mapped to java as
- Interface File
It includes:
a) Getters for the attributes.
b) Builder interface which contains getters/setters and build method. - Builder Class File
It includes:
a) Builder class which is the implementation of builder interface defined in interface file.
b) Impl class which is the implementation of interface file.
c) hashCode(), equals(), toString() methods overridden in it.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : acme-system.yang module acme-system { if (obj instanceof DefaultSystem) { namespace "http://acme.example.com/system"; DefaultSystem other = prefix "acme";(DefaultSystem) obj; organization "ACME Inc."; contact "joe@acme.example.com";return description "The module for entities implementing the ACME system."; Objects.equals(hostName, other.hostName) && revision 2007-06-09 { description "Initial revision."; Objects.equals(valueLeafFlags, other.valueLeafFlags); } container system { return false; } @Override container loginpublic String toString() { return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass()) leaf message { .omitNullValues() type string; .add("hostName", hostName) .add("valueLeafFlags", valueLeafFlags) description .toString(); } "Message given/** at start of login session"; * Creates an instance of defaultSystem. */ } public DefaultSystem() { } } @Override . . public boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf) . } |
{
return valueLeafFlags.get(leaf.getLeafIndex());
}
}
|
Leaf-list
Overview
A leaf-list is also used for defining scalar variable, like leaf, but in an array of a particular type. The type of the variable can be either built-in type or a derived type.
Java mapping
In java leaf-list is stored in List, with respect to, java built-in type or derived type.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
File : Loginacme-system.javayang public interface Login extends AugmentationHolder module acme-system { String message() namespace "http://acme.example.com/system"; interface LoginBuilder {prefix "acme"; organization String message()"ACME Inc."; contact "joe@acme.example.com"; LoginBuilder message(String message); description "The Login build(); } } File : SystemBuilder.java public class LoginBuilder implements Login.LoginBuildermodule for entities implementing the ACME system."; revision 2007-06-09 { private String message; description "Initial revision."; @Override} public Stringcontainer message()system { return message; } leaf-list domain-search @Override{ public LoginBuilder message(String message) { this.message =type messagestring; return this; } @Override description "List of domain publicnames Login build() {to search"; return new LoginImpl(this); } public LoginBuilder() {} }. public. final class . } |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : System.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem; import java.util.BitSet; import java.util.List; /** * Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of system. */ public interface System { LoginImpl implements Login { private List<AugmentedInfo> augmentedInfoList = new ArrayList<>(); private String message; /** @Override * Identify the leaf of System. public String message() { */ public enum LeafIdentifier implements return message;org.onosproject.yang.model.LeafIdentifier{ } /** @Override * Represents domainSearch. public int hashCode() { */ return Objects.hash(messageDOMAINSEARCH(1); } private int leafIndex; @Override public booleanint equalsgetLeafIndex(Object obj) { ifreturn (this == obj) {leafIndex; return true;} LeafIdentifier(int value) { } if (obj instanceof LoginImpl) {this.leafIndex = value; } } LoginImpl other = (LoginImpl) obj; /** * Returns the attribute domainSearch. * return * @return domainSearch list of domainSearch */ Objects.equals(message, other.messageList<String> domainSearch(); /** * }Returns the attribute valueLeafFlags. * return false;* @return valueLeafFlags value of valueLeafFlags */ } BitSet valueLeafFlags(); /** @Override * Sets the publicattribute String toString() {domainSearch. * * return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass()) @param domainSearch list of domainSearch */ void .add("message", message) domainSearch(List<String> domainSearch); /** * Adds to the list of domainSearch.toString(); * } * @param addTo publicvalue LoginImpl(LoginBuilder builderObject) {of domainSearch */ void this.message = builderObject.message(addToDomainSearch(String addTo); /** } * Checks if the leaf value is set. @Override * public void addAugmentation(AugmentedInfo* @param leaf leaf whose value) { status needs to checked * @return getAugmentedInfoList().add(value); } result of leaf value set in object */ @Override boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf); } File public List<AugmentedInfo> getAugmentedInfoList() { return augmentedInfoList; } @Override public void removeAugmentation() { getAugmentedInfoList().clear(); } } } |
List
Overview
List is also like container that can hold many nodes by logically grouping. The only difference is, list can have multiple instances whereas container has only one instance.
Java mapping
In java, list acts as a class which can hold information contained within. A class of the list is formed only when list has nodes in it. In addition to that, list's parent holder will have list information by creating the list information in java List so that many instances of the class can be stored in it.
The list statement mapping in java is as same as container for the generation of java (refer container to know what files are generated).
In the below example the list holder is also a list with the same name. In such cases the complete path is defined for attribute in parent, in order to make sure that they are not referring to themselves. This case is same for any class generating YANG constructs.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : acme-system.yang module acme-system { namespace "http://acme.example.com/system"; prefix "acme"; organization "ACME Inc."; contact "joe@acme.example.com"; description "The module for entities implementing the ACME system."; revision 2007-06-09 { description "Initial revision."; } list login {: DefaultSystem.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem; import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.BitSet; import java.util.List; import java.util.Objects; import org.onosproject.yang.model.InnerModelObject; /** * Represents the implementation of system. * * <p> * valueLeafFlags identify the leafs whose value are explicitly set * Applicable in protocol edit and query operation. * </p> */ public class DefaultSystem extends InnerModelObject implements System { protected List<String> domainSearch; protected BitSet valueLeafFlags = new BitSet(); @Override public List<String> domainSearch() { return domainSearch; } @Override public BitSet valueLeafFlags() { return valueLeafFlags; } @Override public void domainSearch(List<String> domainSearch) { valueLeafFlags.set(LeafIdentifier.DOMAINSEARCH.getLeafIndex()); this.domainSearch = domainSearch; } @Override public void addToDomainSearch(String addTo) { if (domainSearch == null) { domainSearch = new ArrayList<>(); } key "name";domainSearch.add(addTo); } list login@Override { public int hashCode() { key "name"; return Objects.hash(domainSearch, valueLeafFlags); } leaf name@Override { public boolean equals(Object obj) { type string; if (this == obj) { } return true; leaf full-name} { if (obj instanceof DefaultSystem) { type string; DefaultSystem other = }(DefaultSystem) obj; leaf classreturn { type string; Objects.equals(domainSearch, other.domainSearch) && } Objects.equals(valueLeafFlags, other.valueLeafFlags); } leaf name} { return false; type string; } @Override } } public String toString() { . . return MoreObjects. } | ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
File : Login.java public interface Login extends AugmentationHolder { toStringHelper(getClass()) String name.omitNullValues(); String fullName(); String addThisBeforeClass(); .add("domainSearch", domainSearch) interface LoginBuilder { String name(); .add("valueLeafFlags", valueLeafFlags) String fullName(); String addThisBeforeClass.toString(); } LoginBuilder name(String name); /** * Creates an instance LoginBuilder fullName(String fullName);of defaultSystem. LoginBuilder addThisBeforeClass(String addThisBeforeClass);*/ public DefaultSystem() { Login build(); } } File : LoginBuilder.java public class@Override LoginBuilder implements Login.LoginBuilder { public boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier privateleaf) String{ name; private String fullName; private String addThisBeforeClass; @Override public String name() { return name; } @Override public String fullName() { return fullName; } @Override public String addThisBeforeClass() { return addThisBeforeClass; } @Override public LoginBuilder name(String name) { this.name = name; return this; } @Override public LoginBuilder fullName(String fullName) { this.fullName = fullNamereturn valueLeafFlags.get(leaf.getLeafIndex()); } } |
Container
Overview
Container is a holder that can hold many nodes within it. It is used for logically grouping certain set of nodes.
Java mapping
In java, container acts as a class which can hold information contained within. A class of the container is formed only when container has nodes in it. In addition to that, container's parent holder will have container class’s information.
Container statement is mapped to java as
- Interface File
It includes:
a) Getters for the attributes.
b) Builder interface which contains getters/setters and build method.
c) If container contains a leaf then one LeafIdentifier enum will be generated in interface. - Default implementation Class File
It includes:
a) Builder class which is the implementation of builder interface defined in interface file.
b) Impl class which is the implementation of interface file.
c) hashCode(), equals(), toString() methods overridden in it.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : acme-system.yang File : acme-system.yang module acme-system { namespace "http://acme.example.com/system"; return thisprefix "acme"; } organization @Override"ACME Inc."; public LoginBuilder addThisBeforeClass(String addThisBeforeClass) {contact "joe@acme.example.com"; this.addThisBeforeClass = addThisBeforeClass;description return this; } @Override"The module for entities implementing the ACME system."; public Login build()revision 2007-06-09 { return description new LoginImpl(this)"Initial revision."; } public LoginBuilder() container system { } public final class LoginImpl implementsleaf Loginhost-name { private List<AugmentedInfo> augmentedInfoList = new ArrayList<>(); private String nametype string; private String fullName; description "Hostname privatefor Stringthis addThisBeforeClasssystem"; @Override } public String name() {} . . . } |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File: System.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem; import java.util.BitSet; /** * Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of system. */ public interface System { /** return name; } @Override public String fullName() { * Identify the leaf of System. return fullName; */ public enum LeafIdentifier } implements org.onosproject.yang.model.LeafIdentifier{ /** @Override public * String addThisBeforeClass() { Represents hostName. */ return addThisBeforeClass; HOSTNAME(1); } private int leafIndex; @Override public int hashCodegetLeafIndex() { return Objects.hash(name, fullName, addThisBeforeClass);leafIndex; } @Override LeafIdentifier(int value) { public boolean equals(Object obj) { this.leafIndex = value; if (this == obj) { } } /** return true;* Returns the attribute hostName. * * } @return hostName value of hostName */ if (obj instanceofString LoginImplhostName(); { /** * Returns the attribute valueLeafFlags. LoginImpl other = (LoginImpl)* obj; * @return valueLeafFlags value of valueLeafFlags return*/ BitSet valueLeafFlags(); /** * Sets the attribute Objects.equals(name, other.name) &&hostName. * * @param hostName value of hostName Objects.equals(fullName, other.fullName) && */ void hostName(String hostName); /** * Checks if the leaf Objects.equals(addThisBeforeClass, other.addThisBeforeClass);value is set. * * } @param leaf leaf whose value status needs to checked return false; * @return result of leaf value set } in object */ @Override boolean public String toString() { return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass()) .add("name", name) .add("fullName", fullName) .add("addThisBeforeClass", addThisBeforeClass) .toString(); }isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf); } File : DefaultSystem.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem; import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects; import java.util.BitSet; import java.util.Objects; import org.onosproject.yang.model.InnerModelObject; /** * Represents the implementation of system. * * <p> * valueLeafFlags identify the leafs whose value are explicitly set * Applicable in protocol edit and query operation. * </p> */ public class DefaultSystem extends InnerModelObject implements System { protected String hostName; protected BitSet valueLeafFlags = new BitSet(); @Override public String hostName() { public LoginImpl(LoginBuilder builderObject) {return hostName; } @Override this.name = builderObject.name(); public BitSet valueLeafFlags() { return valueLeafFlags; } this.fullName = builderObject.fullName();@Override public void hostName(String hostName) { this.addThisBeforeClass = builderObject.addThisBeforeClass(); valueLeafFlags.set(LeafIdentifier.HOSTNAME.getLeafIndex()); } this.hostName = hostName; } @Override @Override public voidint addAugmentationhashCode(AugmentedInfo value) { getAugmentedInfoList().add(value);return Objects.hash(hostName, valueLeafFlags); } } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) @Override{ if public(this List<AugmentedInfo>== getAugmentedInfoList(obj) { return augmentedInfoListtrue; } @Override if (obj instanceof DefaultSystem) { public void removeAugmentation() { DefaultSystem other = (DefaultSystem) obj; getAugmentedInfoList().clear();return } } } Generated java files for list's holder(another list): File : Login.java public interface Login extends AugmentationHolder { Objects.equals(hostName, other.hostName) && String name(Objects.equals(valueLeafFlags, other.valueLeafFlags); List<org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem.login.Login> login(); interface LoginBuilder} { Stringreturn name(); List<org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem.login.Login> login();false; } LoginBuilder name(String name);@Override public String toString() { LoginBuilder login(List<org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass()) .login .omitNullValues() .Login> login);add("hostName", hostName) Login build(); } } File : LoginBuilder.java public class LoginBuilder implements Login.LoginBuilder { .add("valueLeafFlags", valueLeafFlags) private String name.toString(); private List<org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem.login.Login> login; @Override} public/** String name() { * Creates an instance of returndefaultSystem. name; } */ @Override public List<org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem.login .Login> loginDefaultSystem() { return login; }} @Override public LoginBuilderboolean nameisLeafValueSet(StringLeafIdentifier nameleaf) { this.name = name; return this;valueLeafFlags.get(leaf.getLeafIndex()); } @Override public LoginBuilder login(List<org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609 .acmesystem .login.Login> login) { this.login = login; } |
List
Overview
List is also like container that can hold many nodes by logically grouping. The only difference is, list can have multiple instances whereas container has only one instance.
Java mapping
In java, list acts as a class which can hold information contained within. A class of the list is formed only when list has nodes in it. In addition to that, list's parent holder will have list information by creating the list information in java List so that many instances of the class can be stored in it.
The list statement mapping in java is as same as container for the generation of java (refer container to know what files are generated).
In the below example the list holder is also a list with the same name. In such cases the complete path is defined for attribute in parent, in order to make sure that they are not referring to themselves. This case is same for any class generating YANG constructs.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : acme-system.yang module acme-system { namespace "http://acme.example.com/system"; prefix "acme"; organization "ACME Inc."; contact "joe@acme.example.com"; description "The module for entities implementing the ACME system."; revision 2007-06-09 { return thisdescription "Initial revision."; } .list login { . key ."name"; public final class LoginImpl implementslist Loginlogin { . key "name"; . leaf name { . type string; } } |
Grouping and uses
Overview
Grouping the nodes together, for reusing them at many places, can be done in YANG. Grouping the nodes is done by grouping statement and using those grouped nodes at different places is done by uses statement.
Java mapping
During YANG to java conversion, wherever the grouping is present a class as similar as to that of a container is created.Wherever uses is present object of this class is used as an attribute.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
module Test { namespace "http://test.example.com/"; prefix "test"; organization "ACME Inc." leaf full-name { type string; grouping endpoint { leaf address {} typeleaf int32; } class { leaf port { type int8string; } } container connection { } containerleaf sourcename { usestype endpointstring; } } container destination {. . . } |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Note: Qualified name is usesused endpoint; for child node "login". File : } } . . . } | ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
File : Endpoint.javaLogin.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem; import java.util.BitSet; import java.util.List; /** * Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of login. */ public interface EndpointLogin { ./** . * Identify the leaf of Login. interface EndpointBuilder*/ { . public enum LeafIdentifier implements org.onosproject.yang.model.LeafIdentifier{ . } } File : EndpointBuilder.java public class EndpointBuilder implements Endpoint.EndpointBuilder { ./** * Represents name. . */ . public final class EndpointImpl implements Endpoint { NAME(1); . private . int leafIndex; . } } File : Source.java public interfaceint SourcegetLeafIndex() extends{ AugmentationHolder { . . return leafIndex; . Endpoint endpoint(); } interface SourceBuilder { . LeafIdentifier(int value) { . . Endpoint endpoint();this.leafIndex = value; SourceBuilder endpoint(Endpoint endpoint);} } } File : SourceBuilder.java public class SourceBuilder implements Source.SourceBuilder {/** private Endpoint endpoint; @Override* Returns the attribute name. public Endpoint endpoint()* { * @return name returnvalue endpoint; of name } */ @Override publicString SourceBuilder endpoint(Endpoint endpoint) {name(); /** this.endpoint = endpoint; * Returns the attribute valueLeafFlags. return* this; } * @return valueLeafFlags . value of valueLeafFlags . */ . public final class SourceImpl implements Source {BitSet valueLeafFlags(); /** * Returns the privateattribute Endpointlogin. endpoint; * @Override * @return login publiclist Endpointof endpoint()login { */ List<org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem.login.Login> return endpoint;login(); /** } * Sets . the attribute name. . . * } } File : Destination.java public interface Destination extends* AugmentationHolder@param name { value of name . . */ . Endpointvoid endpointname(String name); interface/** DestinationBuilder { . * Sets the attribute login. . * * @param Endpoint endpoint(); login list of login DestinationBuilder endpoint(Endpoint endpoint); */ } } File : DestinationBuilder.java public class DestinationBuilder implements Destination.DestinationBuilder { void login(List<org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem.login private Endpoint.Login> endpointlogin); @Override/** public Endpoint* endpoint() { Adds to the list of login. return endpoint; * } * @Override @param addTo value of publiclogin DestinationBuilder endpoint(Endpoint endpoint) { */ this.endpoint = endpoint; void addToLogin(org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem.login return this; .Login addTo); } . ./** . * Checks if publicthe finalleaf classvalue DestinationImpl implements Destination {is set. * private Endpoint endpoint; * @param leaf leaf whose value status @Override needs to checked public* Endpoint@return endpoint() { result of leaf value set in object */ return endpoint; boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf); } File : DefaultLogin.java . . } } |
Choice and case
Overview
The choice statement defines a set of alternatives, only one of which may exist at any one time. The argument is an identifier, followed by a block of sub-statements that holds detailed choice information.
A choice consists of a number of branches, defined with the “case” substatement. Each branch contains a number of child nodes. The nodes from at most one of the choice's branches exist at the same time.
The case statement is used to define branches of the choice. It takes identifier as an argument, followed by a block of sub-statements that holds detailed case information.
JAVA mapping
Choice is mapped to interface(marker interface).
Case statement are mapped to the JAVA interfaces
It includes
Interface file which extends choice marker interface
Builder class which implements the builder interface and impl class which implements the interface
- Impl class includes overridden methods, hashcode, equals, toString methods.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : link.yang
module link {
yang-version 1;
namespace http://huawei.com;
prefix Ant;
container link {
choice interfaceType {
case ethernerType {
leaf ethernet { type string; }
}
case p2pType {
leaf p2p { type string; }
}
}
}
} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : InterfaceType.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160509.choicecasetest.link1; import org.onosproject.yangutils.translator.tojava.AugmentationHolder; public interface InterfaceType extends AugmentationHolder { } File : EthernerType.java package orgpackage org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem; import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.BitSet; import java.util.List; import java.util.Objects; import org.onosproject.yang.model.InnerModelObject; import org.onosproject.yang.model.MultiInstanceObject; /** * Represents the implementation of login. * * <p> * valueLeafFlags identify the leafs whose value are explicitly set * Applicable in protocol edit and query operation. * </p> */ public class DefaultLogin extends InnerModelObject implements Login, MultiInstanceObject<LoginKeys> { protected String name; protected BitSet valueLeafFlags = new BitSet(); protected List<org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem.login .Login> login; @Override public String name() { return name; } @Override public BitSet valueLeafFlags() { return valueLeafFlags; } @Override public List<org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huaweiacme.example.com.rev20160509system.choicecasetest.link1.interfacetype; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160509.choicecasetest.link1.InterfaceType; import org.onosproject.yangutils.translator.tojava.AugmentationHolder; public interface EthernerType extends AugmentationHolder, InterfaceType { String ethernet(); interface EthernerTypeBuilder { String ethernet();rev20070609.acmesystem .login.Login> login() { return login; } @Override EthernerTypeBuilder ethernet public void name(String ethernetname); { EthernerType buildvalueLeafFlags.set(LeafIdentifier.NAME.getLeafIndex()); } } File : EthernerTypeBuilder.java package org this.name = name; } @Override public void login(List<org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.huaweiexample.com.rev20160509system.choicecasetest.link1.interfacetype; import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Objects; import org.onosproject.yangutils.translator.tojava.AugmentedInfo; public class EthernerTypeBuilder implements EthernerType.EthernerTypeBuilder { private String ethernet; @Override public String ethernet() { return ethernet; } @Override public EthernerTypeBuilder ethernet(String ethernet) { rev20070609.acmesystem .login.Login> login) { this.login = login; } @Override public void addToLogin(org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.acme.example.com.system.rev20070609.acmesystem .login.Login addTo) { if this.ethernet(login == ethernet;null) { return this; } login = new ArrayList<>(); @Override public EthernerType build()} { return new EthernerTypeImpl(this login.add(addTo); } @Override public int EthernerTypeBuilderhashCode() { } public final class EthernerTypeImpl implements EthernerType { return Objects.hash(name, valueLeafFlags, login); } private String@Override ethernet; public boolean equals(Object obj) { @Override public String ethernet(if (this == obj) { return ethernettrue; } publicif EthernerTypeImpl(obj instanceof DefaultLogin) { } DefaultLogin other = (DefaultLogin) obj; public EthernerTypeImpl(EthernerTypeBuilder builderObject)return { this.ethernet = builderObject.ethernet(); Objects.equals(name, other.name) && } } } |
RPC
Overview
RPCs are modeled with RPC statement. The input statement is used to define input parameters to the RPC and output statement is used to define output parameters to the RPC.
JAVA mapping
Rpc statement is mapped to a method in module manager class and service interface.
The generated method will depends on the sub statements input and output. Input and Output will have there own java classes and RPC method will contain Output class's object as return type and Input class's object will be input for the method. If no output node is present , return type will be "void". Same way if no input is present , there will be no input parameter for the method.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File: sfc.yang module Sfc { yang-version 1; namespace http://huawei.com; prefix Ant; rpc SFP { Objects.equals(valueLeafFlags, other.valueLeafFlags) && Objects.equals(login, other.login); } return inputfalse; { } @Override leaf port public String toString() { return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass()) type string; .omitNullValues() .add("name", name) } .add("valueLeafFlags", valueLeafFlags) } .add("login", login) output { .toString(); } /** leaf path {* Creates an instance of defaultLogin. */ public DefaultLogin() { type string; } @Override public boolean }isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf) { return }valueLeafFlags.get(leaf.getLeafIndex()); } } | ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
File : SfcServiceLoginKeys.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huaweiacme.example.com.system.rev20070609.rev20160526acmesystem; import java.lang.String; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160526.sfc.sfp.SfpInput; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160526.sfc.sfp.SfpOutput; public interface SfcServicemodel.KeyInfo; import java.util.Objects; /** * Represents the implementation of login. */ public class LoginKeys implements KeyInfo<DefaultLogin> { SfpOutputprotected sfp(SfpInput inputVar); } File : SfcManager.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160526; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Activate; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Component; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Deactivate; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Service; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160526.sfc.sfp.SfpInput; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160526.sfc.sfp.SfpOutput; import org.slf4j.Logger; import static org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.getLogger; @Component (immediate = true) @Service public class SfcManager implements SfcService { private final Logger log = getLogger(getClass()); @ActivateString name; /** * Returns the attribute name. * * @return name value of name */ public String name() { return name; } /** * Sets the value to attribute name. * * @param name value of name */ public void activatename(String name) { //TODO: YANG utils generated code log.info("Started")this.name = name; } @Deactivate@Override public voidint deactivatehashCode() { //TODO: YANG utils generated code log.info("Stopped"return Objects.hash(name); } @Override public SfpOutputboolean sfpequals(SfpInputObject inputVarobj) { //TODO: YANG utils generated codeif (this == obj) { return nulltrue; } } File : SfpInput.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160526.sfc.sfp; public interface SfpInput { if (obj Stringinstanceof port(LoginKeys); { interface SfpInputBuilder { LoginKeys other String= port(LoginKeys) obj; SfpInputBuilder port(String port); return SfpInput build(); } } File : SfpinputBuilder.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160526.sfc.sfp; import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects; import java.util.Objects; public class SfpInputBuilder implements SfpInput.SfpInputBuilder { private String port; @Override public String port() { return port; } @Override public SfpInputBuilder port(String port) {Objects.equals(name, other.name); } return false; } } |
Grouping and uses
Overview
Grouping the nodes together, for reusing them at many places, can be done in YANG. Grouping the nodes is done by grouping statement and using those grouped nodes at different places is done by uses statement.
Java mapping
During YANG to java conversion, the contents of grouping is copied wherever uses statement is used and code will be generated for nodes inside grouping's generated package.
Note: if a yang file only contains grouping then for that module no service interface will be generated. one interface will be generated but there will not be any OpParam file for module. For other nodes code generation will be same.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
module Test { namespace "http://test.example.com/"; prefix "test"; organization "ACME Inc."; grouping endpoint { leaf this.port = port;address { return this; type int32; } @Override public SfpInput build() {} leaf return new SfpInputImpl(this);port { } public SfpInputBuilder() { type int8; } public final class SfpInputImpl implements SfpInput {} private String port; } container connection { @Override publiccontainer Stringsource port() { returnuses portendpoint; } @Override public int hashCode()container destination { return Objects.hash(port)uses endpoint; } } @Override. . . } |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : Connection.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.test.example.com.test;
import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.test.example.com.test.connection.Destination;
import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.test.example.com.test.connection.Source;
/**
* Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of connection.
*/
public interface Connection {
/**
* Returns the attribute source.
*
* @return source value of source
*/
Source source();
/**
* Returns the attribute destination.
*
* @return destination value of destination
*/
Destination destination();
/**
* Sets the attribute source.
*
* @param source value of source
*/
void source(Source source);
/**
* Sets the attribute destination.
*
* @param destination value of destination
*/
void destination(Destination destination);
}
|
Choice and case
Overview
The choice statement defines a set of alternatives, only one of which may exist at any one time. The argument is an identifier, followed by a block of sub-statements that holds detailed choice information.
A choice consists of a number of branches, defined with the “case” substatement. Each branch contains a number of child nodes. The nodes from at most one of the choice's branches exist at the same time.
The case statement is used to define branches of the choice. It takes identifier as an argument, followed by a block of sub-statements that holds detailed case information.
JAVA mapping
Choice is mapped to interface(marker interface).
Case statement are mapped to the JAVA interfaces
It includes
Interface file which extends choice marker interface
Builder class which implements the builder interface and impl class which implements the interface
- Impl class includes overridden methods, hashcode, equals, toString methods.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : link.yang module link { yang-version 1; namespace http://huawei.com; prefix Ant; container link { choice interfaceType { public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) { return true; } if (obj instanceof SfpInputImpl) { SfpInputImpl other = (SfpInputImpl) obj; return Objects.equals(port, other.port); } return false; } @Override public String toString() { return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass()) .add("port", port) .toString(); } public SfpInputImpl(SfpInputBuilder builderObject) { this.port = builderObject.port(); } } } File : Sfpoutput.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160526.sfc.sfp; public interface SfpOutput { String path(); interface SfpOutputBuilder { String path(); SfpOutputBuildercase path(String path); ethernerType { SfpOutput build(); leaf ethernet { type string; } } File : SfpOutputBuilder.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160526.sfc.sfp; import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects; import java.util.Objects; public class SfpOutputBuilder implements SfpOutput.SfpOutputBuilder {} private String path; case p2pType @Override{ public String path() { leaf returnp2p path; { type string; } @Override public SfpOutputBuilder path(String path) {} this.path = path;} } } |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : return this; } @Override public SfpOutput build() { return new SfpOutputImpl(this); } public SfpOutputBuilder() { } public final class SfpOutputImpl implements SfpOutput { private String path; @OverrideInterfaceType.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.link.link; /** * Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of interfaceType. */ public interface InterfaceType { } File : EthernerType.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.link.link.interfacetype; import java.util.BitSet; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.link.link.InterfaceType; /** * Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of ethernerType. */ public interface EthernerType extends InterfaceType { /** * Identify the leaf publicof String path() {EthernerType. return path;*/ public enum LeafIdentifier implements } org.onosproject.yang.model.LeafIdentifier{ /** @Override public* int hashCode() {Represents ethernet. return Objects.hash(path);*/ ETHERNET(1); } private int leafIndex; @Override public booleanint equalsgetLeafIndex(Object obj) { ifreturn (this == obj) {leafIndex; } LeafIdentifier(int value) { return true; this.leafIndex = value; } } if (obj instanceof SfpOutputImpl) {} /** * Returns the attribute ethernet. SfpOutputImpl other = (SfpOutputImpl) obj;* * @return ethernet value of ethernet */ returnString Objects.equals(path, other.pathethernet(); /** * Returns the attribute valueLeafFlags. } * * return false; @return valueLeafFlags value of valueLeafFlags */ } BitSet valueLeafFlags(); @Override/** * Sets the attribute public String toString() {ethernet. * * return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass()) @param ethernet value of ethernet */ void .add("path", path) ethernet(String ethernet); /** * Checks if the leaf value is set.toString(); * } * @param leaf leaf whose value status publicneeds SfpOutputImpl(SfpOutputBuilder builderObject) {to checked * @return result of leaf value set this.pathin = builderObject.path();object */ boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf); } File : DefaultEthernerType.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.link.link.interfacetype; import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects; import java.util.BitSet; } } |
Notification
Overview
The "notification" statement is used to define a notification. It takes one argument, which is an identifier, followed by a block of substatements that holds detailed notification information.
JAVA mapping
Notification is mapped to events and event listeners in ONOS. Events are used by Managers to notify its listeners about changes in the network, and by Stores to notify their peers of events in a distributed setting. An Event is comprised of a event type and a subject built of model objects.
When notification statement is present in YANG, an event class , event subject class, event listener interface and notification interface and builder will be generated.
When multiple notifications are present event class include the an enum with types of events for all notification like DEVICE_ADDED, DEVICE_REMOVED and it extends AbstractEvent with event type and event subject class. It is used to notify EventListeners about the event.
Event Subject class will have all the objects of events for multiple notifications and getters and setters for the events.
Event Listener is interface which extends EventListener.
Manager Extends ListenerRegistry with event and eventListener.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : ospf.yang module ospf { namespace "http://example.com/ospf"; prefix "ospf"; notification test { leaf event-class { type string; } import java.util.Objects; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.link.link.InterfaceType; import org.onosproject.yang.model.InnerModelObject; /** * Represents the implementation of ethernerType. * * <p> * valueLeafFlags identify the leafs whose value are explicitly set * Applicable in protocol edit and query operation. * </p> */ public class DefaultEthernerType extends InnerModelObject implements EthernerType { protected String ethernet; protected BitSet valueLeafFlags = new BitSet(); @Override public String ethernet() { leafreturn severityethernet; { } @Override type string;public BitSet valueLeafFlags() { return valueLeafFlags; } @Override } } | ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
File : OspfManager.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.rev20160519; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Activate; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Component; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Deactivate; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Service; import org.onosproject.event.ListenerRegistry; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.rev20160519.ospf.OspfEvent; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.rev20160519.ospf.OspfListener; import org.slf4j.Logger; import static org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.getLogger; @Component (immediate = true) @Service public class OspfManager public void ethernet(String ethernet) { valueLeafFlags.set(LeafIdentifier.ETHERNET.getLeafIndex()); this.ethernet = ethernet; } @Override public int hashCode() { extends ListenerRegistry<OspfEvent, OspfListener>return Objects.hash(ethernet, valueLeafFlags); } implements OspfService@Override { privatepublic finalboolean Logger log = getLogger(getClass()); equals(Object obj) { @Activate if public(this void== activate(obj) { //TODO: YANG utils generated code return true; log.info("Started"); } @Deactivate publicif void deactivate((obj instanceof DefaultEthernerType) { //TODO: YANG utils generatedDefaultEthernerType code other = (DefaultEthernerType) obj; log.info("Stopped"); } } File : OspfService.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.rev20160519; import org.onosproject.event.ListenerService; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.rev20160519.ospf.OspfEvent; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.rev20160519.ospf.OspfListener; public interface OspfService return extends ListenerService<OspfEvent, OspfListener> { } File : OspfEvent.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.rev20160527.ospf; import org.onosproject.event.AbstractEvent; public class OspfEvent extends AbstractEvent<OspfEvent.Type, OspfEventSubject> { Objects.equals(ethernet, other.ethernet) && public enum Type { Objects.equals(valueLeafFlags, other.valueLeafFlags); TEST } public OspfEvent(Type type, OspfEventSubjectreturn subject)false; { } super(type, subject);@Override public String toString() { } public OspfEvent(Type type, OspfEventSubject subject, long timereturn MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass()) { super(type, subject, time); .omitNullValues() } } File : OspfEventSubject.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.rev20160519.ospf; public class OspfEventSubject { .add("ethernet", ethernet) private Test test; public Test test(.add("valueLeafFlags", valueLeafFlags) { return test; .toString(); } public void test(Test test) { /** * Creates an instance of thisdefaultEthernerType.test = test; } } File : OspfListener.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.rev20160519.ospf; import org.onosproject.event.EventListener; public interface OspfListener extends EventListener<OspfEvent> { } File : Test.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.rev20160519.ospf; import org.onosproject.yangutils.translator.tojava.AugmentationHolder; public interface Test extends AugmentationHolder { String eventClass(); String severity(); interface TestBuilder { */ public DefaultEthernerType() { } @Override public boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf) { String eventClassreturn valueLeafFlags.get(leaf.getLeafIndex()); String severity(); TestBuilder eventClass(String eventClass); TestBuilder severity(String severity); Test build(); } } File : TestBuilder.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.rev20160519.ospf; import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.} } |
RPC
Overview
RPCs are modeled with RPC statement. The input statement is used to define input parameters to the RPC and output statement is used to define output parameters to the RPC.
JAVA mapping
Rpc statement is mapped to a method in module manager class and service interface.
The generated method will depends on the sub statements input and output. Input and Output will have there own java classes and RPC method will contain Output class's object as return type and Input class's object will be input for the method. If no output node is present , return type will be "void". Same way if no input is present , there will be no input parameter for the method.
Rpc node is an non operation type node so all the nodes under it will not contain operationType, processSubTreeFiltereing, select leaf flags in their generated code.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File: sfc.yang module Sfc { yang-version 1; namespace http://huawei.com; prefix Ant; rpc SFP { input { leaf portutil.Objects; import org.onosproject.yangutils.translator.tojava.AugmentedInfo; public class TestBuilder implements Test.TestBuilder { private String eventClass; private String severity; @Override public String eventClass() { return eventClass; } type @Overridestring; public String severity() { return severity; } @Override public TestBuilder eventClass(String eventClass) { } this.eventClass = eventClass;output { return this; leaf } @Overridepath { public TestBuilder severity(String severity) { this.severity = severitytype string; return this; } @Override public Test build() {} } } |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : SfcService.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.sfc.sfp.SfpInput; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.sfc.sfp.SfpOutput; /** * Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of sfc. */ public interface SfcService { /** return new TestImpl(this); } public TestBuilder() { } public final class TestImpl implements Test { private List<AugmentedInfo> augmentedInfoList = new ArrayList<>(); * Service interface privateof Stringsfp. eventClass; private String severity; * * @param inputVar @Override input of service interface sfp public String eventClass() { * @return sfpOutput output of service interface sfp return*/ eventClass; SfpOutput sfp(SfpInput inputVar); } } File : SfpInput.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.sfc.sfp; import java.util.BitSet; /** @Override * Abstraction of an entity which represents the publicfunctionality String severity() {of sfpInput. */ public interface SfpInput { /** return severity; * Identify the leaf of SfpInput. } */ @Override public enum LeafIdentifier public int hashCode() {implements org.onosproject.yang.model.LeafIdentifier{ /** return Objects.hash(eventClass, severity); * Represents port. } @Override */ public boolean equalsPORT(Object obj1); { private int leafIndex; if (this == obj) { public int getLeafIndex() { return true; return leafIndex; } } if LeafIdentifier(objint instanceof TestImplvalue) { this.leafIndex = value; TestImpl other = (TestImpl)} obj; } /** * return Objects.equals(eventClass, other.eventClass) &&Returns the attribute port. * * @return port value of port Objects.equals(severity, other.severity);*/ String port(); /** } * Returns the attribute valueLeafFlags. return false; * } * @return valueLeafFlags value of valueLeafFlags @Override */ publicBitSet String toStringvalueLeafFlags(); { /** * Sets the returnattribute MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass())port. * * @param port value of port .add("eventClass", eventClass) */ void port(String port); /** .add("severity", severity) * Checks if the leaf value is set. * * @param .toString(); } leaf leaf whose value status needs to checked * @return result publicof TestImpl(TestBuilder builderObject) { leaf value set in object */ this.eventClass =boolean builderObject.eventClass(isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf); } File : DefaultSfpInput.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.sfc.sfp; import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects; import java.util.BitSet; import java.util.Objects; this.severity = builderObject.severity(); } @Override public void addAugmentation(AugmentedInfo value) { import org.onosproject.yang.model.InnerModelObject; /** * Represents the implementation of sfpInput. */ public class DefaultSfpInput extends InnerModelObject implements SfpInput { protected String port; protected BitSet valueLeafFlags = new BitSet(); @Override public String getAugmentedInfoListport().add(value); { } return port; } @Override @Override public List<AugmentedInfo>BitSet getAugmentedInfoListvalueLeafFlags() { return augmentedInfoListvalueLeafFlags; } } @Override @Override public void port(String port) { valueLeafFlags.set(LeafIdentifier.PORT.getLeafIndex()); this.port = port; } @Override public voidint removeAugmentationhashCode() { return Objects.hash(port, valueLeafFlags); } getAugmentedInfoList().clear();@Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) { return true; } } } |
Augment
Overview
Augment means “make (something) greater by adding to it; increase.” in YANG augment adds some information in target node. Here in YANG, container, list, choice, case, input, output, or notification node can come as a target node.
As the child node of augment node only "container", "leaf", "list", "leaf-list", "uses", and "choice" can come. If augment comes under a module or submodule.
If a target node is a choice node the "case" statement, or a case shorthand statement can be come as a child node of augment node.
If a target node is from some other YANG file than a mandatory node which is is one of:
A leaf, choice, or anyxml node with a "mandatory" statement with the value "true".
A list or leaf-list node with a "min-elements" statement with a value greater than zero.
A container node without a "presence" statement, which has at least one mandatory node as a child.
should not come as a child node of augment node.
| Info | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Java mapping
For a given augment node in the YANG file one interface file and one builder class file will be generated. Generated files will be having attributes, getters and setters for augment node's child nodes and leaf or leaf-list.
For augment we have given two interface named as “AugmentationHolder” and “AugmentedInfo” as part of YANG utils plugin.
File generated for augment node will be implementing AugmentedInfo class.
Node in data model tree which can be augmented as per the YANG rules, will be implementing AugmentationHolder class. We have given 3 api in AugmentationHolder class, which are :
addAugmentation(AugmentedInfo augmentedInfo);
removeAugmentation();
getAugmentation();
these apis will be providing augmentation functionalities for augmented nodes. These class will be keeping a list of augmentedInfo , which is nothing but a list of augment nodes which are augmenting this node.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : Test.yang
module Test {
yang-version 1;
namespace "http://huawei.com";
prefix Ant;
description "Interval before a route is declared invalid";
container interface {
leaf ifType {
type string;
}
}
augment "/Test/interface" {
leaf ds0ChannelNumber {
type int16;
}
}
} |
if (obj instanceof DefaultSfpInput) {
DefaultSfpInput other = (DefaultSfpInput) obj;
return
Objects.equals(port, other.port) &&
Objects.equals(valueLeafFlags, other.valueLeafFlags);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass())
.omitNullValues()
.add("port", port)
.add("valueLeafFlags", valueLeafFlags)
.toString();
}
/**
* Creates an instance of defaultSfpInput.
*/
public DefaultSfpInput() {
}
@Override
public boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf) {
return valueLeafFlags.get(leaf.getLeafIndex());
}
}
File : Sfpoutput.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.sfc.sfp;
import java.util.BitSet;
/**
* Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of sfpOutput.
*/
public interface SfpOutput {
/**
* Identify the leaf of SfpOutput.
*/
public enum LeafIdentifier implements org.onosproject.yang.model.LeafIdentifier{
/**
* Represents path.
*/
PATH(1);
private int leafIndex;
public int getLeafIndex() {
return leafIndex;
}
LeafIdentifier(int value) {
this.leafIndex = value;
}
}
/**
* Returns the attribute path.
*
* @return path value of path
*/
String path();
/**
* Returns the attribute valueLeafFlags.
*
* @return valueLeafFlags value of valueLeafFlags
*/
BitSet valueLeafFlags();
/**
* Sets the attribute path.
*
* @param path value of path
*/
void path(String path);
/**
* Checks if the leaf value is set.
*
* @param leaf leaf whose value status needs to checked
* @return result of leaf value set in object
*/
boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf);
}
File : DefaultSfpOutput.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.sfc.sfp;
import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects;
import java.util.BitSet;
import java.util.Objects;
import org.onosproject.yang.model.InnerModelObject;
/**
* Represents the implementation of sfpOutput.
*/
public class DefaultSfpOutput extends InnerModelObject implements SfpOutput {
protected String path;
protected BitSet valueLeafFlags = new BitSet();
@Override
public String path() {
return path;
}
@Override
public BitSet valueLeafFlags() {
return valueLeafFlags;
}
@Override
public void path(String path) {
valueLeafFlags.set(LeafIdentifier.PATH.getLeafIndex());
this.path = path;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(path, valueLeafFlags);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
if (obj instanceof DefaultSfpOutput) {
DefaultSfpOutput other = (DefaultSfpOutput) obj;
return
Objects.equals(path, other.path) &&
Objects.equals(valueLeafFlags, other.valueLeafFlags);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass())
.omitNullValues()
.add("path", path)
.add("valueLeafFlags", valueLeafFlags)
.toString();
}
/**
* Creates an instance of defaultSfpOutput.
*/
public DefaultSfpOutput() {
}
@Override
public boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf) {
return valueLeafFlags.get(leaf.getLeafIndex());
}
}
File : DefaultRpcHandler.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import org.onosproject.config.RpcHandler;
import org.onosproject.config.RpcCommand;
import org.onosproject.config.RpcInput;
/**
* Represents the implementation of RPC handler.
*/
public class DefaultRpcHandler implements RpcHandler {
private ExecutorService executor;
@Override
public void executeRpc(Integer msgId, RpcCommand cmd, RpcInput input) {
executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
executor.execute(new RpcExecuter(msgId, (RpcExtendedCommand) cmd, input));
}
/**
* Runnable capable of invoking the appropriate RPC command's execute method.
*/
public class RpcExecuter implements Runnable {
Integer msgId;
RpcExtendedCommand cmd;
RpcInput input;
/**
* Constructs a RPC executor for the given msg id, RPC command and
* RPC input.
*
* @param msgId msgId of the RPC message to be executed
* @param cmd RPC command to be executed
* @param input input data to the RPC command
*/
public RpcExecuter(Integer msgId, RpcExtendedCommand cmd, RpcInput input) {
this.msgId = msgId;
this.cmd = cmd;
this.input = input;
}
@Override
public void run() {
cmd.execute(input, msgId);
}
}
}
File : RegisterRpc.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com;
import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.sfc.SfpCommand;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import org.onosproject.config.RpcCommand;
import org.onosproject.config.RpcHandler;
import org.onosproject.config.DynamicConfigService;
import org.onosproject.yang.model.ModelConverter;
/**
* Represents the implementation of register RPC.
*/
public class RegisterRpc {
private List<RpcCommand> rpcCommands;
private RpcHandler rpcHandler;
private DynamicConfigService storeService;
private ModelConverter modelConverter;
private SfcService sfcService;
/**
* Constructs a register rpc for the given store service, mode converter and
* application service.
*
* @param store dynamic config service
* @param modelConverter model converter for convertion
* @param allService application service
*/
public RegisterRpc(DynamicConfigService store, ModelConverter modelConverter, SfcService sfcService) {
this.rpcCommands = new LinkedList<RpcCommand>();
this.rpcHandler = new DefaultRpcHandler();
this.storeService = store;
this.modelConverter = modelConverter;
this.sfcService = sfcService;
}
/**
* Registers RPC handler with dynamic config service.
*/
public void registerRpc() {
createRpcCommands();
for (RpcCommand rpcCommand : rpcCommands) {
storeService.registerHandler(rpcHandler, rpcCommand);
}
}
/**
* Creates RPC command for all the RPC.
*/
public void createRpcCommands() {
RpcCommand sfp = new SfpCommand(storeService, modelConverter, sfcService);
rpcCommands.add(sfp);
}
}
File : RpcExtendedCommand.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com;
import org.onosproject.yang.model.ResourceId;
import org.onosproject.config.RpcInput;
import org.onosproject.config.RpcCommand;
/**
* Abstract implementation of an RPC extended command.
*/
public abstract class RpcExtendedCommand extends RpcCommand {
/**
* Creates an instance of RPC extended command.
*
* @param cmdId of RPC command
*/
public RpcExtendedCommand(ResourceId cmdId) {
super(cmdId);
}
/**
* Executes the RPC command.
*
* @param input input data to the RPC command
* @param msgId of the RPC message to be executed
*/
public abstract void execute(RpcInput rpcInput, int msgId);
}
File : SfpCommand.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.sfc;
import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.RpcExtendedCommand;
import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.SfcService;
import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.sfc.sfp.DefaultSfpOutput;
import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.sfc.sfp.SfpInput;
import org.onosproject.yang.model.ModelConverter;
import org.onosproject.yang.model.ResourceId;
import org.onosproject.config.RpcInput;
import org.onosproject.config.RpcOutput;
import org.onosproject.config.DynamicConfigService;
import org.onosproject.yang.model.ResourceData;
import org.onosproject.yang.model.ModelObjectData;
import org.onosproject.yang.runtime.DefaultResourceData;
import org.onosproject.yang.model.DefaultModelObjectData;
import static org.onosproject.config.RpcOutput.Status.RPC_SUCCESS;
/**
* Represents the implementation of sfp.
*/
public class SfpCommand extends RpcExtendedCommand {
private ModelConverter modelConverter;
private SfcService sfcService;
private DynamicConfigService storeService;
/**
* Constructs a sfp command for the given cmd id, model converter,
* application service.
*
* @param cmdId identifier of RPC command
* @param modelConverter model converter for convertion
* @param allService application service
*/
public SfpCommand(DynamicConfigService store, ModelConverter modelConverter, SfcService sfcService) {
super(getResourceId());
this.storeService = store;
this.modelConverter = modelConverter;
this.sfcService = sfcService;
}
@Override
public void execute(RpcInput rpcInput) {
}
/**
* Executes the RPC command.
*
* @param rpcInput input data to the RPC command
* @param msgId msgId of the RPC message to be executed
*/
public void execute(RpcInput rpcInput, int msgId) {
ResourceData inputData = DefaultResourceData.builder()
.resourceId(getResourceId())
.addDataNode(rpcInput.input()).build();
ModelObjectData inputMo = modelConverter.createModel(inputData);
SfpInput inputObject = ((SfpInput) inputMo.modelObjects().get(0));
DefaultSfpOutput outputObject = (DefaultSfpOutput) sfcService.sfp(inputObject);
ModelObjectData outputMo = DefaultModelObjectData.builder()
.addModelObject(outputObject).build();
ResourceData outputData = modelConverter.createDataNode(outputMo);
RpcOutput output = new RpcOutput(RPC_SUCCESS, outputData.dataNodes().get(0));
storeService.rpcResponse(msgId, output);
}
private static ResourceId getResourceId() {
return new ResourceId.Builder().addBranchPointSchema("/", null)
.addBranchPointSchema("SFP", "http://huawei.com").build();
}
}
|
Notification
Overview
The "notification" statement is used to define a notification. It takes one argument, which is an identifier, followed by a block of substatements that holds detailed notification information.
JAVA mapping
Notification is mapped to events and event listeners in ONOS. Events are used by Managers to notify its listeners about changes in the network or topology etc, and by Stores to notify their peers of events in a distributed setting. An Event is comprised of a event type and a subject built of model objects.
When notification statement is present in YANG, an event class , event subject class, event listener interface and notification interface and builder will be generated.
When multiple notifications are present event class include the an enum with types of events for all notification like DEVICE_ADDED, DEVICE_REMOVED and it extends AbstractEvent with event type and event subject class. It is used to notify EventListeners about the event.
xxxEvent Subject class will have all the objects of events for multiple notifications and getters and setters for the events.
xxxEvent Listener is interface which extends EventListener.
Notification is an non operation type node so all the nodes under it will not contains operation type, process sub tree filtering and select leaf flag in generated code.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : ospf.yang
module ospf {
namespace "http://example.com/ospf";
prefix "ospf";
notification test {
leaf event-class {
type string;
}
leaf severity {
type string;
}
}
} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : OspfService.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf;
import org.onosproject.event.ListenerService;
import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.ospf.OspfEvent;
import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.ospf.OspfEventListener;
/**
* Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of ospf.
*/
public interface OspfService extends ListenerService<OspfEvent, OspfEventListener> {
}
File : OspfEvent.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.ospf;
import org.onosproject.event.AbstractEvent;
/**
* Represents event implementation of ospf.
*/
public class OspfEvent extends AbstractEvent<OspfEvent.Type, OspfEventSubject> {
public enum Type {
/**
* Represents test.
*/
TEST
}
/**
* Creates OspfEventSubject event with type and subject.
*
* @param type event type
* @param subject subject OspfEventSubject
*/
public OspfEvent(Type type, OspfEventSubject subject) {
super(type, subject);
}
/**
* Creates OspfEventSubject event with type, subject and time.
*
* @param type event type
* @param subject subject OspfEventSubject
* @param time time of event
*/
public OspfEvent(Type type, OspfEventSubject subject, long time) {
super(type, subject, time);
}
}
File : OspfEventSubject.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.ospf;
/**
* Represents the implementation of ospf.
*/
public class OspfEventSubject {
protected Test test;
/**
* Returns the attribute test.
*
* @return test value of test
*/
public Test test() {
return test;
}
/**
* Sets the value to attribute test.
*
* @param test value of test
*/
public void test(Test test) {
this.test = test;
}
}
File : OspfEventListener.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.ospf;
import org.onosproject.event.EventListener;
/**
* Abstraction for event listener of ospf.
*/
public interface OspfEventListener extends EventListener<OspfEvent> {
}
File : Test.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.ospf;
import java.util.BitSet;
/**
* Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of test.
*/
public interface Test {
/**
* Identify the leaf of Test.
*/
public enum LeafIdentifier implements org.onosproject.yang.model.LeafIdentifier{
/**
* Represents eventClass.
*/
EVENTCLASS(1),
/**
* Represents severity.
*/
SEVERITY(2);
private int leafIndex;
public int getLeafIndex() {
return leafIndex;
}
LeafIdentifier(int value) {
this.leafIndex = value;
}
}
/**
* Returns the attribute eventClass.
*
* @return eventClass value of eventClass
*/
String eventClass();
/**
* Returns the attribute severity.
*
* @return severity value of severity
*/
String severity();
/**
* Returns the attribute valueLeafFlags.
*
* @return valueLeafFlags value of valueLeafFlags
*/
BitSet valueLeafFlags();
/**
* Sets the attribute eventClass.
*
* @param eventClass value of eventClass
*/
void eventClass(String eventClass);
/**
* Sets the attribute severity.
*
* @param severity value of severity
*/
void severity(String severity);
/**
* Checks if the leaf value is set.
*
* @param leaf leaf whose value status needs to checked
* @return result of leaf value set in object
*/
boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf);
}
File : DefaultTest.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.example.com.ospf.ospf;
import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects;
import java.util.BitSet;
import java.util.Objects;
import org.onosproject.yang.model.InnerModelObject;
/**
* Represents the implementation of test.
*/
public class DefaultTest extends InnerModelObject implements Test {
protected String eventClass;
protected String severity;
protected BitSet valueLeafFlags = new BitSet();
@Override
public String eventClass() {
return eventClass;
}
@Override
public String severity() {
return severity;
}
@Override
public BitSet valueLeafFlags() {
return valueLeafFlags;
}
@Override
public void eventClass(String eventClass) {
valueLeafFlags.set(LeafIdentifier.EVENTCLASS.getLeafIndex());
this.eventClass = eventClass;
}
@Override
public void severity(String severity) {
valueLeafFlags.set(LeafIdentifier.SEVERITY.getLeafIndex());
this.severity = severity;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(eventClass, severity, valueLeafFlags);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
if (obj instanceof DefaultTest) {
DefaultTest other = (DefaultTest) obj;
return
Objects.equals(eventClass, other.eventClass) &&
Objects.equals(severity, other.severity) &&
Objects.equals(valueLeafFlags, other.valueLeafFlags);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass())
.omitNullValues()
.add("eventClass", eventClass)
.add("severity", severity)
.add("valueLeafFlags", valueLeafFlags)
.toString();
}
/**
* Creates an instance of defaultTest.
*/
public DefaultTest() {
}
@Override
public boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf) {
return valueLeafFlags.get(leaf.getLeafIndex());
}
}
|
Augment
Overview
Augment means “make (something) greater by adding to it; increase.” in YANG augment adds some information in target node. Here in YANG, container, list, choice, case, input, output, or notification node can come as a target node.
As the child node of augment node only "container", "leaf", "list", "leaf-list", "uses", and "choice" can come. If augment comes under a module or submodule.
If a target node is a choice node the "case" statement, or a case shorthand statement can be come as a child node of augment node.
If a target node is from some other YANG file than a mandatory node which is is one of:
A leaf, choice, or anyxml node with a "mandatory" statement with the value "true".
A list or leaf-list node with a "min-elements" statement with a value greater than zero.
A container node without a "presence" statement, which has at least one mandatory node as a child.
should not come as a child node of augment node.
| Info |
|---|
A augment node can't add the same augmented info to an augmented node multiple times. |
Java mapping
For a given augment node in the YANG file one interface file and one builder class file will be generated. Generated files will be having attributes, getters and setters for augment node's child nodes and leaf or leaf-list.
For augment we have given one interface named as "YangAugmentedInfo” as part of YANG tools plugin.
File generated for augment node will be implementing AugmentedInfo class.
Node in data model tree which can be augmented as per the YANG rules for them we have given 3 methods , which are :
public void addAugmentedInfo(YangAugmentedInfo value, Class classObject) {
yangAugmentedInfoMap.put(classObject, value);
}
public YangAugmentedInfo getAugmentedInfo(Class classObject) {
return yangAugmentedInfoMap.get(classObject);
}
public Map<Class<?>, YangAugmentedInfo> getYangAugmentedInfoMap() {
return yangAugmentedInfoMap;
}these methods will be providing augmentation functionalities for augmentable nodes. These class will be storing augmentedInfo , which is nothing but a augment node which are augmenting this node. Also we have provides one code snippet in OpParam file which checks if augmented info is set or not in IsFilterMatchMethod().
OpParam file will extend "YangAugmentedOpParamInfo" interface provides by Yangtools.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : Test.yang
module Test {
yang-version 1;
namespace "http://huawei.com";
prefix Ant;
description "Interval before a route is declared invalid";
container interface {
leaf ifType {
type string;
}
}
augment "/interface" {
leaf ds0ChannelNumber {
type int16;
}
}
} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : AugmentedInterface.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.test.yangautoprefixinterface;
import java.util.BitSet;
/**
* Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of augmentedInterface.
*/
public interface AugmentedInterface {
/**
* Identify the leaf of AugmentedInterface.
*/
public enum LeafIdentifier implements org.onosproject.yang.model.LeafIdentifier{
/**
* Represents ds0ChannelNumber.
*/
DS0CHANNELNUMBER(1);
private int leafIndex;
public int getLeafIndex() {
return leafIndex;
}
LeafIdentifier(int value) {
this.leafIndex = value;
}
}
/**
* Returns the attribute ds0ChannelNumber.
*
* @return ds0ChannelNumber value of ds0ChannelNumber
*/
short ds0ChannelNumber();
/**
* Returns the attribute valueLeafFlags.
*
* @return valueLeafFlags value of valueLeafFlags
*/
BitSet valueLeafFlags();
/**
* Sets the attribute ds0ChannelNumber.
*
* @param ds0ChannelNumber value of ds0ChannelNumber
*/
void ds0ChannelNumber(short ds0ChannelNumber);
/**
* Checks if the leaf value is set.
*
* @param leaf leaf whose value status needs to checked
* @return result of leaf value set in object
*/
boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf);
}
File : DefaultAugmentedInterface.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.test.yangautoprefixinterface;
import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects;
import java.util.BitSet;
import java.util.Objects;
import org.onosproject.yang.model.InnerModelObject;
/**
* Represents the implementation of augmentedInterface.
*
* <p>
* valueLeafFlags identify the leafs whose value are explicitly set
* Applicable in protocol edit and query operation.
* </p>
*/
public class DefaultAugmentedInterface extends InnerModelObject implements AugmentedInterface {
protected short ds0ChannelNumber;
protected BitSet valueLeafFlags = new BitSet();
@Override
public short ds0ChannelNumber() {
return ds0ChannelNumber;
}
@Override
public BitSet valueLeafFlags() {
return valueLeafFlags;
}
@Override
public void ds0ChannelNumber(short ds0ChannelNumber) {
valueLeafFlags.set(LeafIdentifier.DS0CHANNELNUMBER.getLeafIndex());
this.ds0ChannelNumber = ds0ChannelNumber;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(ds0ChannelNumber, valueLeafFlags);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
if (obj instanceof DefaultAugmentedInterface) {
DefaultAugmentedInterface other = (DefaultAugmentedInterface) obj;
return
Objects.equals(ds0ChannelNumber, other.ds0ChannelNumber) &&
Objects.equals(valueLeafFlags, other.valueLeafFlags);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass())
.omitNullValues()
.add("ds0ChannelNumber", ds0ChannelNumber)
.add("valueLeafFlags", valueLeafFlags)
.toString();
}
/**
* Creates an instance of defaultAugmentedInterface.
*/
public DefaultAugmentedInterface() {
}
@Override
public boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf) {
return valueLeafFlags.get(leaf.getLeafIndex());
}
}
|
Type
Overview
The "type" statement takes as an argument a string that is the name of a YANG built-in type or a derived type, followed by an optional block of sub statements that are used to put further restrictions on the type.
Java mapping
YANG | Description | JAVA |
|---|---|---|
binary | Any binary data | byte[] |
bits | A set of bits or flags | BitSet in container class (A enum class for bits leaf) |
boolean | "True" or "false" | boolean |
decimal64 | 64-bit signed decimal number | BigDecimal |
empty | A leaf that does not have any value | boolean |
enumeration | Enumerated strings | Enum class will be generated |
identityref | A reference to an abstract identity | To be implemented |
instance-identifier | References a data tree node | String |
int8 | 8-bit signed integer | byte |
int16 | 16-bit signed integer | short |
int32 | 32-bit signed integer | int |
int64 | 64-bit signed integer | long |
leafref | A reference to a leaf instance | The type of referenced leaf/leaf-list will be used |
string | Human-readable string | String |
uint8 | 8-bit unsigned integer | short |
uint16 | 16-bit unsigned integer | int |
uint32 | 32-bit unsigned integer | long |
uint64 | 64-bit unsigned integer | BigInteger |
union | Choice of member types | Union class will be generated |
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
leaf one {
type string;
}
leaf two {
type int32;
}
leaf-list three {
type boolean;
}
leaf-list four {
type int16;
}
leaf mybits {
type bits {
bit disable-nagle {
position 0;
}
bit auto-sense-speed {
position 1;
}
bit Mb-only {
position 2;
}
}
default "auto-sense-speed";
} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : Test.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com;
import java.util.BitSet;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of test.
*/
public interface Test {
/**
* Identify the leaf of Test.
*/
public enum LeafIdentifier implements org.onosproject.yang.model.LeafIdentifier{
ONE(1),
/**
* Represents two.
*/
TWO(2),
/**
* Represents mybits.
*/
MYBITS(3),
/**
* Represents three.
*/
THREE(4),
/**
* Represents four.
*/
FOUR(5);
private int leafIndex;
public int getLeafIndex() {
return leafIndex;
}
LeafIdentifier(int value) {
this.leafIndex = value;
}
}
/**
* Returns the attribute one.
*
* @return one value of one
*/
String one();
/**
* Returns the attribute two.
*
* @return two value of two
*/
int two();
/**
* Returns the attribute mybits.
*
* @return mybits value of mybits
*/
BitSet mybits();
/**
* Returns the attribute three.
*
* @return three list of three
*/
List<Boolean> three();
/**
* Returns the attribute four.
*
* @return four list of four
*/
List<Short> four();
/**
* Returns the attribute valueLeafFlags.
*
* @return valueLeafFlags value of valueLeafFlags
*/
BitSet valueLeafFlags();
/**
* Sets the attribute one.
*
* @param one value of one
*/
void one(String one);
/**
* Sets the attribute two.
*
* @param two value of two
*/
void two(int two);
/**
* Sets the attribute mybits.
*
* @param mybits value of mybits
*/
void mybits(BitSet mybits);
/**
* Sets the attribute three.
*
* @param three list of three
*/
void three(List<Boolean> three);
/**
* Sets the attribute four.
*
* @param four list of four
*/
void four(List<Short> four);
/**
* Adds to the list of three.
*
* @param addTo value of three
*/
void addToThree(Boolean addTo);
/**
* Adds to the list of four.
*
* @param addTo value of four
*/
void addToFour(Short addTo);
/**
* Checks if the leaf value is set.
*
* @param leaf leaf whose value status needs to checked
* @return result of leaf value set in object
*/
boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf);
}
File : TestOpParam
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com;
import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.BitSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
import org.onosproject.yang.model.InnerModelObject;
/**
* Represents the implementation of test.
*
* <p>
* valueLeafFlags identify the leafs whose value are explicitly set
* Applicable in protocol edit and query operation.
* </p>
*/
public class TestOpParam extends InnerModelObject implements Test {
protected String one;
protected int two;
protected BitSet mybits;
protected List<Boolean> three;
protected List<Short> four;
protected BitSet valueLeafFlags = new BitSet();
@Override
public String one() {
return one;
}
@Override
public int two() {
return two;
}
@Override
public BitSet mybits() {
return mybits;
}
@Override
public List<Boolean> three() {
return three;
}
@Override
public List<Short> four() {
return four;
}
@Override
public BitSet valueLeafFlags() {
return valueLeafFlags;
}
@Override
public void one(String one) {
valueLeafFlags.set(LeafIdentifier.ONE.getLeafIndex());
this.one = one;
}
@Override
public void two(int two) {
valueLeafFlags.set(LeafIdentifier.TWO.getLeafIndex());
this.two = two;
}
@Override
public void mybits(BitSet mybits) {
valueLeafFlags.set(LeafIdentifier.MYBITS.getLeafIndex());
this.mybits = mybits;
}
@Override
public void three(List<Boolean> three) {
valueLeafFlags.set(LeafIdentifier.THREE.getLeafIndex());
this.three = three;
}
@Override
public void four(List<Short> four) {
valueLeafFlags.set(LeafIdentifier.FOUR.getLeafIndex());
this.four = four;
}
@Override
public void addToThree(Boolean addTo) {
if (three == null) {
three = new ArrayList<>();
}
three.add(addTo);
}
@Override
public void addToFour(Short addTo) {
if (four == null) {
four = new ArrayList<>();
}
four.add(addTo);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(one, two, mybits, three, four, valueLeafFlags);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
if (obj instanceof TestOpParam) {
TestOpParam other = (TestOpParam) obj;
return
Objects.equals(one, other.one) &&
Objects.equals(two, other.two) &&
Objects.equals(mybits, other.mybits) &&
Objects.equals(three, other.three) &&
Objects.equals(four, other.four) &&
Objects.equals(valueLeafFlags, other.valueLeafFlags);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass())
.omitNullValues()
.add("one", one)
.add("two", two)
.add("mybits", mybits)
.add("three", three)
.add("four", four)
.add("valueLeafFlags", valueLeafFlags)
.toString();
}
/**
* Creates an instance of testOpParam.
*/
public TestOpParam() {
}
@Override
public boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf) {
return valueLeafFlags.get(leaf.getLeafIndex());
}
@Override
public void addAugmentation(InnerModelObject obj) {
}
@Override
public void removeAugmentation(InnerModelObject obj) {
}
@Override
public Map<Class<? extends InnerModelObject>, InnerModelObject> augmentations() {
return null;
}
@Override
public <T extends InnerModelObject> T augmentation(Class<T> c) {
return null;
}
} |
Typedef
Overview
Typedef is user defined type for his implementation. It has the base type which is must for typedef. To give more information about the typedef there should be sub statements to describe it. Unit statement is optional for typedef which give info about the unit of the type. Default is like a value which will be assigned to the typedef if no value is given.default value should follow all restriction defined for the base-type.
Java mapping
For a given typedef node one class file will be generated which will have an attribute with the base type of typedef. There will be a constructor and a getter method, of method and implementation of hashcode, equals and toString methods.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : test.yang
module test {
yang-version 1;
namespace "http://huawei.com";
prefix "test";
typedef percent {
type uint8;
description "Percentage";
}
leaf completed {
type percent;
}
} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : Percent.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.test;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* Represents the implementation of percent.
*/
public final class Percent {
private short uint8;
/**
* Creates an instance of percent.
*/
private Percent() {
}
/**
* Creates an instance of uint8.
*
* @param uint8 value of uint8
*/
public Percent(short uint8) {
this.uint8 = uint8;
}
/**
* Returns the object of percent for type uint8.
*
* @param value value of percent for type uint8
* @return percent for type uint8
*/
public static Percent of(short value) {
return new Percent(value);
}
/**
* Returns the attribute uint8.
*
* @return uint8 value of uint8
*/
public short uint8() {
return uint8;
}
/**
* Sets the attribute uint8.
*
* @param uint8 value of uint8
*/
public void uint8(short uint8) {
this.uint8 = uint8;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(uint8);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
if (obj instanceof Percent) {
Percent other = (Percent) obj;
return
Objects.equals(uint8, other.uint8);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.valueOf(uint8);
}
/**
* Returns the object of percent fromString input String percent.
*
* @param valInString value of input String
* @return percent
*/
public static Percent fromString(String valInString) {
try {
short tmpVal = Short.parseShort(valInString);
return of(tmpVal);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a valid input element");
}
}
} |
Enumeration
Overview
Enum statement only can come when a leaf is of type enumeration. Each enum has one string then should be unique . The string must not be empty string and must not have white spaces. Enum can have sub statements, value statement will give the info about its value. If the enum statement in enumeration has no value statement then its value is considered as zero and subsequently incremented by one for next values.
Java mapping
For a given enumeration node one enum file will be generated which will have all the enum as its attributes. There will be a constructor and a getter method for the values.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File: test.yang
module Test {
yang-version 1;
namespace "http://huawei.com";
prefix Ant;
description "Interval before a route is declared invalid";
leaf packetType {
type enumeration {
enum "unbounded";
enum ZERO;
enum two;
enum four;
}
}
} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : PacketTypeEnum.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.test;
/**
* Represents ENUM data of packetTypeEnum.
*/
public enum PacketTypeEnum {
/**
* Represents unbounded.
*/
UNBOUNDED(0, "unbounded"),
/**
* Represents zERO.
*/
ZERO(1, "ZERO"),
/**
* Represents two.
*/
TWO(2, "two"),
/**
* Represents four.
*/
FOUR(3, "four");
private int packetTypeEnum;
private String schemaName;
/**
* Creates an instance of packetTypeEnum.
*
* @param packetTypeEnum value of packetTypeEnum
*/
PacketTypeEnum(int packetTypeEnum, String schemaName) {
this.packetTypeEnum = packetTypeEnum;
this.schemaName = schemaName;
}
/**
* Returns the object of packetTypeEnum for.
*
* @param value value of packetTypeEnum for
* @return packetTypeEnum for
*/
public static PacketTypeEnum of(int value) {
switch (value) {
case 0:
return PacketTypeEnum.UNBOUNDED;
case 1:
return PacketTypeEnum.ZERO;
case 2:
return PacketTypeEnum.TWO;
case 3:
return PacketTypeEnum.FOUR;
default :
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a valid input element");
}
}
/**
* Returns the object of packetTypeEnum for.
*
* @param value value of packetTypeEnum for
* @return packetTypeEnum for
*/
public static PacketTypeEnum of(String value) {
switch (value) {
case "unbounded":
return PacketTypeEnum.UNBOUNDED;
case "ZERO":
return PacketTypeEnum.ZERO;
case "two":
return PacketTypeEnum.TWO;
case "four":
return PacketTypeEnum.FOUR;
default :
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a valid input element");
}
}
/**
* Returns the attribute packetTypeEnum.
*
* @return packetTypeEnum value of packetTypeEnum
*/
public int packetTypeEnum() {
return packetTypeEnum;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return schemaName;
}
}
|
Union
Overview
Union is a built in type which represents its member types. Union can have multiple member types. To use union there must be a type statement. Except empty and leafref all types can come under union.
When a value comes for union , which can match to multiple member types of union, then in that case to whichever type value matches from the member types defined in union value, will be taken from union as the values type.
Java mapping
For a given union node one class file will be generated which will have all the an attribute with the type union is having. There will be a constructor , getter method, of method, fromString, HashCode, equals and ToString methods for the values.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : test.yang
module test {
yang-version 1;
namespace "http://huawei.com";
prefix "test";
typedef ip-address {
type union {
type int32;
type uint32;
}
}
} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : IpAddressUnion.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.test.ipaddress;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.BitSet;
/**
* Represents the implementation of ipAddressUnion.
*/
public final class IpAddressUnion {
private int int32;
private long uint32;
private BitSet setValue = new BitSet();
/**
* Creates an instance of ipAddressUnion.
*/
private IpAddressUnion() {
}
/**
* Creates an instance of int32.
*
* @param int32 value of int32
*/
public IpAddressUnion(int int32) {
setValue.set(0);
this.int32 = int32;
}
/**
* Creates an instance of uint32.
*
* @param uint32 value of uint32
*/
public IpAddressUnion(long uint32) {
setValue.set(1);
this.uint32 = uint32;
}
/**
* Returns the object of ipAddressUnion for type int32.
*
* @param value value of ipAddressUnion for type int32
* @return ipAddressUnion for type int32
*/
public static IpAddressUnion of(int value) {
return new IpAddressUnion(value);
}
/**
* Returns the object of ipAddressUnion for type uint32.
*
* @param value value of ipAddressUnion for type uint32
* @return ipAddressUnion for type uint32
*/
public static IpAddressUnion of(long value) {
return new IpAddressUnion(value);
}
/**
* Returns the attribute int32.
*
* @return int32 value of int32
*/
public int int32() {
return int32;
}
/**
* Returns the attribute uint32.
*
* @return uint32 value of uint32
*/
public long uint32() {
return uint32;
}
/**
* Sets the attribute int32.
*
* @param int32 value of int32
*/
public void int32(int int32) {
this.int32 = int32;
}
/**
* Sets the attribute uint32.
*
* @param uint32 value of uint32
*/
public void uint32(long uint32) {
this.uint32 = uint32;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(int32, uint32);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
if (obj instanceof IpAddressUnion) {
IpAddressUnion other = (IpAddressUnion) obj;
return
Objects.equals(int32, other.int32) &&
Objects.equals(uint32, other.uint32);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
if (setValue.get(0)) {
return String.valueOf(int32);
}
if (setValue.get(1)) {
return String.valueOf(uint32);
}
return null;
}
/**
* Returns the object of ipAddressUnion fromString input String ipAddressUnion.
*
* @param valInString value of input String
* @return ipAddressUnion
*/
public static IpAddressUnion fromString(String valInString) {
try {
int tmpVal = Integer.parseInt(valInString);
return of(tmpVal);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
try {
long tmpVal = Long.parseLong(valInString);
return of(tmpVal);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a valid input element");
}
}
} |
When there are two types with same java mapping. for resolving this conflict we will be checking the range of the value and then we will assign it to the right attribute. Order will be taken care of while code generation and conflict range validation . for example : if union have type int32 followed by uint16, then range validation will be done on basis of int32 , in other case range will be validated on basis of uint16.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : test.yang
module test {
yang-version 1;
namespace "http://huawei.com";
prefix "test";
typedef ip-address {
type union {
type int32;
type uint16;
type int64;
type uint32;
type string;
}
}
} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : IpAddressUnion.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.test.ipaddress;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.BitSet;
import java.util.Objects;
/**
* Represents the implementation of ipAddressUnion.
*/
public final class IpAddressUnion {
private static final int INT32_MIN_RANGE = -2147483648;
private static final int INT32_MAX_RANGE = 2147483647;
private static final BigInteger INT64_MIN_RANGE = new BigInteger("-9223372036854775808");
private static final BigInteger INT64_MAX_RANGE = new BigInteger("9223372036854775807");
private int int32;
private int uint16;
private long int64;
private long uint32;
private String string;
private BitSet setValue = new BitSet();
/**
* Creates an instance of ipAddressUnion.
*/
private IpAddressUnion() {
}
/**
* Creates an instance of string.
*
* @param string value of string
*/
public IpAddressUnion(String string) {
setValue.set(4);
this.string = string;
}
/**
* Creates an instance of int32.
*
* @param int32 value of int32
*/
public IpAddressUnion(int int32) {
setValue.set(0);
if (validateRange(INT32_MIN_RANGE, INT32_MAX_RANGE, int32)) {
this.int32 = int32;
} else {
this.uint16 = int32;
}
}
/**
* Creates an instance of int64.
*
* @param int64 value of int64
*/
public IpAddressUnion(long int64) {
setValue.set(2);
if (validateRange(INT64_MIN_RANGE, INT64_MAX_RANGE, int64)) {
this.int64 = int64;
} else {
this.uint32 = int64;
}
}
/**
* Returns the object of ipAddressUnion for type string.
*
* @param value value of ipAddressUnion for type string
* @return ipAddressUnion for type string
*/
public static IpAddressUnion of(String value) {
return new IpAddressUnion(value);
}
/**
* Returns the object of ipAddressUnion for type int32.
*
* @param value value of ipAddressUnion for type int32
* @return ipAddressUnion for type int32
*/
public static IpAddressUnion of(int value) {
return new IpAddressUnion(value);
}
/**
* Returns the object of ipAddressUnion for type int64.
*
* @param value value of ipAddressUnion for type int64
* @return ipAddressUnion for type int64
*/
public static IpAddressUnion of(long value) {
return new IpAddressUnion(value);
}
/**
* Returns the attribute int32.
*
* @return int32 value of int32
*/
public int int32() {
return int32;
}
/**
* Returns the attribute int64.
*
* @return int64 value of int64
*/
public long int64() {
return int64;
}
/**
* Returns the attribute string.
*
* @return string value of string
*/
public String string() {
return string;
}
/**
* Sets the attribute int32.
*
* @param int32 value of int32
*/
public void int32(int int32) {
this.int32 = int32;
}
/**
* Sets the attribute uint16.
*
* @param uint16 value of uint16
*/
public void uint16(int uint16) {
this.uint16 = uint16;
}
/**
* Sets the attribute int64.
*
* @param int64 value of int64
*/
public void int64(long int64) {
this.int64 = int64;
}
/**
* Sets the attribute uint32.
*
* @param uint32 value of uint32
*/
public void uint32(long uint32) {
this.uint32 = uint32;
}
/**
* Sets the attribute string.
*
* @param string value of string
*/
public void string(String string) {
this.string = string;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(int32, uint16, int64, uint32, string);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
if (obj instanceof IpAddressUnion) {
IpAddressUnion other = (IpAddressUnion) obj;
return
Objects.equals(int32, other.int32) &&
Objects.equals(uint16, other.uint16) &&
Objects.equals(int64, other.int64) &&
Objects.equals(uint32, other.uint32) &&
Objects.equals(string, other.string);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
if (setValue.get(0)) {
return String.valueOf(int32);
}
if (setValue.get(1)) {
return String.valueOf(uint16);
}
if (setValue.get(2)) {
return String.valueOf(int64);
}
if (setValue.get(3)) {
return String.valueOf(uint32);
}
if (setValue.get(4)) {
return string;
}
return null;
}
/**
* Returns the object of ipAddressUnion fromString input String ipAddressUnion.
*
* @param valInString value of input String
* @return ipAddressUnion
*/
public static IpAddressUnion fromString(String valInString) {
try {
int tmpVal = Integer.parseInt(valInString);
return of(tmpVal);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
try {
long tmpVal = Long.parseLong(valInString);
return of(tmpVal);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
try {
String tmpVal = (valInString);
return of(tmpVal);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a valid input element");
}
}
/**
* Validates if value is in given range.validateRange.
*
* @param minRange value of minRange
* @param minRange value of maxRange
* @return true if value is in range
*/
private boolean validateRange(int minRange, int maxRange, int value) {
return value >= minRange && value <= maxRange;
}
/**
* Validates if value is in given range.validateRange.
*
* @param minRange value of minRange
* @param minRange value of maxRange
* @return true if value is in range
*/
private boolean validateRange(BigInteger minRange, BigInteger maxRange, long value) {
BigInteger bigInteger = new BigInteger(" " + value);
return bigInteger.compareTo(minRange) == 1 && bigInteger.compareTo(maxRange) == 1;
}
}
|
Leafref
Overview
The leafref type is used to reference a particular leaf instance in the data tree. Path statement must be present for leafref type. The path under leafref must refer to existing leaf or leaf-list. The leaf or leaf-list with leafref will use the instance of the referred leaf or leaf-list.
If leafref comes under grouping and typedef, it will be resolved where it is used. It will not be resolved where it is defined.
Java mapping
The leaf or leaf-list with type leafref, will copy the type of referred leaf or leaf-list, during java file generation. If leaf-ref is directly inside grouping then the generated return type of that leaf will be Object.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : ietf-network.yang
module ietf-network {
yang-version 1;
namespace "urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:yang:ietf-network";
prefix nd;
container networks {
description
"Serves as top-level container for a list of
networks.";
leaf id {
type uint8;
description
"Identifies a network.";
}
container network {
leaf network-id {
type leafref {
path "/nd:networks/nd:id";
}
}
}
uses network-id;
}
grouping network-id {
description
"Serves as top-level container for a list of
networks.";
leaf network-id {
type leafref {
path "/nd:networks/nd:id";
}
}
}
} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : Networks.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.ietf.params.xml.ns.yang.ietf.network.ietfnetwork;
import java.util.BitSet;
import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.ietf.params.xml.ns.yang.ietf.network.ietfnetwork.networks.Network;
/**
* Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of networks.
*/
public interface Networks {
/**
* Identify the leaf of Networks.
*/
public enum LeafIdentifier implements org.onosproject.yang.model.LeafIdentifier{
/**
* Represents id.
*/
ID(1),
/**
* Represents networkId.
*/
NETWORKID(2);
private int leafIndex;
public int getLeafIndex() {
return leafIndex;
}
LeafIdentifier(int value) {
this.leafIndex = value;
}
}
/**
* Returns the attribute id.
*
* @return id value of id
*/
short id();
/**
* Returns the attribute networkId.
*
* @return networkId value of networkId
*/
Object networkId();
/**
* Returns the attribute valueLeafFlags.
*
* @return valueLeafFlags value of valueLeafFlags
*/
BitSet valueLeafFlags();
/**
* Returns the attribute network.
*
* @return network value of network
*/
Network network();
/**
* Sets the attribute id.
*
* @param id value of id
*/
void id(short id);
/**
* Sets the attribute networkId.
*
* @param networkId value of networkId
*/
void networkId(Object networkId);
/**
* Sets the attribute network.
*
* @param network value of network
*/
void network(Network network);
/**
* Checks if the leaf value is set.
*
* @param leaf leaf whose value status needs to checked
* @return result of leaf value set in object
*/
boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf);
}
File : Networks.java
| ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
File : AugmentedInterface.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160428.test; import org.onosproject.yangutils.utils.AugmentedInfo; public interface AugmentedInterface extends AugmentedInfo { short getDs0ChannelNumber(); .urn.ietf.params.xml.ns.yang.ietf.network.ietfnetwork.networks; import java.util.BitSet; /** * Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of network. */ public interface Network { /** interface AugmentedInterfaceBuilder* { Identify the leaf of Network. short getDs0ChannelNumber(); */ public enum LeafIdentifier AgmentedInterfaceBuilder setDs0ChannelNumber(short ds0ChannelNumber); implements org.onosproject.yang.model.LeafIdentifier{ AugmentedInterface build(); /** } } File : AugmentedInterfaceBuilder.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160428.test; import java.util.Objects; import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160428.test.InterfaceBuilder.InterfaceImpl; public class AugmentedInterfaceBuilder implements AugmentedInterface.AugmentedInterfaceBuilder { private short ds0ChannelNumber; @Override public short getDs0ChannelNumber() { * Represents networkId. */ NETWORKID(1); private returnint ds0ChannelNumberleafIndex; } @Override public AugmentedInterfaceBuilderint setDs0ChannelNumbergetLeafIndex(short ds0ChannelNumber) { this.ds0ChannelNumber = ds0ChannelNumber; return leafIndex; return this; } @Override public AugmentedInterface buildLeafIdentifier(int value) { return new AugmentedInterfaceImpl(this)this.leafIndex = value; } public AugmentedInterfaceBuilder() {} } public final/** class AugmentedInterfaceImpl implements AugmentedInterface { * Returns the attribute networkId. private short ds0ChannelNumber;* * @Override@return networkId value of networkId */ public short getDs0ChannelNumbernetworkId() {; /** * Returns return ds0ChannelNumber;the attribute valueLeafFlags. * } * @return valueLeafFlags value of @OverridevalueLeafFlags */ Public intBitSet hashCodevalueLeafFlags() {; /** * Sets returnthe attribute ObjectsnetworkId.hash(ds0ChannelNumber); * } * @param networkId value of @OverridenetworkId */ public booleanvoid equalsnetworkId(Objectshort obj) { networkId); /** if (this == obj)* { Checks if the leaf value is set. * return true; * @param leaf leaf whose value status needs to } checked * @return result of leaf value ifset (objin instanceofobject AugmentedInterfaceImpl) { */ boolean isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf); } |
Identity
Overview
The identity is used to define a new globally unique, abstract, and untyped identity. Its only purpose is to denote its name, semantics, and existence. An identity can iether be defined from scratch or derived from a base identity. The base statement, which is optional, takes as an argument a string that is the name of an existing identity, from which the new identity is derived.
Java mapping
For a given identity one abstract class file will be generated.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : ietf-network.yang module ietf-network { AugmentedInterfaceImpl other = (AugmentedInterfaceImpl) objyang-version 1; namespace "urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:yang:ietf-network"; prefix nd; identity returntunnel-type { description "Base identity from which specific tunnel types are derived."; } } |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : Objects.equals(ds0ChannelNumber, other.ds0ChannelNumber); }TunnelType.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.ietf.params.xml.ns.yang.ietf.network.ietfnetwork; /** * Represents the implementation of tunnelType. */ public abstract class TunnelType { /** * Returns the return false;attribute tunnel-type. * } * @return tunnel-type value of @Overridetunnel-type */ public static String toStringtunnelTypeToString() { return "tunnel-type"; return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass()) } /** * Returns the object of tunnelType fromString input String .add("ds0ChannelNumber", ds0ChannelNumber)tunnelType. * * @param valInString value of input .toString();String * @return } tunnelType */ public static Class Public AugmentedInterfaceImplfromString(AugmentedInterfaceBuilderString builderObjectvalInString) { if this.ds0ChannelNumber = builderObject.getDs0ChannelNumber();(valInString.equals("tunnel-type")) { InterfaceImpl interfaceImpl = new InterfaceBuilder().new InterfaceImpl()return TunnelType.class; interfaceImpl.addAugmentation(this);} } throw } } |
Type
Overview
The "type" statement takes as an argument a string that is the name of a YANG built-in type or a derived type, followed by an optional block of sub statements that are used to put further restrictions on the type.
Java mapping
...
YANG
...
Description
...
JAVA
...
binary
...
Any binary data
...
To be implemented
...
bits
...
A set of bits or flags
...
To be implemented
...
boolean
...
"True" or "false"
...
boolean
...
decimal64
...
64-bit signed decimal number
...
To be implemented
...
empty
...
A leaf that does not have any value
...
boolean
...
enumeration
...
Enumerated strings
...
Enum class will be generated
...
identityref
...
A reference to an abstract identity
...
To be implemented
...
instance-identifier
...
References a data tree node
...
String
...
int8
...
8-bit signed integer
...
byte
...
int16
...
16-bit signed integer
...
short
...
int32
...
32-bit signed integer
...
int
...
int64
...
64-bit signed integer
...
long
...
leafref
...
A reference to a leaf instance
...
The type of referenced leaf/leaf-list will be used
...
string
...
Human-readable string
...
String
...
uint8
...
8-bit unsigned integer
...
short
...
uint16
...
16-bit unsigned integer
...
int
...
uint32
...
32-bit unsigned integer
...
long
...
uint64
...
64-bit unsigned integer
...
BigInteger
...
union
...
Choice of member types
...
Union class will be generated
Example
new IllegalArgumentException("not a valid input element");
}
} |
Identityref
Overview
The identityref type is used to reference an existing identity. Base statement, which is a substatement to the type statement, must be present if the type is identityref. The base under identityref must refer to existing identity.
If identityref comes under grouping and typedef, it will be resolved where it is used. It will not be resolved where it is defined.
Java mapping
The leaf or leaf-list with type identityref, will referred to identity, during java file generation.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : ietf-network.yang
module ietf-network {
yang-version 1;
namespace "urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:yang:ietf-network";
prefix nd;
identity tunnel-type {
description "Base identity from which specific tunnel types are derived.";
}
container network-id {
description "Serves as top-level container for a list of networks.";
leaf leaf-network-id {
| ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
leaf one { type identityref { base tunnel-type string; } leaf two { } } } } |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : TunnelType.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.ietf.params.xml.ns.yang.ietf.network.ietfnetwork; /** * Represents the implementation of tunnelType. */ public abstract class typeTunnelType int32;{ } leaf-list three { /** * Returns the attribute tunnel-type. * * @return tunnel-type boolean; } leaf-list four { value of tunnel-type */ public static String tunnelTypeToString() { return "tunnel-type"; } /** * Returns type int16; } |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
private String one;
private int two;
private List<Boolean> three;
private List<Short> four; |
Typedef
Overview
Typedef is user defined type for his implementation. It has the base type which is must for typedef. To give more information about the typedef there should be sub statements to describe it. Unit statement is optional for typedef which give info about the unit of the type. Default is like a value which will be assigned to the typedef if no value is given.default value should follow all restriction defined for the base-type.
Java mapping
For a given typedef node one class file will be generated which will have an attribute with the base type of typedef. There will be a constructor and a getter method, of method and implementation of hashcode, equals and toString methods.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : test.yang module test { yang-version 1; namespace "http://huawei.com"; prefix "test"; typedef percentthe object of tunnelType fromString input String tunnelType. * * @param valInString value of input String * @return tunnelType */ public static Class fromString(String valInString) { if (valInString.equals("tunnel-type")) uint8;{ description "Percentage"return TunnelType.class; } leaf completed { throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a valid type percentinput element"); } } | ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
File : PercentNetworkId.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160526.test.urn.ietf.params.xml.ns.yang.ietf.network.ietfnetwork; import java.util.ObjectsBitSet; import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects; public final class Percent { private short uint8; private Percent() { } public Percent(short value) { this.uint8 = value; } public static Percent of(short value) { /** * Abstraction of an entity which represents the functionality of networkId. */ public interface NetworkId { /** * Identify the returnleaf new Percent(value);of NetworkId. } */ public short uint8() enum LeafIdentifier implements org.onosproject.yang.model.LeafIdentifier{ /** return uint8; } * Represents @OverrideleafNetworkId. public int hashCode() {*/ return Objects.hash(uint8LEAFNETWORKID(1); } @Override publicprivate boolean equals(Object obj) { int leafIndex; public ifint getLeafIndex(this == obj) { return trueleafIndex; } if LeafIdentifier(objint instanceof Percentvalue) { Percent otherthis.leafIndex = (Percent) objvalue; } } return Objects.equals(uint8, other.uint8); /** * Returns the attribute leafNetworkId. }* * @return leafNetworkId return false;value of leafNetworkId } */ @Override Class<? extends TunnelType> leafNetworkId(); public String toString() { /** * Returns the returnattribute MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass())valueLeafFlags. * * .add("uint8", uint8) @return valueLeafFlags value of valueLeafFlags */ BitSet .toStringvalueLeafFlags(); }/** public static* PercentSets fromString(String valInString) {the attribute leafNetworkId. * try { * @param leafNetworkId value of leafNetworkId */ short tmpVal =void Short.parseShort(valInString);leafNetworkId(Class<? extends TunnelType> leafNetworkId); /** * Checks if the leaf value return of(tmpVal);is set. * * @param leaf leaf whose }value catchstatus (Exceptionneeds e)to {checked * @return result of leaf value }set in object */ boolean return null; } } |
Enumeration
Overview
Enum statement only can come when a leaf is of type enumeration. Each enum has one string then should be unique . The string must not be empty string and must not have white spaces. Enum can have sub statements, value statement will give the info about its value. If the enum statement in enumeration has no value statement then its value is considered as zero and subsequently incremented by one for next values.
Java mapping
For a given enumeration node one enum file will be generated which will have all the enum as its attributes. There will be a constructor and a getter method for the values.
Example
isLeafValueSet(LeafIdentifier leaf);
}
|
Bits
Overview
The bits built-in type represents a bit set. That is, a bits value is a set of flags identified by small integer position numbers starting at 0.
The "bit" statement, which is a substatement to the "type" statement, MUST be present if the type is "bits". It is repeatedly used to specify each assigned named bit of a bits type. It takes as an argument a string that is the assigned name of the bit. All assigned names in a bits type MUST be unique.
The "position" statement, which is optional, takes as an argument a non-negative integer value that specifies the bit's position.
Java mapping
Container BitSet is used to store bits during code generation.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File | ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
File: test.yang module Test { yang-version 1; namespace "http://huawei.com"; prefix Ant; description "Interval before a route is declared invalid"; leaf packetType { typedef MyBits { type enumeration { enum "unbounded"; enum ZERO; enum two; enum four; } } } | ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
File : PacketTypeEnum.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160526.test; public enum PacketTypeEnum { UNBOUNDED(0), ZERO(1), TWO(2), FOUR(3); private int packetTypeEnum; PacketTypeEnum(int value) { type bits { bit disable-nagle { position 0; packetTypeEnum = value;} } public static PacketTypeEnum of(int value)bit auto-sense-speed { switch (value) { position 1; case 0:} bit Mb-only { return PacketTypeEnum.UNBOUNDED; case 1: position 2; } return PacketTypeEnum.ZERO; } } } |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : Bits.java package case 2: org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.test.mybits; import java.util.BitSet; import java.util.regex.Pattern; /** * Represents ENUM data of bits. */ public enum Bits { /** * returnRepresents PacketTypeEnumdisable-nagle.TWO; */ DISABLE_NAGLE(0, "disable-nagle"), case 3:/** * Represents auto-sense-speed. */ AUTO_SENSE_SPEED(1, "auto-sense-speed"), return PacketTypeEnum.FOUR; /** * Represents mb-only. default :*/ MB_ONLY(2, "Mb-only"); private int bits; private String schemaName; return null;/** * Creates an instance of bits. } } * public int* packetTypeEnum() { @param bits value of bits */ return packetTypeEnum; } Bits(int bits, String schemaName) { public static PacketTypeEnum fromString(String valInString) { this.bits = bits; this.schemaName try {= schemaName; } /** * Returns the intobject tmpValof =bits Integerfor.parseInt(valInString); * * @param value value of return of(tmpVal);bits for * @return bits for } catch*/ (Exception e) { public static Bits of(int value) }{ return null; } } |
Union
Overview
Union is a built in type which represents its member types. Union can have multiple member types. To use union there must be a type statement. Except empty and leafref all types can come under union.
When a value comes for union , which can match to multiple member types of union, then in that case to whichever type value matches from the member types defined in union value, will be taken from union as the values type.
Java mapping
For a given union node one class file will be generated which will have all the an attribute with the type union is having. There will be a constructor , getter method, of method, fromString, HashCode, equals and ToString methods for the values.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : test.yang
module test {
yang-version 1;
namespace "http://huawei.com";
prefix "test";
typedef ip-address {
type union {
type int32;
type uint32;
}
}
} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : IpAddressUnion.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160526.test.ipaddress; import java.util.Objects; import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects; public final class IpAddressUnion { private int int32; private long uint32; private IpAddressUnion() { } public IpAddressUnion(int value) { this.int32 = value; } public IpAddressUnion(long value) { this.uint32 = value; } public static IpAddressUnion of(int value) { switch (value) { case 0: return Bits.DISABLE_NAGLE; case 1: return Bits.AUTO_SENSE_SPEED; case 2: return Bits.MB_ONLY; default : throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a valid input element"); } } /** * Returns the object of bits for. * * @param value value of bits for * @return bits for */ public static Bits of(String value) { switch (value) { case "disable-nagle": return Bits.DISABLE_NAGLE; case "auto-sense-speed": return Bits.AUTO_SENSE_SPEED; case "Mb-only": return new IpAddressUnion(value)Bits.MB_ONLY; } public static IpAddressUnion of(long value)default {: return new IpAddressUnion(value); } throw new IllegalArgumentException("not a publicvalid intinput int32() {element"); return int32;} } /** * publicReturns longthe uint32() {attribute bits. * return uint32; } * @return bits value of bits @Override*/ public int hashCodebits() { return Objects.hash(int32, uint32)bits; } @Override/** public boolean* equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) {Returns the object of bits fromString input String bits. * * @param valInString value of input return true;String } if (obj instanceof IpAddressUnion) { * @return bits */ IpAddressUnionpublic otherstatic =BitSet fromString(IpAddressUnionString valInString) obj;{ BitSet tmpVal = new returnBitSet(); String[] bitNames Objects.equals(int32, other.int32) &&= valInString.trim().split(Pattern.quote(" ")); for (String bitName : bitNames) { Objects.equals(uint32, other.uint32); Bits bits = }of(bitName); return false; if } @Override(bits != null) { public String toString() { return MoreObjectstmpVal.toStringHelperset(getClassbits.bits()); .omitNullValues()} } .add("int32", int32) if (tmpVal.isEmpty()) { throw .addnew IllegalArgumentException("uint32", uint32)not a valid input element"); } .toString() return tmpVal; } public static IpAddressUnionString fromStringtoString(StringBitSet valInStringbits) { tryStringBuilder { sBuild = new StringBuilder(""); int tmpVal = Integer.parseInt(valInString);if (bits.get(Bits.DISABLE_NAGLE.bits())) { return of(tmpValsBuild.append("disable-nagle"); } catch sBuild.append(Exception" e") {; } try if (bits.get(Bits.AUTO_SENSE_SPEED.bits())) { long tmpVal = LongsBuild.parseLong(valInStringappend("auto-sense-speed"); return of(tmpValsBuild.append(" "); } catch (Exception e) { if }(bits.get(Bits.MB_ONLY.bits())) { return null; } } | ||
| Code Block | ||
| ||
File : FlowClassifierService.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.sfc.flowclassifier.rev20160524; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.ietf.params.xml.ns.yang.ietf.yang.types.rev20100924.ietfyangtypes.Uuid; public interface FlowClassifierService { Uuid getId(); void setId(Uuid id); } File : FlowClassifierManager.java sBuild.append("Mb-only"); sBuild.append(" "); } return sBuild.toString(); } } File: MyBits.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.sfchttp.huawei.flowclassifiercom.rev20160524test; import orgjava.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Activateutil.BitSet; import org.apacheonosproject.felixyang.scrgen.annotations.Component; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Deactivatev1.http.huawei.com.test.mybits.Bits; import orgjava.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Service; import org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.ietf.params.xml.ns.yang.ietf.yang.types.rev20100924.ietfyangtypes.Uuid; import org.slf4j.Logger; import static org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.getLogger; @Component (immediate = true) @Service public class FlowClassifierManager implements FlowClassifierService { private final Logger log = getLogger(getClass()); @Activateutil.Objects; /** * Represents the implementation of myBits. */ public final class MyBits { private BitSet bits; /** * Creates an instance of myBits. */ private MyBits() { } /** * Creates an instance of bits. * * @param bits value of bits */ public void activate(MyBits(BitSet bits) { this.bits = bits; //TODO: YANG utils generated code log.info("Started"); } /** * Returns the object of myBits for type bits. } @Deactivate public void deactivate() { * * @param value value of myBits for type bits * @return myBits for type bits */ //TODO: YANG utils generated code public static MyBits of(BitSet value) { return new log.info("Stopped"MyBits(value); } @Override/** public Uuid getId() { * Returns the attribute bits. * //TODO: YANG utils* generated@return code bits value of bits return null;*/ } public BitSet bits() { @Override public void setId(Uuid id)return {bits; } //TODO: YANG utils generated code } } File : IetfYangTypesService.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.ietf.params.xml.ns.yang.ietf.yang.types.rev20100924; public interface IetfYangTypesService { } File : IetfYangTypesManager.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.ietf.params.xml.ns.yang.ietf.yang.types.rev20100924; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Activate; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Component; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Deactivate; import org.apache.felix.scr.annotations.Service; import org.slf4j.Logger; import static org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.getLogger; @Component (immediate = true) @Service public class IetfYangTypesManager implements IetfYangTypesService { private final Logger log = getLogger(getClass()); @Activate public void activate() { //TODO: YANG utils generated code** * Sets the attribute bits. * * @param bits value of bits */ public void bits(BitSet bits) { this.bits = bits; } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(bits); } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) { return true; } if log.info("Started"); (obj instanceof MyBits) { } @Deactivate MyBits publicother void= deactivate(MyBits) {obj; //TODO: YANG utils generated codereturn log.info("Stopped"); } } File : Uuid.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.urn.ietf.params.xml.ns.yang.ietf.yang.types.rev20100924.ietfyangtypes; import java.util.Objects; import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects; public final class Uuid { private String string; private Uuid() {Objects.equals(bits, other.bits); } return false; } @Override public Uuid(String valuetoString() { this.string = valuereturn Bits.toString(bits); } /** * publicReturns staticthe Uuidobject of(String value) { myBits fromString input String myBits. * * @param valInString returnvalue of new Uuid(value);input String } * @return myBits public String string() { */ public static MyBits fromString(String returnvalInString) string;{ } try @Override{ public int hashCode() { BitSet tmpVal = return ObjectsBits.hashfromString(stringvalInString); } @Override publicreturn boolean equals(Object obj) { of(tmpVal); } ifcatch (this == objException e) { returnthrow true; }new IllegalArgumentException("not a valid input element"); if} (obj instanceof Uuid) { Uuid other = (Uuid) obj} } |
Binary
Overview
The binary built-in type represents any binary data, i.e., a sequence of octets.
A binary can be restricted with the "length" statement. The length of a binary value is the number of octets it contains.
Binary values are encoded with the base64 encoding scheme.
Java mapping
Byte array is used to store decoded binary during code generation.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : test.yang module Test { yang-version 1; namespace http://huawei.com; prefix Ant; typedef MyBinary return{ type binary { Objects.equals(string, other.string); length "4"; } } } |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File: MyBinary.java package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160718.test; import java.util.Objects; import return false; } @Overridecom.google.common.base.MoreObjects; import java.util.Base64; public final class MyBinary { private byte[] binary; private public String toStringMyBinary() { } public return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass()) MyBinary(byte[] value) { this.binary = value; } .add("string", string) public static MyBinary of(byte[] value) { return new .toStringMyBinary(value); } public static Uuid fromString(String valInStringbyte[] binary() { try {return binary; } @Override public String tmpVal = (valInString); int hashCode() { return ofObjects.hash(tmpValbinary); } catch (Exception e) {@Override public boolean equals(Object obj) }{ if (this return null; } } |
Leafref
Overview
The leafref type is used to reference a particular leaf instance in the data tree. Path statement must be present for leafref type. The path under leafref must refer to existing leaf or leaf-list. The leaf or leaf-list with leafref will use the instance of the referred leaf or leaf-list.
If leafref comes under grouping and typedef, it will be resolved where it is used. It will not be resolved where it is defined.
Java mapping
The leaf or leaf-list with type leafref, will copy the type of referred leaf or leaf-list, during java file generation.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : ietf-network.yang module ietf-network { yang-version 1; namespace "urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:yang:ietf-network"; prefix nd; container networks== obj) { return true; } if (obj instanceof MyBinary) { MyBinary other = (MyBinary) obj; return Objects.equals(binary, other.binary); } return false; } @Override public String toString() { return description Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(binary); } public static MyBinary fromString(String valInString) { try { "Serves as top-level container for a list of byte[] tmpVal = Base64.getDecoder().decode(valInString); networks."return of(tmpVal); } catch leaf network-id(Exception e) { } typereturn uint8null; description "Identifies a network."; } } container network-id { description "Serves as top-level container for a list of networks."; leaf network-id { type leafref { path "/nd:networks/nd:network-id"; } } } } |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : Networks.java
public interface Networks {
short networkId();
interface NetworksBuilder {
short networkId();
NetworksBuilder networkId(short networkId);
Networks build();
}
}
File : NetworkId.java
public interface NetworkId {
short networkRef();
interface NetworkIdBuilder {
short networkRef();
NetworkIdBuilder networkRef(short networkRef);
NetworkId build();
}
} |
Identity
Overview
The identity is used to define a new globally unique, abstract, and untyped identity. Its only purpose is to denote its name, semantics, and existence. An identity can iether be defined from scratch or derived from a base identity. The base statement, which is optional, takes as an argument a string that is the name of an existing identity, from which the new identity is derived.
Java mapping
}
}
|
Decimal64
Overview
The decimal64 type represents a subset of the real numbers, which can be represented by decimal numerals.
A decimal64 type can be restricted with the "range" statement.
The "fraction-digits" statement, which is a substatement to the "type" statement, MUST be present if the type is "decimal64". It takes as an argument an integer between 1 and 18, inclusively. It controls the size of the minimum difference between values of a decimal64 type.
The Minimum and Maximum decimal64 value table for each fraction-digit value.
| fraction-digits | min | max |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | -922337203685477580.8 | 922337203685477580.7 |
| 2 | -92233720368547758.08 | 92233720368547758.07 |
| 3 | -9223372036854775.808 | 9223372036854775.807 |
| 4 | -922337203685477.5808 | 922337203685477.5807 |
| 5 | -92233720368547.75808 | 92233720368547.75807 |
| 6 | -9223372036854.775808 | 9223372036854.775807 |
| 7 | -922337203685.4775808 | 922337203685.4775807 |
| 8 | -92233720368.54775808 | 92233720368.54775807 |
| 9 | -9223372036.854775808 | 9223372036.854775807 |
| 10 | -922337203.6854775808 | 922337203.6854775807 |
| 11 | -92233720.36854775808 | 92233720.36854775807 |
| 12 | -9223372.036854775808 | 9223372.036854775807 |
| 13 | -922337.2036854775808 | 922337.2036854775807 |
| 14 | -92233.72036854775808 | 92233.72036854775807 |
| 15 | -9223.372036854775808 | 9223.372036854775807 |
| 16 | -922.3372036854775808 | 922.3372036854775807 |
| 17 | -92.23372036854775808 | 92.23372036854775807 |
| 18 | -9.223372036854775808 | 9.223372036854775807 |
Java mapping
BigDecimal is used to store decimal64 value during code generationFor a given identity one abstract class file will be generated.
Example
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : |
...
test.yang module |
...
Test { yang-version 1; namespace |
...
http://huawei.com; prefix |
...
Ant; |
...
typedef |
...
MyDecimal { type decimal64 { |
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
fraction-digits 2; |
...
range "1 .. 3.14 | 10 | 20..max";
}
}
} |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File: MyDecimal.java
package org.onosproject.yang.gen.v1.http.huawei.com.rev20160718.test;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.util.Objects;
import com.google.common.base.MoreObjects;
public final class MyDecimal |
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
File : TunnelType.java
public abstract class TunnelType {
} |
Identityref
Overview
The identityref type is used to reference an existing identity. Base statement, which is a substatement to the type statement, must be present if the type is identityref. The base under identityref must refer to existing identity.
If identityref comes under grouping and typedef, it will be resolved where it is used. It will not be resolved where it is defined.
Java mapping
The leaf or leaf-list with type identityref, will referred to identity, during java file generation.
Example
...
| title | input YANG file |
|---|
...
{
|
...
private BigDecimal decimal64; private |
...
MyDecimal() { |
...
} |
...
public MyDecimal(BigDecimal value) { |
...
this.decimal64 = value; } public static MyDecimal of(BigDecimal value) { |
...
return new MyDecimal(value); } public BigDecimal decimal64() { |
...
return decimal64; } @Override public |
...
int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(decimal64); |
...
|
...
} @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) |
...
{ if (this == obj) { |
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
return true; |
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
} |
...
if (obj instanceof MyDecimal) { |
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
MyDecimal |
...
other |
...
= |
...
(MyDecimal) obj; |
...
return |
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
Objects.equals(decimal64, other.decimal64); } |
...
return false; } @Override |
...
public String toString() { |
...
|
...
| title | Generated java files |
|---|
...
return MoreObjects.toStringHelper(getClass()) |
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
.add("decimal64", decimal64) |
...
|
...
.toString(); } public static |
...
MyDecimal |
...
fromString( |
...
String |
...
valInString) |
...
{ |
...
try { |
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
BigDecimal tmpVal = |
...
new |
...
BigDecimal(valInString); |
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
|
...
return |
...
of(tmpVal); |
...
} catch |
...
( |
...
Exception |
...
e) { } |
...
return |
...
null; } } |
Unknown Statement
Overview
Golden Eye Demo
Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ipbu0x0LcDk
Presentation: YANG Demo.pptx
Note :
In case of typedef or identity when both have same name, But follow different typographical conventions is supported in compilation (It is limited to only one pair of identity and typedef naming conflict), other then that any name conflict is not supported as of now.
References
RFC6020 - https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc6020
...