Software Modules
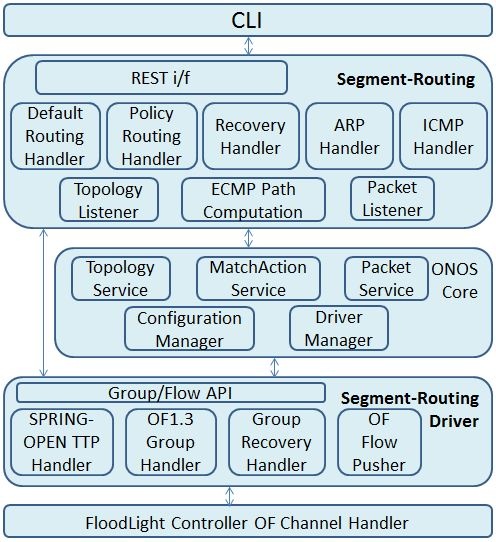
The following figure illustrates the Segment Routing application components, and the relationship among those components
The boxes with bold text represents Segment Routing application modules while rest of the components represent ONOS modules that segment routing application depends on. Segment Routing application exposes two external interfaces: REST and CLI.
SPRING-OPEN TTP
It is important for the switch and the controller to have the same (abstract) view of the switch-forwarding pipeline. This view is essentially a Table-Typed-Pipeline (TTP), the framework for which is being developed by the Forwarding Abstractions WG at the ONF. The abstract pipeline used for Segment Routing application is be documented here, and ‘implicitly’ understood by the switch and controller instances. In addition, the view will be exposed by the OpenFlow switch agent via messages such as Table-Features, Switch-Features and Group-Features.
App & Driver
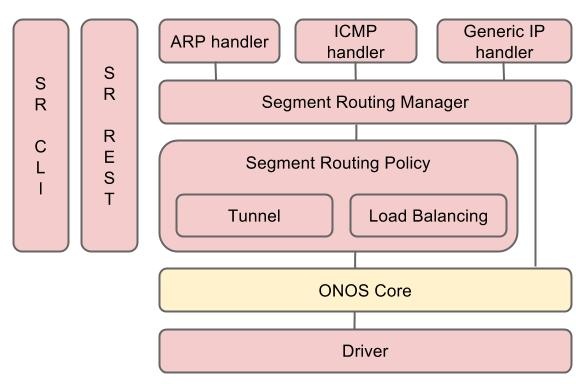
The following figure describes the architecture of the segment routing application.
- Segment Routing Manager - It computes the shortest ECMP path among all routers and populates all routing rules to IP and MPLS table of the switches. Also, it handles all packets to the application and forwards them to appropriate handlers according to the packet type.
- ARP handler - It handles ARP request and response packets. If the APR request is to the any managed routers, then it generates and sends out the ARP response to the corresponding hosts.
- ICMP handler - It handlers ICMP request to the routers. It generates the ICMP response packet and sends out to the corresponding hosts.
- Generic IP handler - It handles any IP packet. If the destination of the IP packet is hosts within subnets of routers, then it set the forwarding rule to the router and sends out the packet to the corresponding hosts. If MAC address of the host is not known, then it sends out APR request to the subnet using ARP handler.
- Segment Routing Policy - It creates the policy and set the policy rule to ACL table of routers. If it is the tunnel policy, then it creates the tunnel for the policy. NOTE: Load balancing policy is not implemented yet.
Configuration Manager
A Network Config Manager provides network configuration service and filtering service
- Configuration Service: Configuration service handles all network element configuration. For Segment Routing use case, the following network information will be configured through Network Config Manager: Router IP and MAC, Node Segments, Subnets, Filtering policy, etc. The Topology publisher, Driver Manager and Segment Routing Driver modules will use the services provided by Network Config manager while constructing global network view and performing any operations on the network elements as illustrated in below figure. Initially the startup configuration will be file based which can be enhanced to run-time CLI based in later phases.
- Filtering Service: Filtering service provides logic to filter the discovered network entities based on the filtering policy as illustrated in below figure.