...
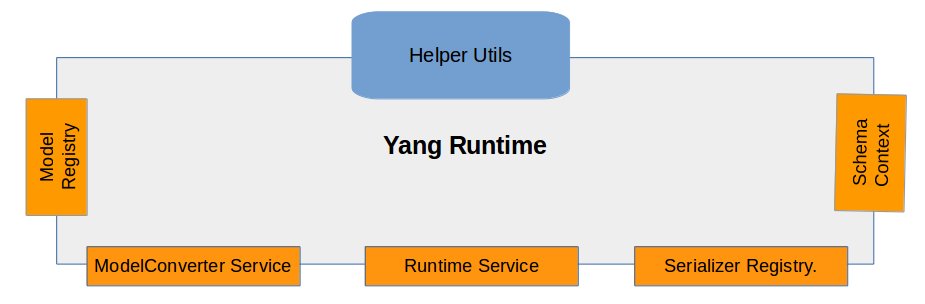
YANG Runtime Architecture
1) Serializer Registry
This service is used for registering and unregistering the available data format serializers. YANG App activation registers the default XML/JSON serializers. User can override the existing registration or can register new data formats. In case of multiple registrations of same data format, last one will take into effect.
Snippet code showing default registration of serializers:
DefaultYangSerializerRegistry serializerRegistry = new DefaultYangSerializerRegistry();
serializerRegistry.registerSerializer(newJsonSerializer());
...
The The YangSerializerRegistry interface provides 2 capabilitiesAPI's:
To register a new serializer or overwrite if the serializer for a particular data format already exists.
...
=>void unregisterSerializer(YANGSerializer serializer)
2)
...
Model Registry
This API is used by schema aware application to register YANG model. Example:L3VPN application and also live compiler.
Example: When L3VPN application wants to register L3VPN service model it has to extend the AbstractYangModelRegistrator which allows the application to attach endpoints to the respective service model.
Code Snippet:
public class L3VpnModelRegistrator extends AbstractYangModelRegistrator {
/**
* Creates L3VPN model registrator.
*/
public L3VpnModelRegistrator() {
super(IetfL3VpnSvc.class, getAppInfo());
}
private static Map<YangModuleId, AppModuleInfo> getAppInfo() {
Map<YangModuleId, AppModuleInfo> appInfo = new HashMap<>();
appInfo.put(new DefaultYangModuleId("ietf-inet-types", "2013-00-15"),
new DefaultAppModuleInfo(IetfInetTypes.class, null));
appInfo.put(new DefaultYangModuleId("ietf-l3vpn-svc", "2016-00-30"),
new DefaultAppModuleInfo(IetfL3VpnSvc.class, null));
appInfo.put(new DefaultYangModuleId("ietf-yang-types", "2013-00-15"),
new DefaultAppModuleInfo(IetfYangTypes.class, null));
appInfo.put(new DefaultYangModuleId("l3vpn-svc-ext", "2016-00-30"),
new DefaultAppModuleInfo(L3VpnSvcExt.class, null));
return ImmutableMap.copyOf(appInfo);
}
}
The YangModelRegistry interface provides the following methods:
Register a new model with parameters specifying any additional information provided by the application.
=>void registerModel(ModelRegistrationParam param)
Unregister the specified model with parameters specifying any addtional information provided by the applciation.
=>void unregisterModel(ModelRegistrationParam param)
Model converter provides a mechanism for converting between DataNode and Model Object instances. It is capable of constructing model POJO objects from the DataNode,including any augmentations which may be present in the DataNode structure and creating immutable tree structure from a given POJO.
//Produces a mutable POJO backed by the specified data node
...
//Produces an immutable tree structure rooted at the returned DataNode using the supplied model POJO object
=> DataNode createDataNode(ModelObject)
3) Runtime Service
It is a service for encoding and decoding between internal and external model representation.This service is used by:
Protocol Application - To encode/decode protocol representation to internal representation
YANG Store – To translate between internal representation and YANG objects for interaction with applications.
The decode method decodes the One of the service is to decode the external representation of a configuration model from the specified composite stream into an in-memory representation. Resource identifier stream “URI” will get decoded to data node.
Protocols like NETCONF may opt only to have resource identifier and resource data stream will get decoded to data nodedata without resource identifier, which implies the data node construction from logical root resource("/").
Also protocols like NETCONF will have decorations around the input stream which will be reported back to protocol in output. Produced annotations will be in order of pre-order traversal.
=>CompositeData decode(CompositeStream external, RuntimeContext context)
Another service is to encode The encode method encodes the internal in-memory representation of a configuration model to an external representation consumable from the resulting input stream.Resource identifier in composite data will get encoded to resource identifier stream and data node will be encoded to resource data streamdata stream.
Logical root node "/" will be removed during encoding and will not be part of either resource identifier or data node.
Protocols like NETCONF may opt only to have data node with resource identifier as null in order to only get complete output in form of body without URI.
Also protocols like NETCONF would like to provide additional decorations for the node. The decoration should be in pre-order traversal order.
=>CompositeStream encode(CompositeData internal, RuntimeContext context)
4)
...
ModelConverter Service
This service provides the utility for registering a new YANG model. This is used by:
Applciation - To register application service interface. Ex:L3VPN etc
Provider - To register device schema.
Compiler(live/offline) - To register the extenal applcations schema / device schema.
This service is capable of the following:
Register a new model with parameters specifying any additional information provided by the application.
=>void registerModel(ModelRegistrationParam param)
Unregister the specified model with parameters specifying any addtional information provided by the applciation.
Model converter provides a mechanism for converting between DataNode and Model Object instances. It is capable of constructing model POJO objects from the DataNode,including any augmentations which may be present in the DataNode structure and creating immutable tree structure from a given POJO. This API mainly gives the following methods:
//Produces a mutable POJO backed by the specified data node
=> ModelObjectcreateModel(DataNode)
//Produces an immutable tree structure rooted at the returned DataNode using the supplied model POJO object
=> DataNode createDataNode(ModelObject=>void unregisterModel(ModelRegistrationParam param)
5) SchemaContext Provider
...
Runtime Helper
Represents utility for runtime.These utilities can be used by the application to get the YANG model for the application and also it can be used by the runtime to get the YANG Node for the given YANG model.
Examples API's :
1. To obtain YANG model for given generated class:
=>YANGModel getModel(Class<?> aClass)
2. To get YANG node for given YANG model
=>Set<YANGNode> getNodes(YANGModel model)
3. To get interface class name of the schema node
=>String getInterfaceClassName(YANGSchemaNode schemaNode)
Serializer Helper
These set of utilities are used by Serializer to build the data node and resource identifier without obtaining schema.
Example API's:
1. To add to resource identifier builder used by applications which are not aware about the schema name association with key's value.This api will also carry out necessary schema related validations.
=>ResourceId.Builder addToResourceId(ResourceId.Builder builder, String name, String namespace, List<String> value)
2. To add a data node to a given data node builder. This API will also carry out necessary schema related validations.
=>Builder addDataNode(Builder builder, String name, String namespace, String value, DataNode.Type type)
3. To get the resource identifier for a given data node. This API will be used by serializer to obtain the resource identifier in the scenario when an annotation is associated with a given data node.
=>ResourceId getResourceId(Builder builder)
Use
...
Case Scenarios Of YANG Runtime
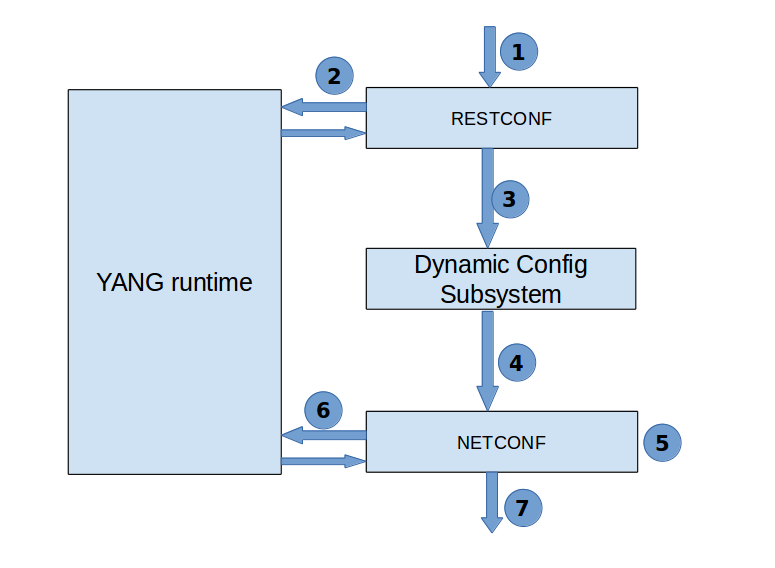
Device Configuration
of devicesControl Flow:
Prerequisite : Onos NB registers the device YANG model with YANG Runtime
Step 1: User/Application sends device configuration data in JSON/XML format to RESTCONF.
Step 2: RESTCONF sends the data to YANG runtime for it to decode the data to DN(data nodes) and then return them back.
Step 3: RESTCONF pushes the decoded data to Dynamic configuration subsystem.
Step 4: Dynamic configuration subsystem then sends a notification to NETCONF.
Step 5: NETCONF removes the additional metadata information and then send it to YANG runtime.
Step 6: YANG runtime encodes the data to JSON/XML format and send it back to NETCONF.
Step 7: NETCONF send the encoded data to the SB devices.
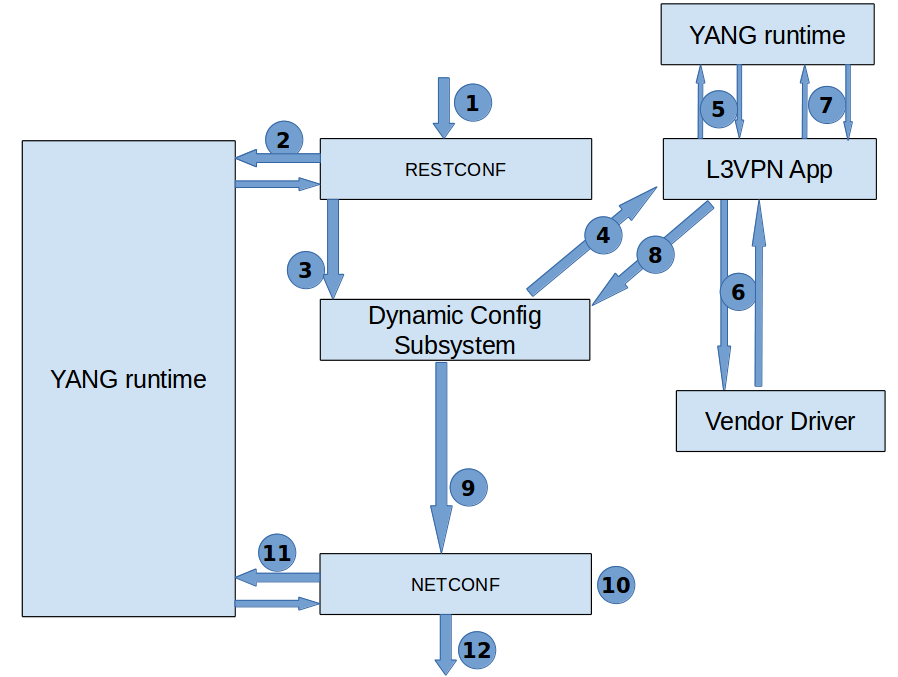
Configuration ofService configuration
Control Flow:
Step 1: Restconf receives the data from user/application in JSON/XML format.
Step 2: It sends this data to YANG runtime which uses serializer to decode it into DN(data nodes).
Step 3: Restconf pushes the encoded data to Dynamic Configuratation subsystem.
Step 4: Dynamic Configuration sends notification to L3VPN application.
Step 5: After receiving the data, it sends it to YANG runtime for a model conversion from DN to POJO and then sends that back to L3VPN application.
Step 6: The L3VPN application creates a Standard device model and sends it to vendor.The vendor modifies it accordingly and creates a vendor specific device model and then sends this to L3VPN application .
Step 7: L3VPN application sends it to YANG runtime for a model conversion from POJO to DN.
Step 8: L3VPN application pushes the vendor model to Dynamic Configuration subsystem.
Step 9: Dynamic configuration subsystem sends notification to Netconf.
Step 10: NETCONF removes the additional metadata information
Step 11: NETCONF sends the data to YANG runtime which enoded it to JSON/XML format and then return the same to NETCONF.
Step 12: Finally NETCONF sends the data to the SB devices.
...