| Table of Contents |
|---|
Overview
NOTE: The GUI architecture is migrating to use the AngularJS framework – some of the information on this page is deprecated (the topo events are still good).
The ONOS GUI is a single-page web-application with hash-navigation. The GUI system comprises client-side code (a single HTML page structured as an AngularJS application, javascript libraries and modules, CSS files, etc.) and server-side code (Java classes that interface to ONOS Server APIs). The GUI web page is served up by a web server running on an ONOS instance.
Client-Side Architecture
...
From the web-browser's point of view, the The client side code is comprised of:
| The main application page |
| ||||
| Third party libraries |
|
| |||
Framework code and supporting modules |
|
|
|
|
|
| Supporting | framework utilities |
|
|
|
|
| Topology view | |||||
| |||||
| |||||
| View module templates |
| ||||
Core Views (installed with out-of-the-box ONOS) |
| Sample views |
|
... along with their associated *.css stylesheets.
The structure of the framework allows for the registration of multiple "views" and the subsequent navigation between them.
For the first release, however, there is but a single view, the Topology View.
View Registration (Deprecated)
A view registers with the framework via a call to the addView(...) function.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
onos.ui.addView('viewId', {
init: init,
reset: reset,
load: load,
unload: unload,
resize: resize,
theme: theme
}); |
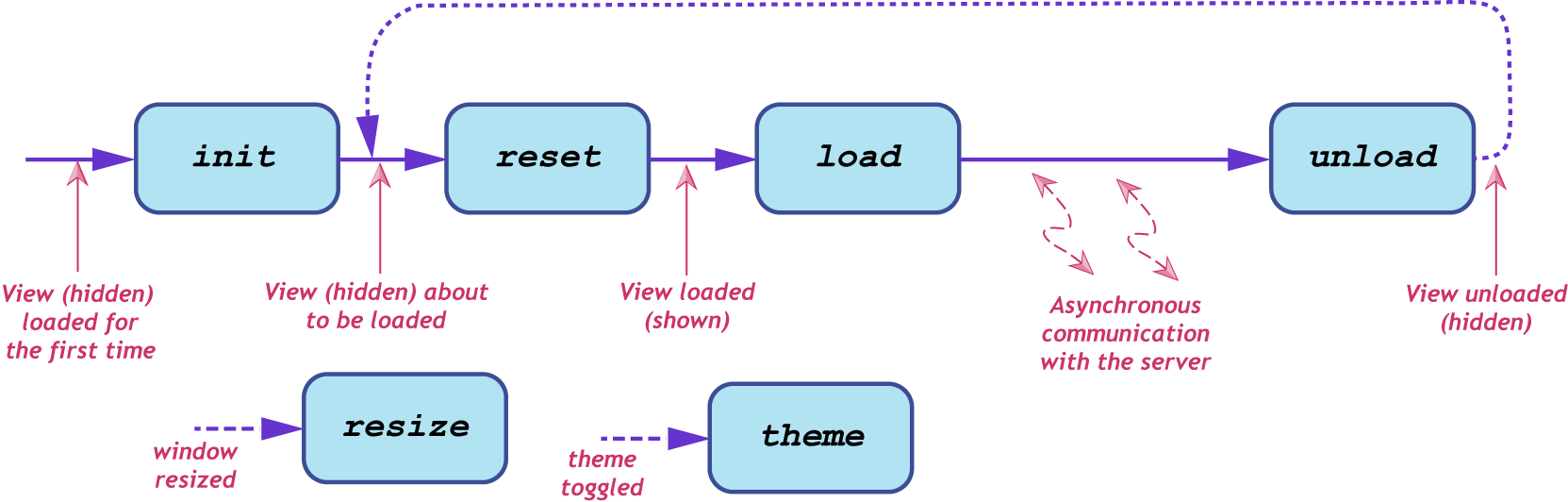
The first argument to the function is a short string identifier for the view.
The second argument to the function is an inline object block with the given keys, whose values are references to view life-cycle callback functions:
| init | This function is called only once, the first time the view is loaded. It is called after the view's <div> has been added to the DOM. |
| reset | This function is called just before the view is shown. It can be used to clear stale data from the view. |
| load | This function is called when the view is loaded. |
| unload | This function is called when the view is unloaded. The view may use this to drop references to cached data, or stop background tasks. |
| resize | This function is called when the view has been resized. |
| theme | This function is called when the user has toggled the theme. |
Topology View (Deprecated)
In the first release, the Topology View is the only view available; it is loaded at GUI startup. The following paragraphs summarize each of the view's callbacks:
Init
The init callback is used to initialize the view's SVG layer (including pan and zoom controls) and the Force Layout used to visualize the topology.
Reset
The reset callback is not needed, and thus not implemented.
Load
The load callback starts by injecting the radio button set into the masthead and registering key bindings and mouse gesture descriptions. After that, it performs an asynchronous load of the background GeoMap (Continental USA), before finally opening a websocket connection to the server.
Once the websocket is established, an initial requestSummary event is sent to the server. The UI then processes incoming events from the server to build up a view of the topology. See Event Descriptions below.
Unload
The unload callback cancels the background timer, if it is running.
Resize
The resize callback updates the size of the SVG layer.
Theme
The theme callback updates instance and device colors.
...
Notes:
For the following notes, the "wiring" can be seen by examining the web.xml configuration file.
(1) index.html is generated dynamically via the MainIndexResource class. The index.html file is used as a template, with javascript <script> elements and style sheet <link> elements injected where indicated. The contents of these sections are composed by querying all UiExtensions registered with the UiExtensionService.
(2) onos.js is generated dynamically via the MainModuleResource class. The onos.js file is used as a template, with view IDs injected where indicated. The list of view IDs is generated by iterating across the UiViews defined by each registered UiExtension.
(3) nav.html is an HTML fragment generated dynamically via the MainNavResource class. The nav.html file is used as a template, with the navigation category headers and links injected where indicated. The headers and links are generated by iterating across the category values, and within each category iterating across the UiViews (for that category) defined by each registered UiExtension.
Injected Views
Additional views can be injected into the GUI at runtime. Each view has a unique identifier (e.g. "myviewid"). Client side resources should be placed in the .oar file using the following convention:
|+-- resources| +-- {UiExtId}| +-- css.html| +-- js.html|+-- webapp +-- app +-- view +-- {viewid1} | +-- *.css | +-- *.html | +-- *.js | +-- {viewid2} +-- *.css +-- *.html +-- *.js
Topology Model (to be moved to another page)
The UI maintains an internal model of the topology by storing data representing ONOS instances, nodes (devices and hosts) and links. The model is empty initially, but is augmented as events (such as addInstance, addDevice, addLink, etc.) come in from the server. As these events arrive, the model is updated and the visual representation modified to reflect the current model.
...