...
2. Create a VM with service network and management network. Management network must be the second interface!
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
$ nova boot --image f04ed5f1-3784-4f80-aee0-6bf83912c4d0 --flavor 1 --nic net-id=aaaf70a4-f2b2-488e-bffe-63654f7b8a82 --nic net-id=0cd5a64f-99a3-45a3-9a78-7656e9f4873a net-A-vm-01 |
...
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
$ sudo dhclient eth1 |
Now, you can access the VM from compute node with the management network IP assigned to the VM.
REST APIs
Here's the list of REST APIs that CORD-VTN provides.
| Method | Path | Description |
|---|---|---|
| POST | onos/cordvtn/service-dependency/{tenant service network UUID}/{provider service netework UUID} | Creates a service dependency with unidirectional access from a tenant service to a provider service |
| POST | onos/cordvtn/service-dependency/{tenant service network UUID}/{provider service netework UUID}/[u/b] | Creates a service dependency with access type extension. "u" is implied to a unidirectional access from a tenant service to a provider service and "b" for bidirectional access between two services. |
| DELETE | onos/cordvtn/service-dependency/{tenant service network UUID}/{provider service netework UUID} | Removes services dependency from a tenant service to a provider service. |
Internet Access from VM (only for test)
...
VLAN for connectivity between VM and underlay network
You can use VLAN for the connectivity between a VM and a server in the underlay network. It's very limited but can be useful if you need a connectivity between a VM and a physical machine or any other virtual machine which is not controlled by CORD-VTN and OpenStack.
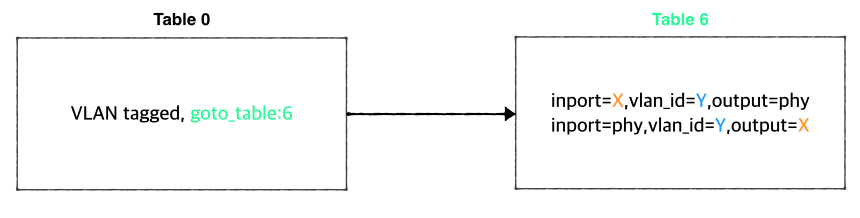
The figure below is the part of the CORD-VTN pipeline, which shows how VLAN tagged packet is handled.
Basically, VLAN tagged packet from a VM is forwarded to the data plane without any modifications and any VLAN tagged packet from data plane is forwarded to a VM based on its VLAN ID. So, assigning the same VLAN ID to multiple VMs in the same virtual switch can break the logic. Anyway, if you want this limited VLAN feature, try the following steps.
1. Create Neutron port with port name "stag-[vid]"
| Code Block |
|---|
$ neutron port-create net-A-private --name stag-100 |
2. Create a VM with the port
| Code Block |
|---|
$ nova boot --image 6ba954df-063f-4379-9e2a-920050879918 --flavor 2 --nic port-id=2c7a397f-949e-4502-aa61-2c9cefe96c74 --user-data passwd.data vsg-01 |
3. Once the VM is up, create a VLAN interface inside the VM with the VID and assign any IP address you want to use with the VLAN. And do the same thing on the server in the underlay.
| Code Block |
|---|
$ sudo vconfig add eth0 100
$ sudo ifconfig eth0.100 10.0.0.2/24 |
Internet Access from VM (only for test)
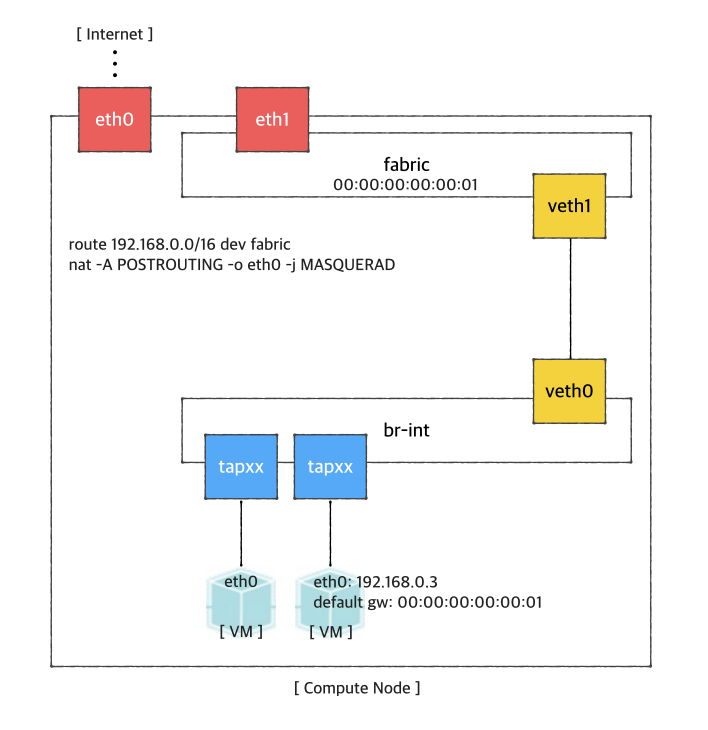
If you want to access a VM through SSH or access the Internet from VM without fabric controller and vRouter, you need to do setup the followings in your compute node. Basically, this settings mimics fabric switch and vRouter inside a compute node, that is, "fabric" bridge corresponds to fabric switch and Linux routing tables corresponds to vRouter. You'll need at least two physical interface for this test setup.
First, you'd create a bridge named "fabric" (it doesn't have to be fabric).
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
$ sudo brctl addbr fabric |
Create a veth pair and set veth0 as a "dataPlaneIntf" in network-cfg.json
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
$ ip link add veth0 type veth peer name veth1 |
Now, add veth1 and the actual physical interface, eth1 here in example, to the fabric bridge.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
$ sudo brctl addif fabric veth1
$ sudo brctl addif fabric eth1
$ sudo brctl show
bridge name bridge id STP enabled interfaces
fabric 8000.000000000001 no eth1
veth1 |
Set fabric bridge MAC address to the virtual gateway MAC address, which is "privateGatewayMac" in network-cfg.json.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
$ sudo ip link set address 00:00:00:00:00:01 dev fabric |
Now, add routes of your virtual network IP ranges and NAT rules.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
$ sudo route add -net 192.168.0.0/16 dev fabric
$ sudo netstat -rn
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags MSS Window irtt Iface
0.0.0.0 45.55.0.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
45.55.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.224.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 0 0 0 fabric
$ sudo iptables -A FORWARD -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j ACCEPT
$ sudo iptables -A FORWARD -s 192.168.0.0/16 -j ACCEPT
$ sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE |
You should enable ip_forward, of course.
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
$ sudo sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 |
It's ready. Make sure all interfaces are activated and able to ping to the other compute nodes with "hostManagementIp".
| Code Block | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
$ sudo ip link set br-int up
$ sudo ip link set veth0 up
$ sudo ip link set veth1 up
$ sudo ip link set fabric up |
REST APIs
Here's the list of REST APIs that CORD-VTN provides.
| Method | Path | Description |
|---|---|---|
| POST | onos/cordvtn/service-dependency/{tenant service network UUID}/{provider service netework UUID} | Creates a service dependency with unidirectional access from a tenant service to a provider service |
| POST | onos/cordvtn/service-dependency/{tenant service network UUID}/{provider service netework UUID}/[u/b] | Creates a service dependency with access type extension. "u" is implied to a unidirectional access from a tenant service to a provider service and "b" for bidirectional access between two services. |
| DELETE | onos/cordvtn/service-dependency/{tenant service network UUID}/{provider service netework UUID} | Removes services dependency from a tenant service to a provider service. |