Overview
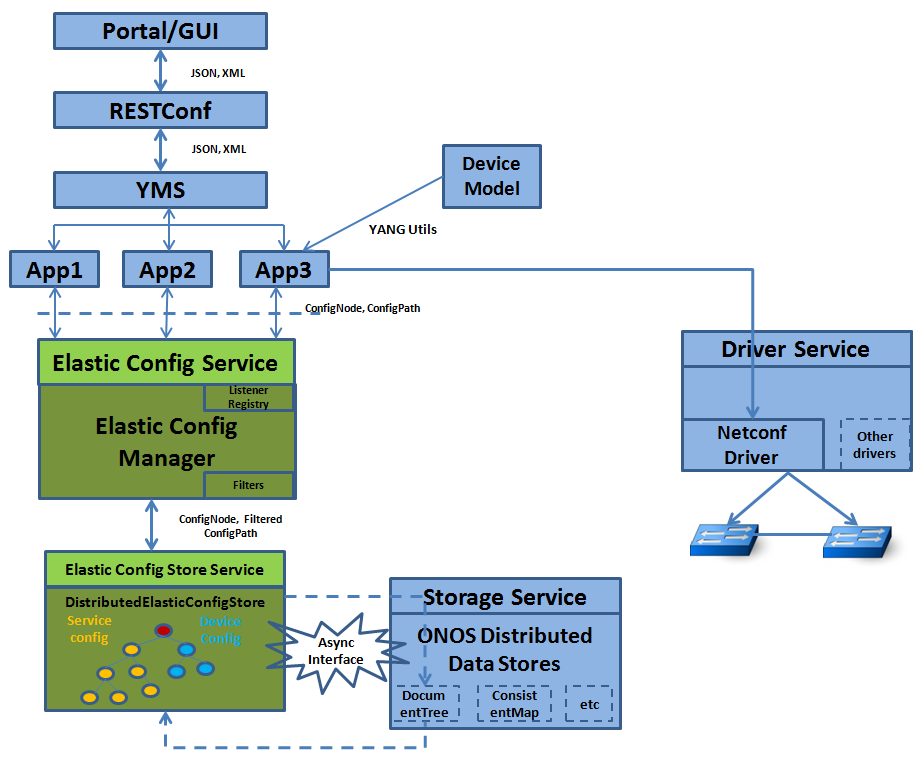
In ONOS, various abstractions collect configuration information pertaining to the network and network elements and store them in the implementation defined system wide models. But often in the brown fields, applications create or collect similar configuration information and work with their own individual information models (let us call this the "elastic configs"). Often these models are heterogeneous and most of them do not directly confirm to the models/abstraction within ONOS. The purpose Purpose of the elastic Dynamic config subsystem is to provide suitable abstractions that would enable ONOS to consume/produce the "elastic configs" configuration in a structured and extensible manner. Parking such "elastic configs" within such abstracted configuartions within ONOS would also allow opportunities for other abstractions (like drivers, providers etc.) to consume or apply modify them.
...
Components
The main components of this subsystem include the elastic Dynamic config service , elastic config manger, elastic and manager, Dynamic config store interface and the distributed elastic the distributed config store. Elastic config Dynamicconfig service is the gateway for applications to inject elastic configs to ONOS. Elastic Dynamic config manger implements this service and is responsible for managing the distributed elastic config store; apart from managing the store, the manger can also do additional south facing processing. Elastic config store provides the APIs and the Distributed elastic config store provides the implementation of the store. the store this component also provides an RPC dispatching framework, for the yang based RPCs. The distributed config store implementation is wrapping the Document Tree primitive and is built on top of the ONOS Distributed storage implementation.
Two other The important abstractions are the ConfigNode and ConfigNodePath. ConfigNode represents the in-memory format of "elastic config" that applications and the implementation of the “elastic config service” that Dyanmic config subsystem provides, are the DataNode, ResourceId, RpcService, RpcInput and RpcOutput. DataNode is the abstraction to hold any configuration that ONOS (any module within ONOS) would deal with. ConfigNodePath represents the in-memory format of “the key to an elastic config node”; in general it would contain the absolute path to a parent and the relative path to the specific node.
ConfigFilter is the abstraction to specify the kind of filtering that needs to be applied while working with elastic config nodes. In its current state it supports key based filtering of nodes and can be extended to include various types of content based filtering as well.
ConfigStoreType would indicate whether the given elastic config is a DEVICE_CONFIG or if it is a SERVICE_CONFIG. TraversalMode would indicate, from a given path, whether the nodes are to be recursively traversed or not.
APIs
ResourceId is the globally unique identifier for any such configuration nodes; this is created by abstracting information available in the schema about a given config node. RpcService, input and output provide abstractions for defining an Rpc interface contatining various Rpc methods, their input and output respectively. The dispatcher framework works on these abstractions.
APIs
Dynamicconfig Elastic config service supports the following APIs currently:
public interface DynamicConfigService
extends ListenerService<DynamicConfigEvent, DynamicConfigListener> {
/**
*
...
Creates a new node ...
in the ...
dynamic config store.
*
...
CompletableFuture<Boolean> addNode(ConfigStoreType store, ConfigNodePath path, ConfigNode node);/**
* Removes a node from the elastic config store.
*/
CompletableFuture<ConfigNode> removeNode(ConfigStoreType store, ConfigNodePath path);
This method would throw an exception if there is a node with the same
* identifier, already present at the specified path or any of the parent
* nodes were not present in the path leading up to the requested node.
* Failure reason will be the error message in the exception.
*
* @param path data structure with absolute path to the parent
* @param node recursive data structure, holding a leaf node or a subtree
* @throws FailedException if the new node could not be created
*/
void createNode(ResourceId path, DataNode node);
/**
*
...
Reads the ...
requested node ...
form the ...
dynamic config store.
*
...
/**
* Creates nodes in the elastic config store, recursively by creating
* all missing intermediate nodes in the path.
*/
CompletableFuture<Boolean> createRecursive(ConfigStoreType store,ConfigNodePath path, ConfigNode node);
This operation would get translated to reading a leaf node or a subtree.
* Will return an empty DataNode if after applying the filter, the result
* is an empty list of nodes. This method would throw an exception if the
* requested node or any parent nodes in the path were not present.
* Failure reason will be the error message in the exception.
*
* @param path data structure with absolute path to the intended node
* @param filter filtering conditions to be applied on the result list of nodes
* @return a recursive data structure, holding a leaf node or a subtree
* @throws FailedException if the requested node could not be read
*/
DataNode readNode(ResourceId path, Filter filter);
/**
*
...
Returns whether the requested node exists in the ...
Dynamic ...
Config store...
.
*
* @param path data structure with absolute path to the intended node
*
...
@return {@code true} if the node existed in the
...
store
* {@code false} otherwise
*/
...
Boolean
...
nodeExist(
...
ResourceId
...
path);
/**
*
...
Updates an existing ...
node in the ...
dynamic config store...
.
* Existing nodes will be updated and missing nodes will be created as needed.
* This method would throw an exception if the requested node or any of the
* parent nodes in the path were not present.
* Failure reason will be the error message in the exception.
*
...
* @param path data structure with absolute path to the parent
* @param node recursive data structure, holding a leaf node or a subtree
...
* @throws FailedException if the update request failed for any reason
*/
...
void
...
updateNode(
...
ResourceId
...
path,
...
DataNode node);
/**
* Replaces nodes
...
in the ...
dynamic config store.
* This will ensure that only the tree structure in the given
...
DataNode will
* be in place after a replace. This method would throw an exception if
* the requested node
...
or any of the parent nodes in the path were not
* present. Failure reason will be the error message in the exception.
*
*
...
@param path data structure with absolute path to the parent
* @param node recursive data structure, holding a leaf node or a subtree
* @throws FailedException if the replace request failed
*/
void replaceNode(ResourceId path,
...
DataNode
...
node);
/**
*
...
Removes a...
node from the dynamic config store.
* If the node pointed to a subtree, that will be
...
deleted recursively.
* It will throw an exception if the requested node or any of the
...
parent nodes ...
in ...
the
* path were not present; Failure reason will be the error
...
message ...
in ...
the ...
exception.
*
...
* @param path data structure with absolute path to the intended node
* @throws FailedException if the delete request failed
*/
void deleteNode(ResourceId path);
/**
* Invokes an RPC.
*
...
* @param id of RPC node
* @param input RPC input
* @return future that will be completed with RpcOutput
* @throws FailedException if the RPC could not be invoked
*/
CompletableFuture<RpcOutput> invokeRpc(ResourceId id, RpcInput input);
}
Use Case
In its current state, the following demo use case is planned to be supported (by ONS 2017)
...
Document Tree primitive
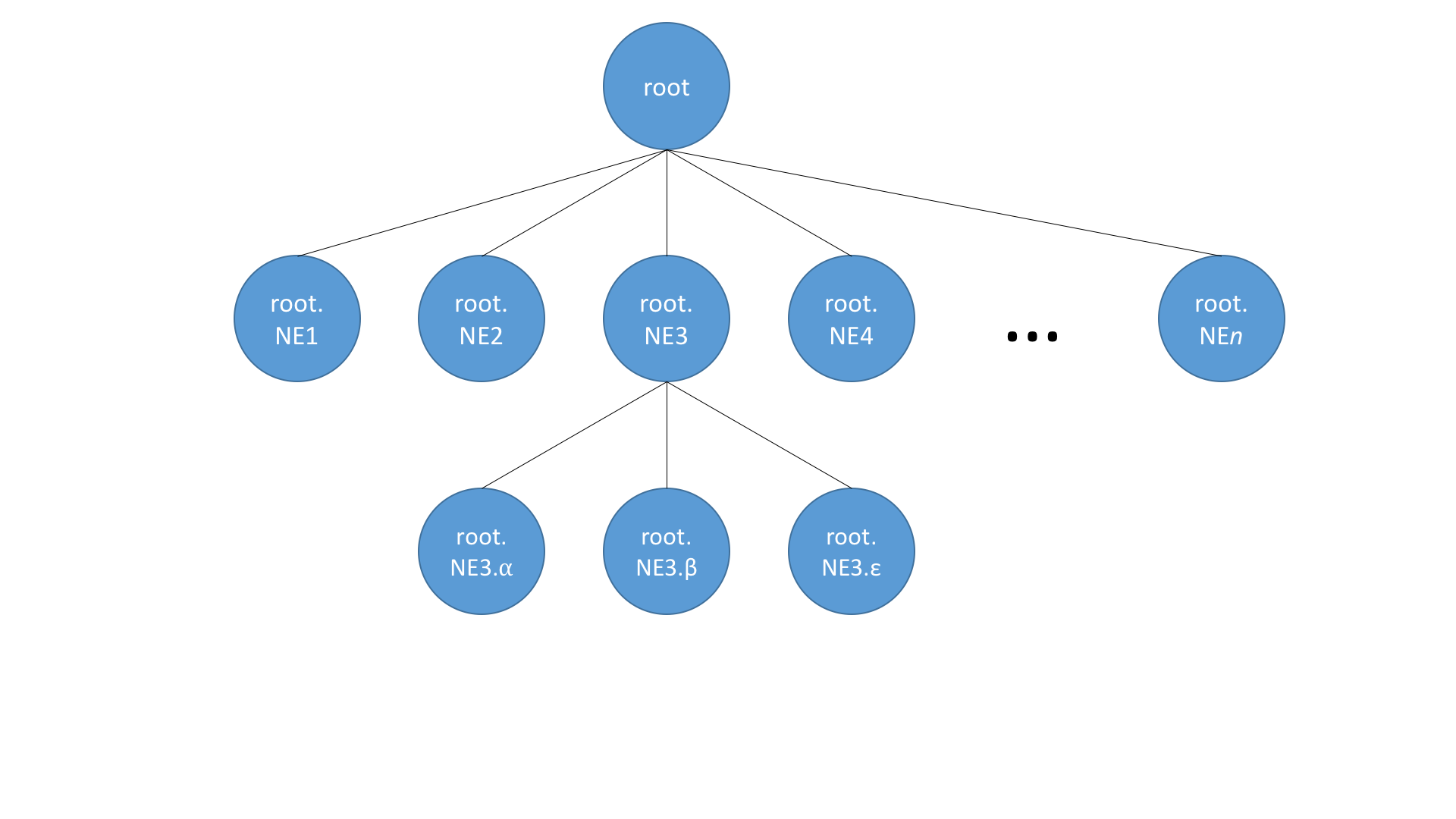
This subsystem makes use of the DocumentTree primitive. The primitive consists of an implementation of AsyncDocumentTree (AtomixDocumentTree) residing on the client machine which submits commands to the remote Copycat state machine (AtomixDocumentTreeState), responsible for maintaining distributed state. The commands submitted to the primitive are found in AtomixDocumentTreeCommands, it should be noted that there will not necessarily be a one to one correspondence between the commands provided in the AsyncDocumentTree API and the command classes, in many cases a single command class can encapsulate the functionality of several API calls.
Behavior
The DocumentTree primitive supports a tree structure which allows nodes with arbitrary numbers of children. The primitive also provides efficient prefix filtering by using qualified names which identify the ancestry of a node (as demonstrated in the image below) which enables listening for notifications from specified subtrees. The structure supports sequential query consistency but makes no guarantees about the linearizability of queries.
Next Steps