...
ARTEMIS consists of three components: a monitoring (1), a detection (2) and a mitigation (3) service as shown in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1: The ARTEMIS architecture.
1) The monitoring service runs continuously and provides control plane information from the AS itself, the streaming services of RIPE RIS [4] and BGPstream [6] (from RIPE RIS and RouteViews), as well as BGPmon [5] and Periscope [7], which return almost real-time BGP updates for a given list of prefixes and ASNs.
...
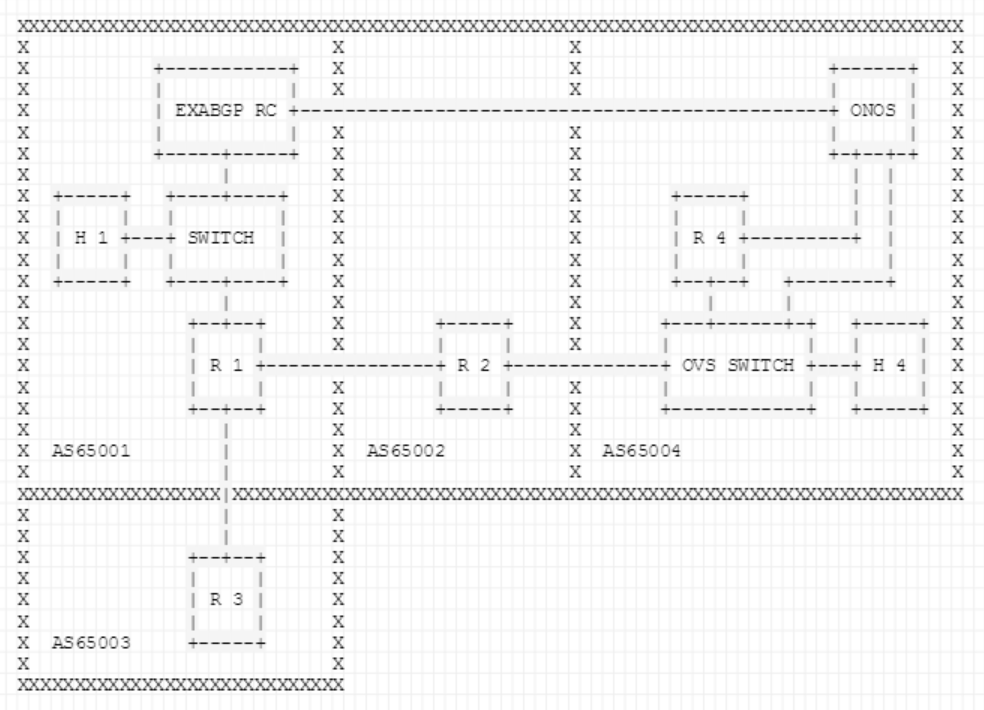
Figures 2 and 3 show the topology that is setup via the topo.py file inside the tutorial folder (TODO: set exact location). The BGP speakers are Quagga routers and the route collector is an ExaBGP router running a custom script to replicate the behavior of a RIPE route collector.
Fig. 3: The full emulated demo topology.
...
AS65001
Intermediate AS that consists of a BGP speaker (R1), a L2 switch, a host (H1) and an ExaBGP Route Collector (RC).R1: Announces 10.0.0.0/8 and is a neighbor of AS65003 and AS65002. Also, it has the exaBGP RC as an iBGP neighbor and propagates BGP update messages to it.
ExaBGP RC: RC connected to R1 but also to the ONOS controller on the protected AS (in real world this connection is done through the underlying network; the only limitation is that the IP endpoint of ONOS should have a non-hijacked IP address so that the monitor can reach ONOS during the hijack).
H1 / 10.0.0.100: Host which is going to be communicating with the host inside the protected AS. It is used to provide us a visualization of the data-plane behavior when the BGP hijack occurs.
...
- AS65002
Intermediate AS that consists of a BGP speaker (R2) that announces 20.0.0.0/8 and its purpose is to add an additional hop to the AS-PATH so that the protected AS can be hijacked. Although in the demo the attacker announces the exact prefix that belongs to the protected AS and not a more specific one, due to the shortest path attribute of the BGP best path selection algorithm, is able to steal the traffic.
AS65003
Hijacker AS that consists of a BGP speaker (R3).R3: By announcing the prefix of the protected AS (40.0.0.0/8) from this BGP speaker, we trigger a BGP hijack, and all traffic generated from AS65001 and directed towards AS65004, will be redirected to the network of AS65003.
AS65004
Protected AS that is employing ONOS. It consists of a BGP speaker, an OVS switch, a host and the ONOS instance.R4: BGP speaker announcing 40.0.0.0/8. It is connected with his neighbor through the OVS switch which is configured by the SDN-IP application to talk with the BGP speaker of AS65002.
OVS: Talks with ONOS on a management interface via 192.168.0.0/24.
ONOS: ONOS is connected with the BGP speaker to retrieve the BGP routing table. Also, it receives the BGP update messages from the ExaBGP router. Also, it has a link with the OVS switch in order to interact with the data plane.
- H4 / 40.0.0.100: Host that receives traffic with the help of the reactive-routing application from the host in AS65001.
...